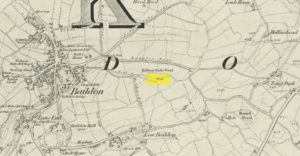
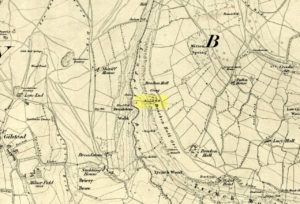
Healing Well (destroyed): OS Grid Reference – SE 22 33
Archaeology & History
Ths curiously-named site is described just once in very early field-name records as the ‘Fukewell’. Included in A.H. Smith’s (1961) magnum opus, he passes over the place-name without comment. But in finding his 12th century literary source, we read that it was located on some land given to the monks of Kirkstall Abbey, Leeds. Written in early disjointed Latin, we find that the Fukewell was mentioned on a grant that described five acres of land given by one Adam Samson to the monks of the Abbey. On one of the acres was a site known as the Cold Well, whilst the Fuke Well was found on a piece of land adjacent to a house, but its precise location seems to have been lost. Nothing is mentioned about it by great Pudsey historan Simeon Raynor, despite him naming a number of other wells in the area – so we must presume that the site had already gone when he came to write his work.
But what does the word fuke actually mean? There is nothing to explain it in Wright’s Dialect Dictionary, nor other regional dialect or place-name works. I was wondering if it derived from the old english word ‘fuck’, which was common parlance in earlier centuries. ‘Fucking’ was a word that didn’t have the debased christian ideology attached to it: of something not to be talked about, or be hidden. To have a fuck, or go fucking, was always quite normal; and to most people in the real world we use the same term with absolute ease – because we all do it! But this etymological idea is pure speculation on my part. Can anyone give clear light to fuke’s real meaning?
References:
- Fryer, Peter, Mrs Grundy, Dennis Dobson: London 1963.
- Lancaster, W.T. & Baildon, W. Paley (eds.), The Coucher Book of the Cistercian Abbey of Kirkstall, Thoresby Society: Leeds 1904.
- Smith, A.H., The Place-Names of the West Riding of Yorkshire – volume 3, Cambridge University Press 1961.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian