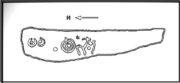
Cup-and-Ring Stone: OS Grid Reference – SE 18066 51251
Also Known as:
- Carving 605
- Northern Earth Mysteries Stone
Getting Here

Sunrise Stone, Snowden Carr
Take the same directions as if you’re going to visit the Naked Jogger Carving (stone 612), not far from the well-known Tree of Life Stone. From the Naked Jogger carving, walk up the small outcrop of rocks that bends above you. Barely 100 yards up when you reach the top, you’ll notice a single large sloping stone barely 50 yards ahead of you in the same field. That’s the spot!
Archaeology & History
This is a little-known beauty of a carving just off the edge of the quiet moors that are littered with prehistoric remains. It was only rediscovered a few years ago — by myself if you believe the writings of rock art student Keith Boughey (2010) in his essay (scattered with mistakes) on the validity of so-called “amateurs” exploring petroglyphs. But I’d never even visited this carving until two years ago! The stone was in fact found during a field-walk by early members of the Northern Earth Mysteries group in August 1989 (Wilson 1990) and subsequently described and illustrated for the first time by Phil Reeder (1990).

Close-up of main cluster
As can be seen in the photos accompanying this site profile, the rock on which the carving has been done has, at some point in the past, been cut into and its edges have been hacked away and destroyed, literally cutting into the overall design. We have no idea what the original size of the stone was, obviously, but this petroglyph was once larger than the design that we see at present. Such is the price of ‘progress’, as some folk call it.
Anyway – a few months after the carving was rediscovered, Phil Reeder (1990) wrote:
“After a visit to the Tree of Life stone…a cursory inspection by the NEM Group was made on nearby rock outcrops, part of which showed evidence of recent exposure due to soil erosion.
“One stone in particular stood out as five shallow cups and associated rings could be discerned. When cleaned, it became apparent that further carvings extended beneath a thin eroding soil layer. When this layer was cleared, a complex set of carvings were revealed.
“Only preliminary work at the site has been carried out to date, but it appears that the carvings comprise of at least 28 cups, 13 of which have associated rings; several of the cups are linked by gutters forming an intricate design, one gutter part enclosing 11 cups. The carvings on the lower edge of the stone have weathered badly and are difficult to interpret.”
Reeder’s so-called “amateur” description is a good one. Certainly more accurate than the subsequent one by Boughey & Vickerman (2003):
“Large rock of coarse grit whose surface slopes with the hill. About forty cups, some large, many with single rings, and many curving grooves, the whole forming a remarkable, complex design.”

Phil Reeder’s 1990 drawing

Boughey & Vickerman’s sketch
We can see in the respective drawings by both Reeder (left) and Boughey & Vickerman (right) that some elements which should have been included in the ‘official’ drawing were missed, yet had been accurately included in the earlier ‘preliminary’ drawing, as Mr Reeder put it. I hope that readers will forgive me pointing out these seemingly minor elements; but I do it to illustrate the ineffectiveness of more recent rock art students who are gaining the title of ‘experts’ in this field. It’s important to recognise that, in this field of study, “experts” are few and far between indeed… I’ve certainly yet to meet any!

Northern end of carving

Southern side of carving
The carving is mentioned briefly in Beckensall’s (1999) introductory study, with little comment. But of note here is not only the curious linear feature running between two cup-and-rings, but the position of the stone in the landscape. For if you sit either upon or next to this carving, you are looking east straight across the gorgeous Fewston valley directly at the prominent wooded hill of Sword Point. As it slopes down into the present-day greenery of fields and scattered woods, the Wharfe Valley spreads out to the distant east and, as the sun rises and scatters its rays onto the wet morning stone here, the design on the rock awakens with much greater visual lucidity than that which our daytime eyes bestow to us. In all likelihood, sunrise was an important element in whatever mythic function underscored this curious carving, with its human-like figure rising on its southern side, emerging from the edge of the rock, personifying perhaps the rising solar disc and the living landscape as the daylight breath awoke Earth’s creatures; or maybe it signifies a symbolic group of people gathered together watching the sunrise…
Of course, I’m dreaming…
References:
- Barnett, T. & Sharpe, K. (eds.), Carving a Future for British Rock Art, Oxbow: Oxford 2010.
- Beckensall, Stan, British Prehistoric Rock Art, Tempus: Stroud 1999.
- Boughey, Keith, “The Role of the Amateur in the Study of UK Prehistoric Cup-and-Ring Art,” in Barnett & Sharpe, Oxford 2010.
- Boughey, Keith & Vickerman, E.A., Prehistoric Rock Art of the West Riding, WYAS: Leeds 2003.
- Chappell, Graeme, “North Yorkshire Rock Art – New Discoveries,” in Northern Earth, no.62, 1995.
- Michell, John, The Earth Spirit, Thames & Hudson: London 1975.
- Reeder, Phil, “Snowden Carr Rock Carvings,” in Northern Earth Mysteries, no.40, 1990.
- Wilson, Rob, “Pateley Bridge Gathering,” in Northern Earth Mysteries, 40, 1990.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian
The map could not be loaded. Please contact the site owner.