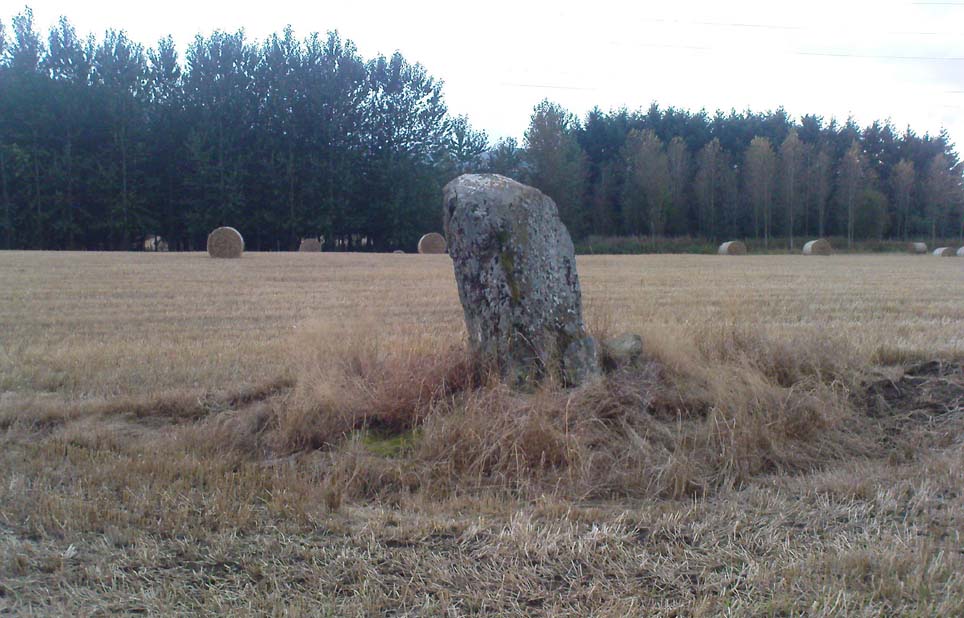
Stone Circle: OS Grid Reference – NN 8022 4873
Also Known as:
- Carse Farm I
- Weem circle
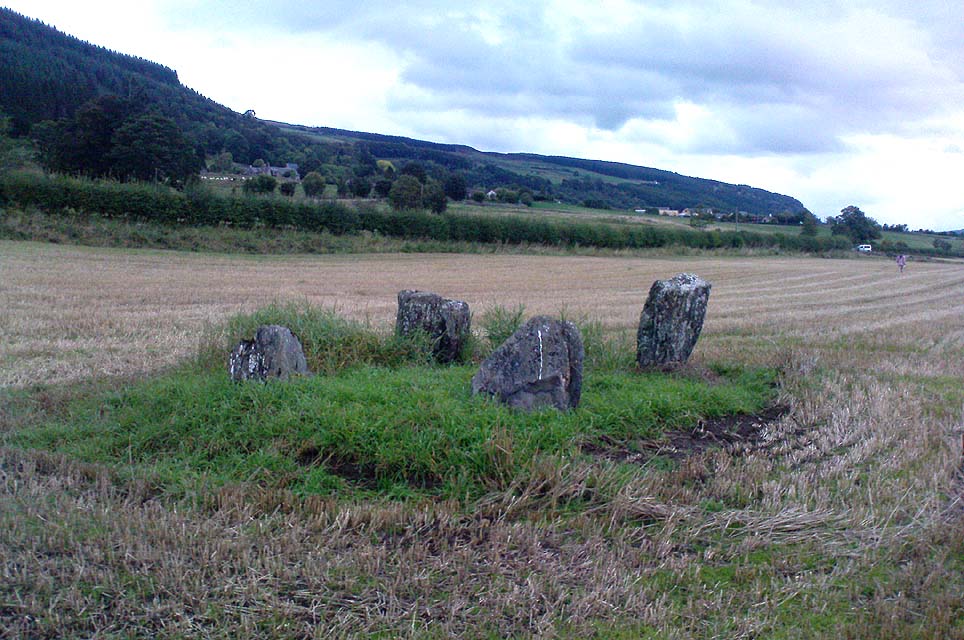

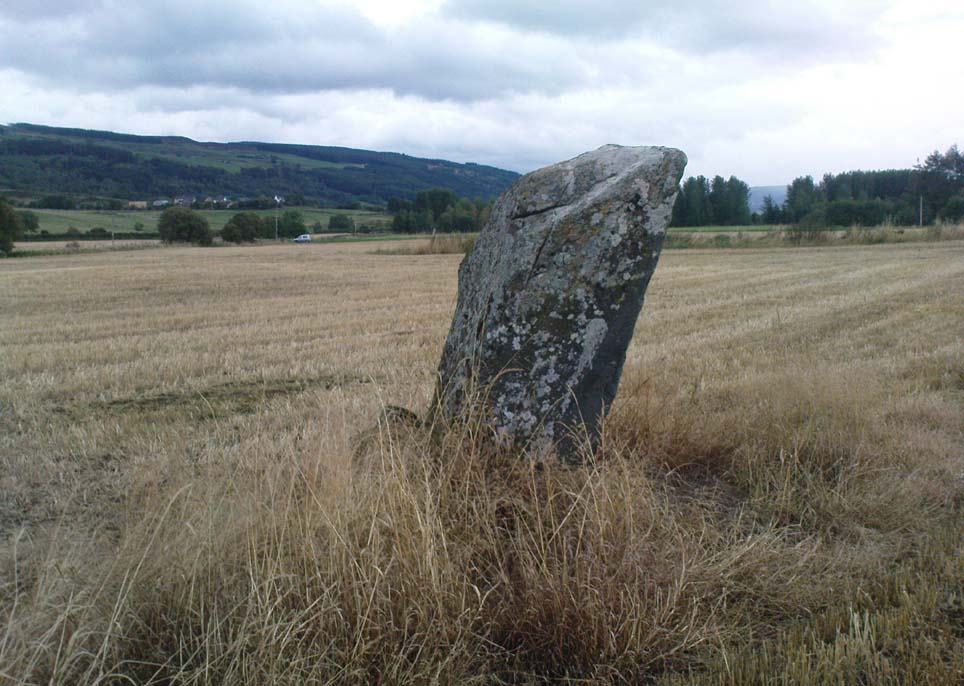
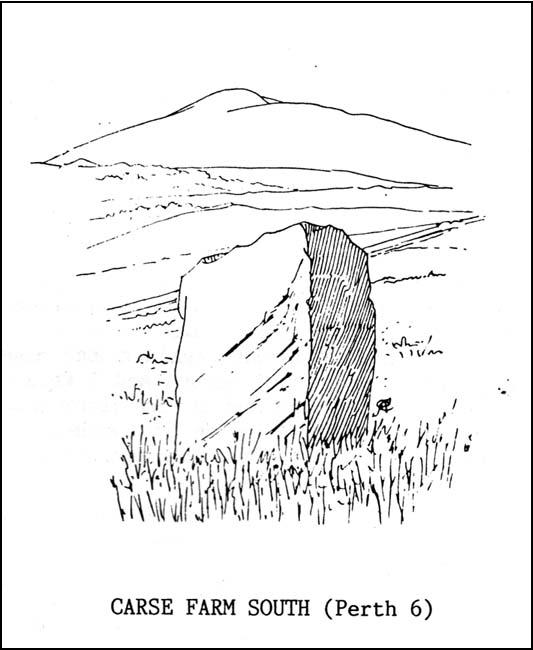
To get here, follow the same directions to reach its nearby colleague of Carse Farm south — but instead of walking down the track to where its companion is found, this small ring of stones is found a coupla hundred yards into the first field by the roadside. Unless the field’s fulla corn (in which case, give it a miss cos even if you do find it, you won’t be able to make much out), y’ can’t really miss it!
Archaeology & History
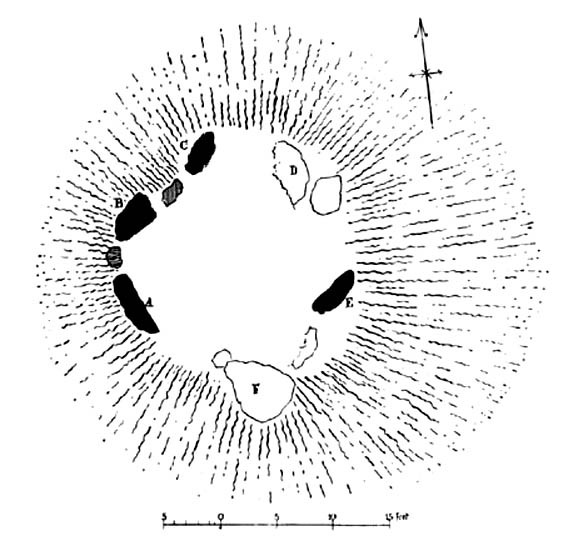
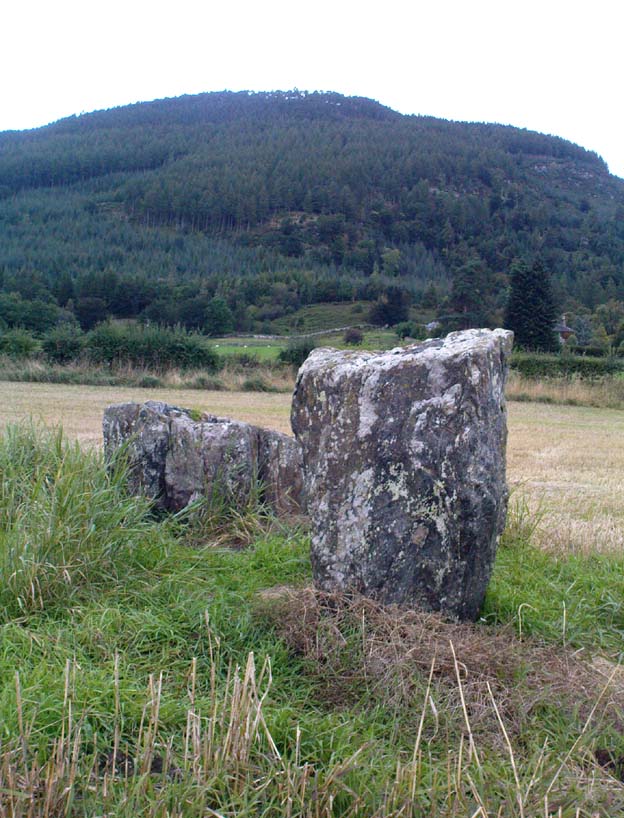
As with its nearby companion of Carse Farm south, this small “ring” of four stones is found along the Tay valley floor and, though cited as a stone circle in many archaeology tomes, should more accurately be defined as a cairn circle of sorts. Structurally akin to other four-posters, it reminded me of a distant companion in North Yorkshire more than 200 miles south: the Druids Altar at Bordley, which is also a robbed prehistoric tomb and not a stone circle. But it’s a fine little site sat amidst the majestic temple of surrounding hills on all sides, bar east, where the Tay valley reaches into the distance.
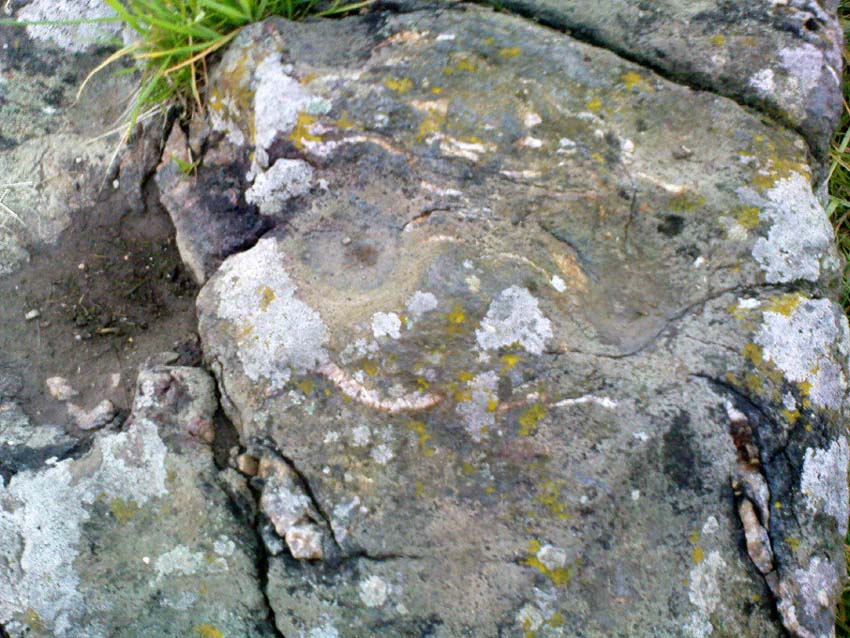


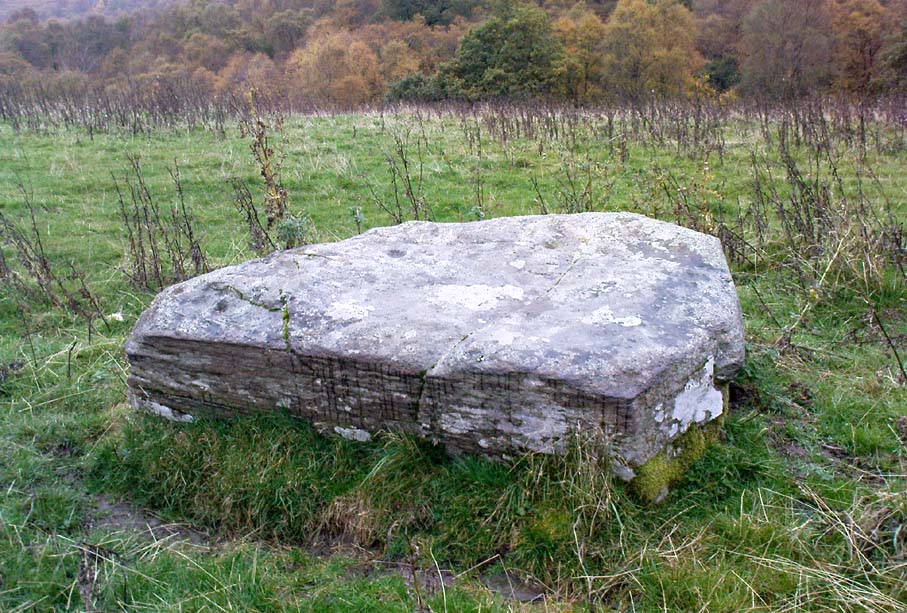
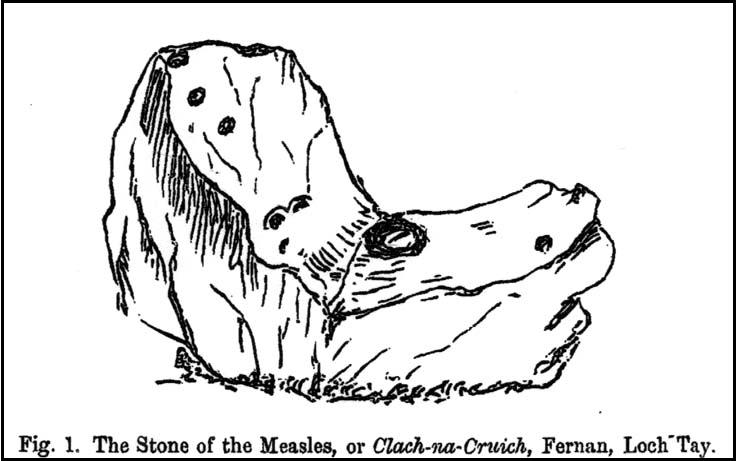
Like its damaged companion in the field below, some of the stones in this circle also have well-defined cup-markings on top of the uprights; although when we visited here, low cloud and late daylight conditions prevented us from getting good images of the cup-marks concerned (as the photo of one of them here illustrates). The cup-markings are, curiously, carved on the top of the small standing stones.
Described briefly in Alexander Thom’s Megalithic Rings (1980), he regarded its geometry as “circular” in structure. Aubrey Burl (1988) gave the lengthier archaeological history of the site, telling:
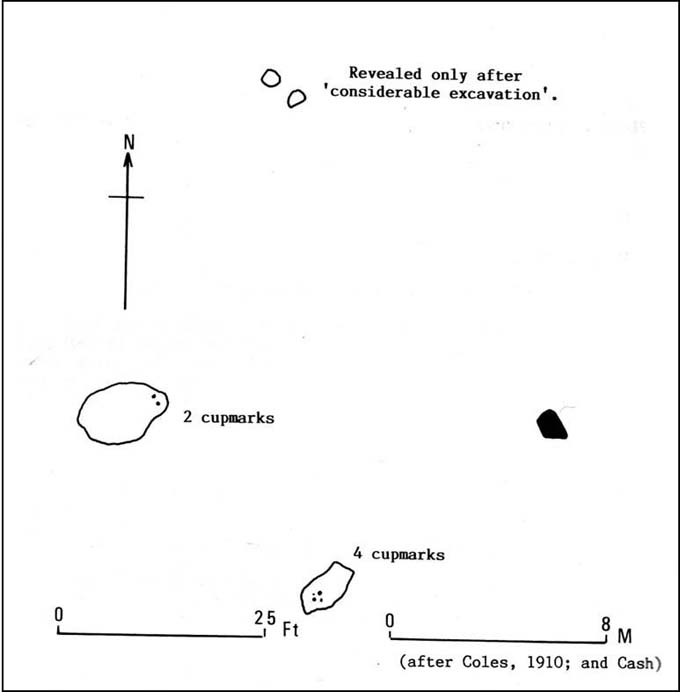
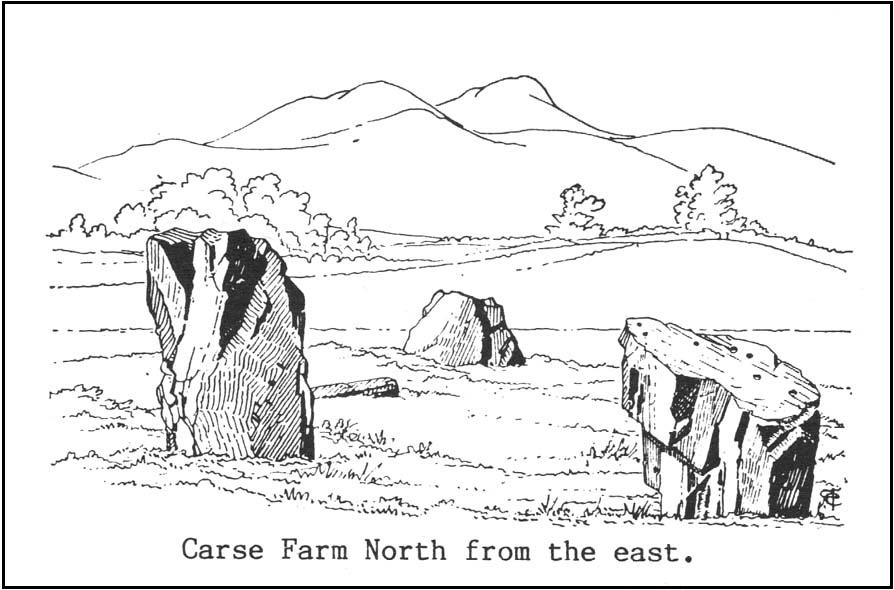
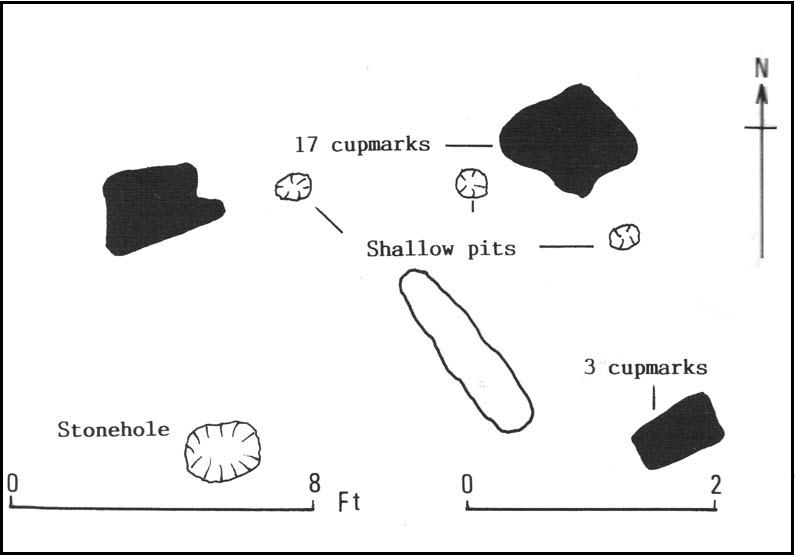
“On the ‘carse’, or lowland…this 4-poster was excavated in 1964. When Coles saw it in 1907 only three smallish stones remained standing although “it seems clear that at this site there were originally four Stones as in so many other Perthshire groups”… The SW stone was missing but halfway between the NW and SE stones a long, thin slab lay half-buried.
“Coles noticed that there were cupmarks on the tops of both the NE and SE stones. The SE had three carvings but the top of the NE had no fewer than 17, the largest ‘cup’ being 4 by 3½in (10 x 9cm). In the group were two ‘dumb-bells’. In the same field the farmer had dragged away a buried stone which was also cupmarked.* (my italics, PB)
“Of the three standing stones, the NE is 3ft 11in (1.2m) high; the SE, 5ft 1in (1.6m); and the NW, 4ft 1in (1.3m). These heights…are almost double those cited by Coles (1908: 126).
“”The 1964 excavation discovered the SW stonehole. The 5ft 10in (1.8m) long stone lying at the centre of the 4-Poster was erected in it, a task made easier by the fact that its base had been keeled… The base was unweathered showing that the stone had been toppled in quite recent times as had the stones of the two Fortingall 4-Posters…3¾ miles to the WSW. The four stones stood at the corners of a rectangle 12ft by 8ft (3.7 x 2.4m) on a long ENE-WSW axis. They also stood on the circumference of a circle 14ft 5in (4.4m) in diameter.
“A tapering pit was discovered against the inner face of the NE stone, about 2ft 6in (76cm) across and 1ft 2in (37cm) deep. It was filled with cremated bone and sticky black earth and charcoal. At the bottom, a collared urn lay on is side, its rim decorated in geometrical designs. A flint flake lay near it. Within the 4-Poster there were three shallow pits, two between the NW and NE stones, another between the SE and SW. Their edges were clean and they had been backfilled with brown loam. The excavators thought they might have “been used for stabilising props during the erection of the stones.” …As the heaviest block, that at the NW, weighed about 6 tons it would have required 20 to 30 people to drag it upright…and the use of such props would have made their insertion safer.”

Unless the people building this site were dwarves, we’ve gotta re-assess this latter remark (which Burl quotes from the earlier archaeologist’s report from the 1960s). Having personally been involved with the creation of modern stone circles with stones larger than the ones here, we know that the uprights here could have been erected by 8-10 people at the very most.
Archaeology and folklore records describe many other prehistoric sites along this section of the upper Tay valley, but it’s also very likely that other “circles” or cairns of similar structure to the two known at Carse Farm once existed close by that are not in modern literary accounts.
References:
- Burl, Aubrey, Four Posters: Bronze Age Stone Circles of Western Europe, BAR 195: Oxford 1988.
- Coles, Fred, “Report on Stone Circles Surveyed in Perthshire – Northeastern Section,” in Proceedings of the Society of Antiquaries of Scotland, volume 42, 1908.
- Stark, Gordon (ed.), Cupmarked Stones in Strathtay, Breadalbane Heritage Centre 2005.
- Stewart, M.E.C., “Carse Farm 1 and 2,” in Discovery & Excavation, Scotland, 1964.
- Thom, A., Thom, A.S. & Burl, H.A.W., Megalithic Rings, BAR 81: Oxford 1980.
* Is anyone aware of further details about this carving? Do we have any sketches of it?
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian
The map could not be loaded. Please contact the site owner.