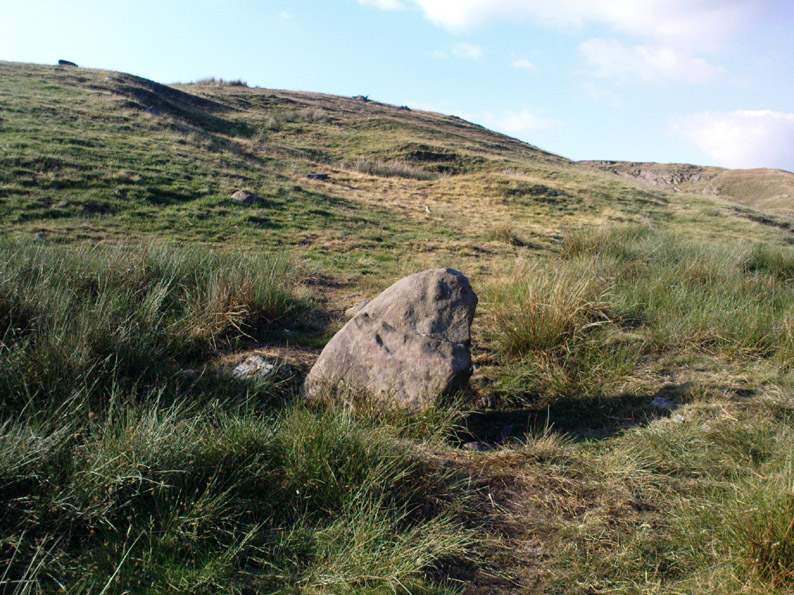
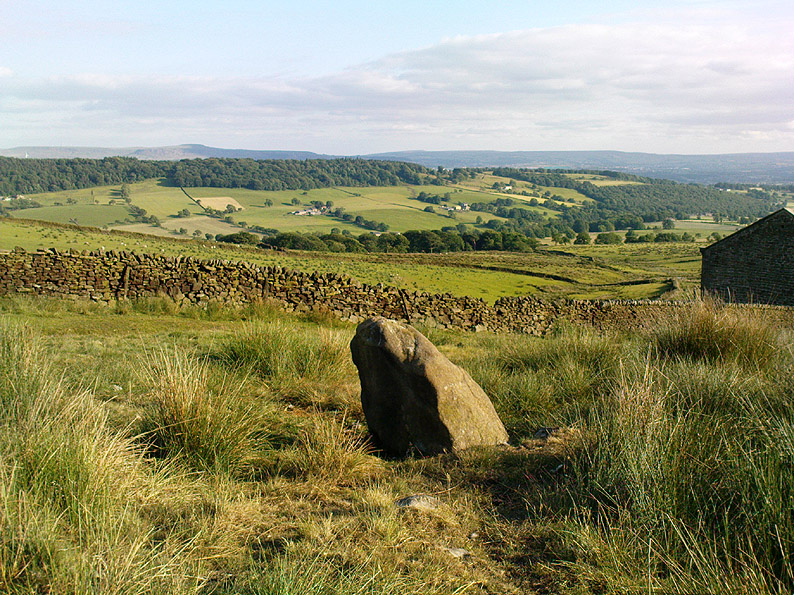
Cairn: OS Grid Reference – SD 7599 3782

From Sabden, head up the steep Clitheroe Road towards the Nick o’ Pendle, turning left 100 yards before the hilltop and along the dirt-track for a few yards, before veering up the winding footpath to the hilltop. When you’re at the peak of this little bit o’ moorland, go to your left (west), following the small path into the grasses and heather all the way on for a few hundred yards till you hit the triangulation pillar. Go past this, over one stile (north) and then immediately at right-angles (west) over another stile and downhill for about 100 yards until you’re on the rough grassland level. Keep your eyes peeled as you’re walking until you see what looks like a denuded stone-lined pit, much overgrown — with the main feature (showing that you’ve hit the target) being the engraving on one of the larger rocks: “Jeppe Knave Grave”.
Archaeology & History
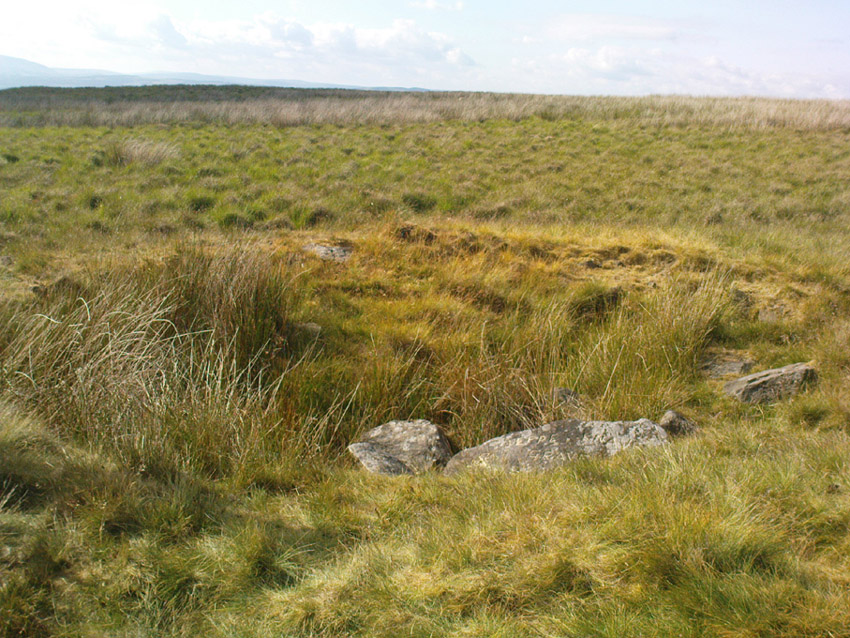

First described in early perambulation records of 1326 CE, this is a small but intriguing site found on the far southwestern slopes of Pendle Hill, on the ridge beneath the triangulation pillar of Wiswell Moor. It’s a small and overgrown cairn with a general archaeological association of prehistory attached—though no detailed excavation has ever been done here, despite local archaeologists having access to a large grant to explore this region a short while ago.¹ But up North, as many of us know, archaeology is given little priority and those who do decent exploratory work under the umbrella of such academic quarters tend to be few and far between. Thankfully we had the northern antiquarian and local writer John Dixon (1993) nearby who gave us the best overview of the site. He wrote:
“This landscape feature, known as Jeppe Knave Grave, stands at a place called The Lows high on Wiswell Moor and takes the form of a low grass-covered mound 16M in diameter with a stone filled depression in the centre 5 x 3 M. This feature appears to be a mutilated cairn and has been tentatively ascribed to the Bronze Age. The outer ring of stones can be discerned in the rough pasture at the perimeter – yellow in dry conditions, showing the circular shape. Given the large size of the stones here, the cairn may have been of a chambered type/passage tomb of the Neolithic period, and if this was the case the burial (or burials?) was one of great importance.
“Upon the largest stone are inscribed the words ‘JEPPE KNAVE GRAVE and a cross (inscribed by the Scouting Association in the 1960’s). The stone marks the final resting place of Jeppe Curteys (Geoffrey Curtis), a local robber who was decapitated for his crimes in the first year of Edward III, 1327. The name first occurs in a record of the boundaries between Wiswall and Pendleton dated 1342.
“…In those times the punishment of decapitation was unusual, being reserved for those of noble birth. So who was this Jeppe Curteys, punished by decapitation and later buried on the high ridge of Wiswell Moor in a pre-Christian burial mound on the then boundary of parishes? That intriguing story we may never know. But to be buried in such a manner and place was indeed a great indignity – interment in what might be considered in those times to be a ‘pagan’ or ‘devilish’ spot. It may be that to bury a man in such a place was to literally ‘send him to the devil’. Alternatively one could ask: ‘Was the site thought then to be the burial spot of some noble ancestor, and Jeppe being of possible noble birth interred with great dignity? Again we may never know, yet it is significant that this lonely spot is still identified with a man who was executed 700 years ago.
In 1608 it was stated that one Robert Lowe had taken a stone from the grave and used it as a cover of his lime kiln.”
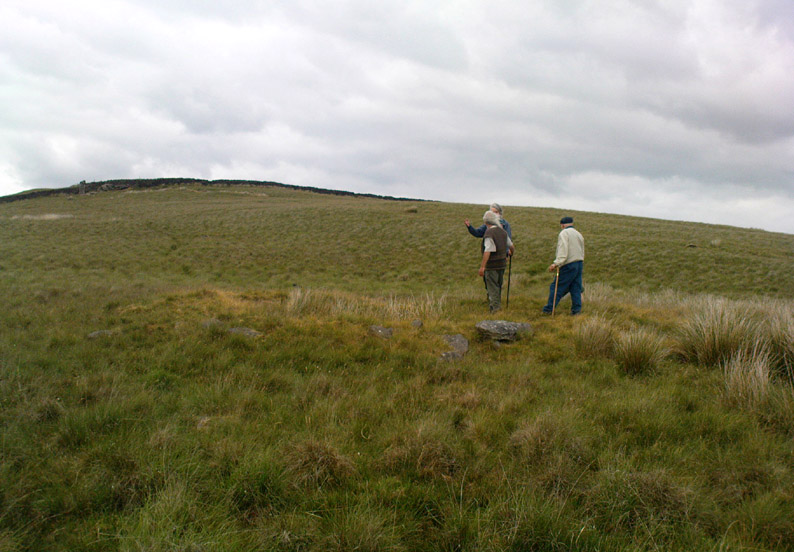

The design of the cairn here is unlike the ones you usually come across on the Lancashire and Yorkshire moorlands. The edges of the Jeppe Knave Grave are walled and much more well-defined than the large rock piles that we find scattering our uplands. A similar though larger cairn with features similar to these can be seen in the large Low Hill tumulus on Elslack Moor near Earby, about ten miles northeast of here…
Other prehistoric remains scatter the many rolling hills that you can see from here: mainly prehistoric tombs sat upon hilltops as far as the eye can see. John pointed out what may be the remains of another tumulus that can be seen on the nearby horizon a few hundred yards NNW from here, overlooking the gorgeous village of Pendleton and the landscape beyond…
References:
- Dixon, John, Journeys through Brigantia – volume 9: The Ribble Valley, Aussteiger Publications: Barnoldswick 1993.
- Dixon, John, Pendle – A Mythic Landscape, Aussteiger Publications: Barnoldswick 2010.
- Whitaker, Thomas Dunham, An History of the Original Parish of Whalley – volume 2, George Routledge: London 1876.
¹ John Dixon informed us how the people in question spent the grant — somewhere in the region of £50,000 — on exploring some modern architectural features, instead of exploring some of the little-known sites and seeking out others on these hills.
* John is the author of many fine historical travel guides, including the Journeys through Brigantia series. See the titles in the Lancashire Bibliography and Yorkshire Bibliography for a more complete listing of all his books to date. If you wanna buy any of his works, or make enquiries regarding them, email John at: lancashirebooks@fsmail.net – or write to him direct, at: John Dixon, Aussteiger Publications, 21 Lowergate, Clitheroe, Lancashire BB7 1AD.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian
The map could not be loaded. Please contact the site owner.

