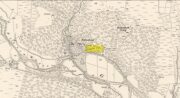
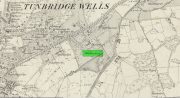
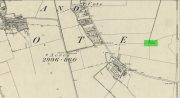
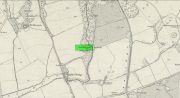
Holy Well: OS Grid Reference – SE 9622 2709
Archaeology & History
Shown on the early 25-inch-to-the-mile Ordnance Survey map of the area, this is a frustrating site. In Thompson’s (1870) early history of Welton village, he says very little about this place, other than:
“Then there is Saint Ann’s Well, which supplies Welton House with spring water.”
Even worse is the fact that in William Smith’s (1923) survey of East Yorkshire holy wells, he merely copies Thompson; and in Jeremy Harte’s magnum opus he does exactly the same thing! Not good. Thankfully the local artist and singer, Gaynor Perry, helped us out big time! She grew up in this area and used to play here when she was young, but at the time she had no idea that the well where she’d played had any magical traditions attached to it. This discovery happened many years later. Regarding the present condition of the well (as of 2017), she told:
“The well has been covered with stone slabs for a long time (and) a tree has tried to grow over it. It has been sheltered here over the years in the grounds of Welton House, a large estate which was demolished in 1952.”
The well can still be seen in the small copse of trees immediately north of St Anne’s College. There is the possibility that this holy well gave its name to the village of Welton itself. First mentioned in 1080 CE, the place-name means “the well near the farm,” (Smith 1937) although there is no direct linguistic association with St. Anne, so we don’t know for sure.
Folklore
St. Anne is a curious saintly figure and one of my personal favourites. St Anne (saint’s day – July 26) was a giant in early christian and Islamic myths. An apocryphal figure, She was the Great Mother of the mother of Christ—the Virgin Mary—and was Herself a Virgin until, in Her old age, after seeing a bird feeding a chick, decided She wanted a child and so eventually gave birth to Mary. An old woman giving birth when the Springtime appears (when birds and other animals become fertile) is the same motif found in the lore of the Cailleach in Ireland and Scotland (and parts of northern England). A pre-christian mythos was obviously at play here in bygone times…
References:
- Harte, Jeremy, English Holy Wells – volume 2, HOAP: Wymeswold 2008.
- Smith, A.H., The Place-Names of the East Riding of Yorkshire and York, Cambridge University Press 1937.
- Smith, William, Ancient Springs and Streams of the East Riding of Yorkshire, A. Brown: Hull 1923.
- Thompson, Thomas, Researches into the History of Welton and its Neighbourhood, Leng & Co.: Kingston-upon-Hull 1870.
Links:
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian
The map could not be loaded. Please contact the site owner.