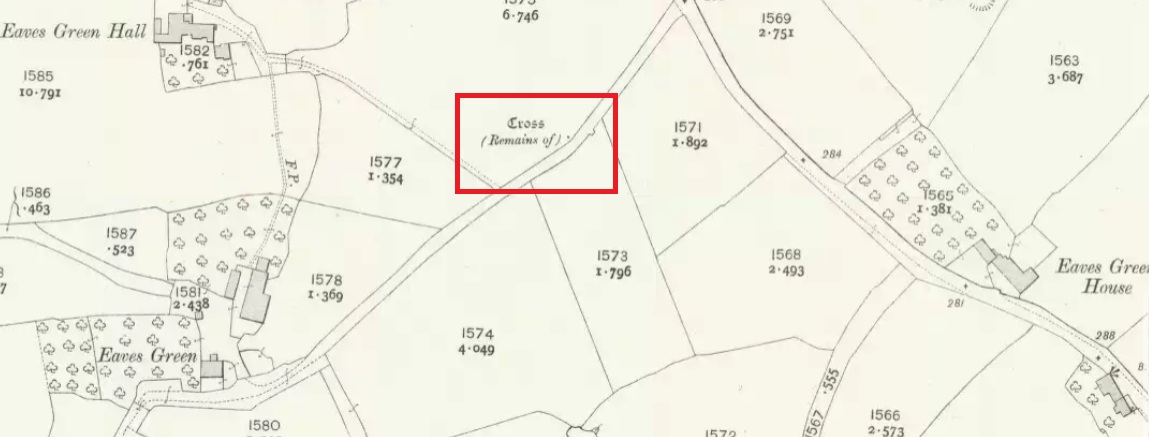
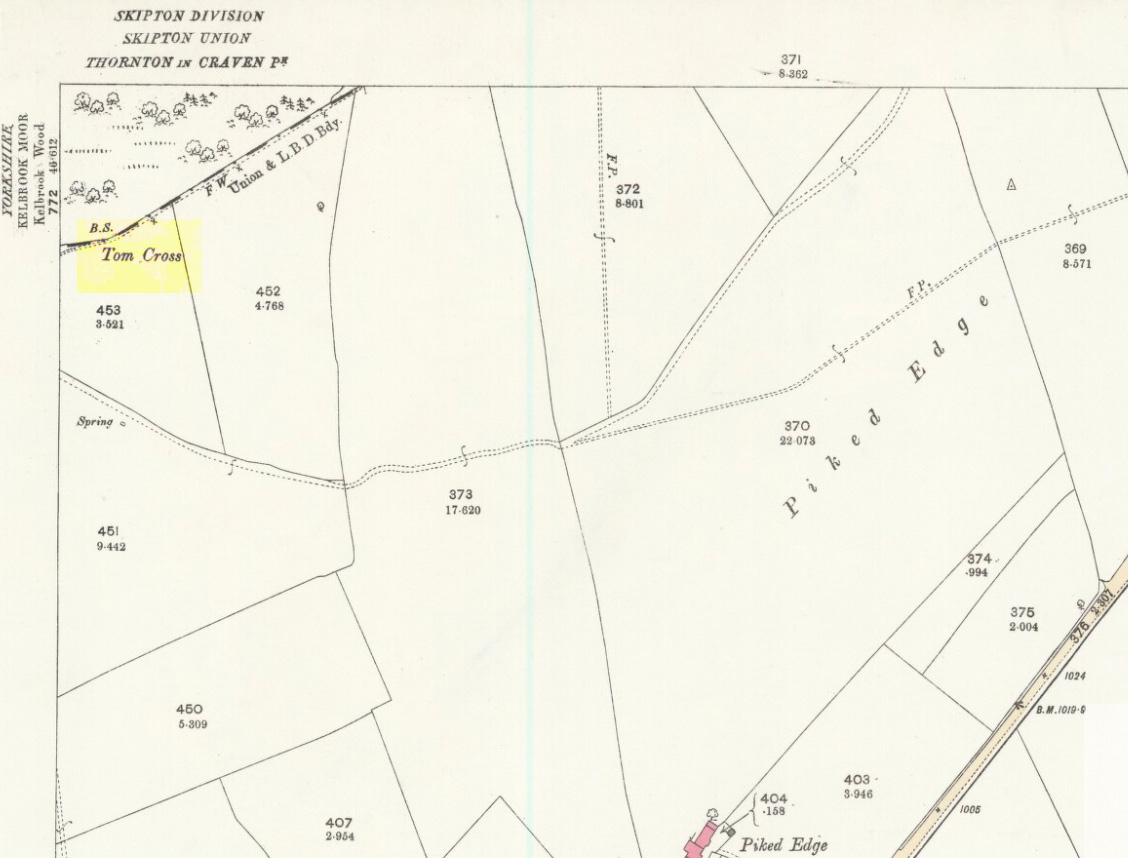
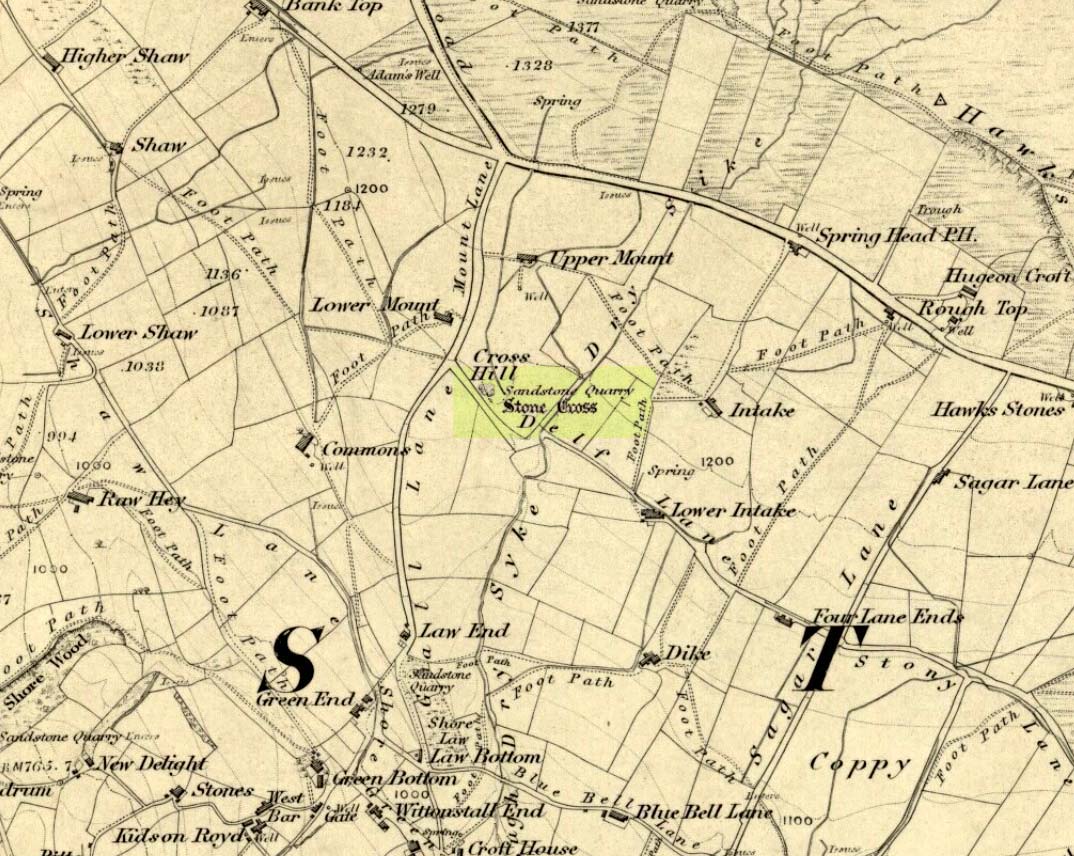
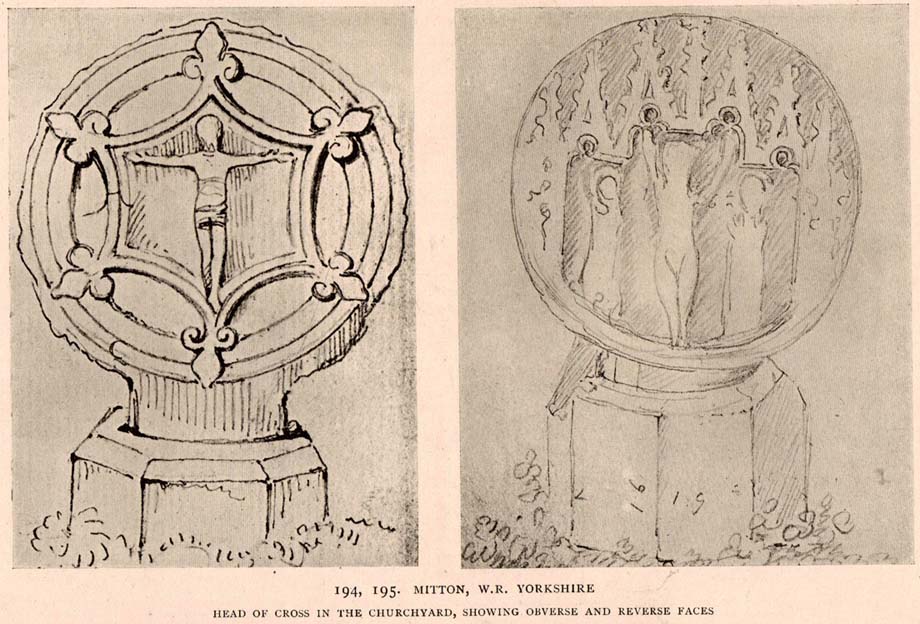
Cross: OS Grid Reference – SD 94360 30269
Also Known as:
- Long Stoop
- Ralph’s Cross
From Hebden Bridge go up the Heptonstall road, going round the village and onto and through Slack, keeping straight on the road until it goes uphill for a short distance, then levels out; then watch out for the small right-turn at Colden and the single-track road heading to a dead-end. Go right to the end, the very end, and go through the gate and walk up the track onto the moor. As you reach the ridge and the moorlands open up before you, note the small ‘standing stone’ on your right, about 10 yards off-path— and there, 100 yards the opposite direction to your west, the tall upright Reaps Cross is sat on the moortop. Y’ can’t miss it!
Archaeology & History
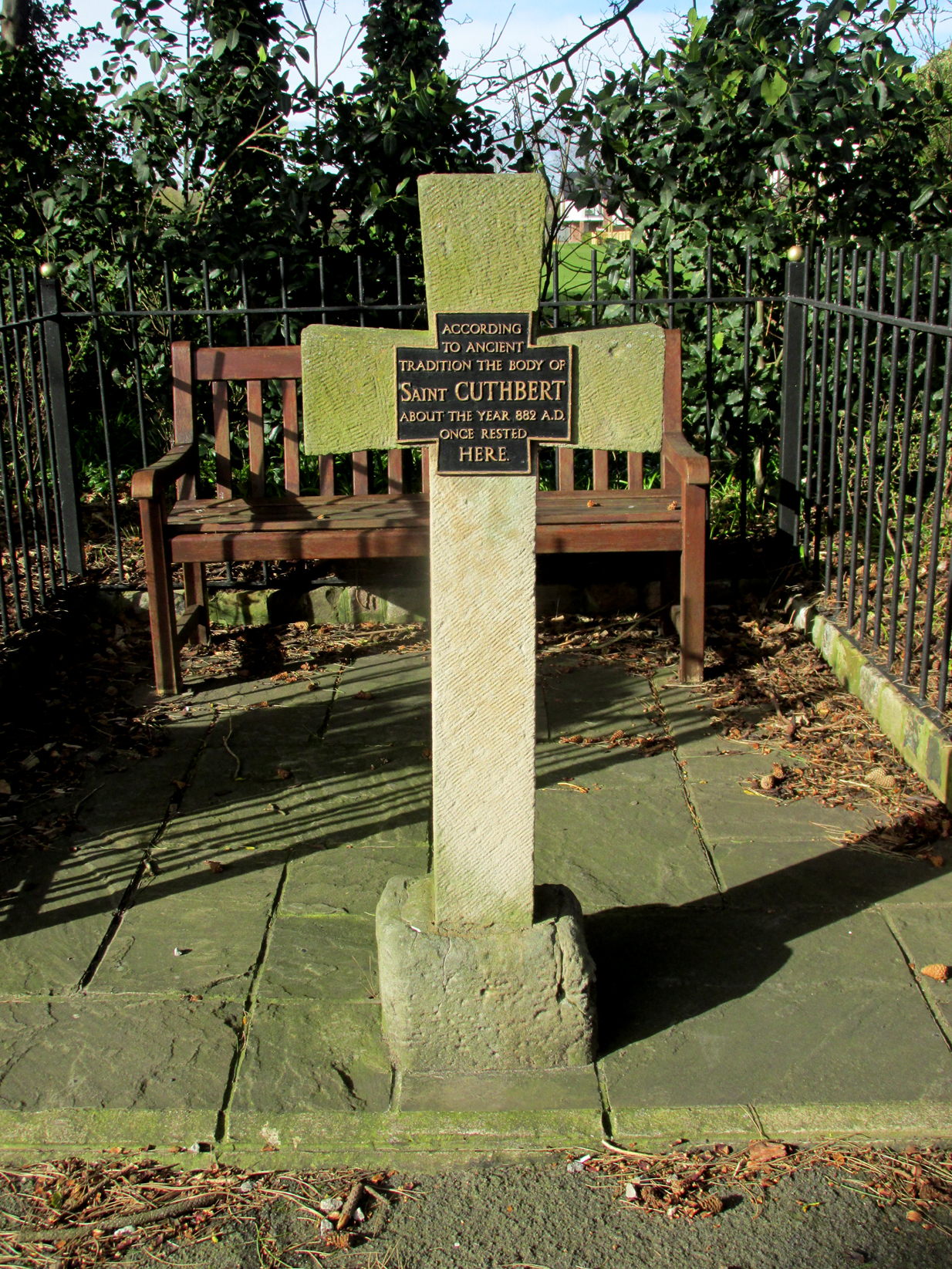
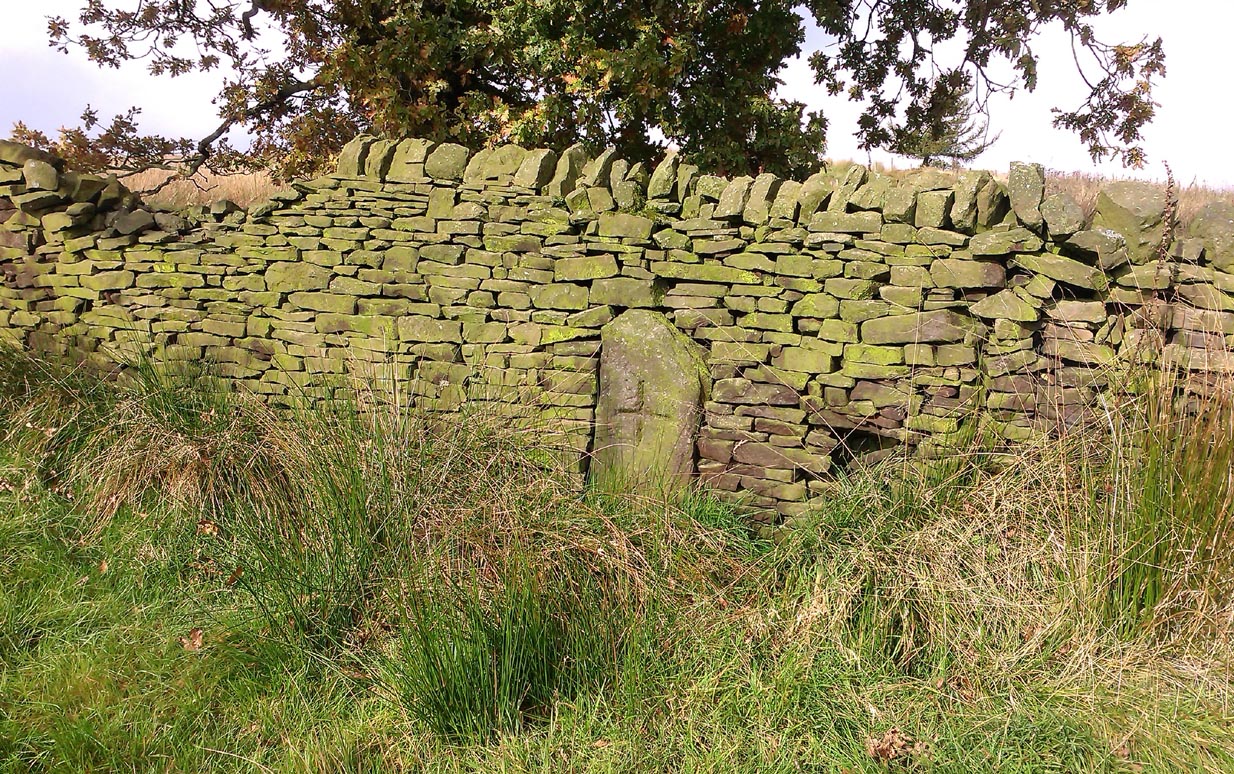
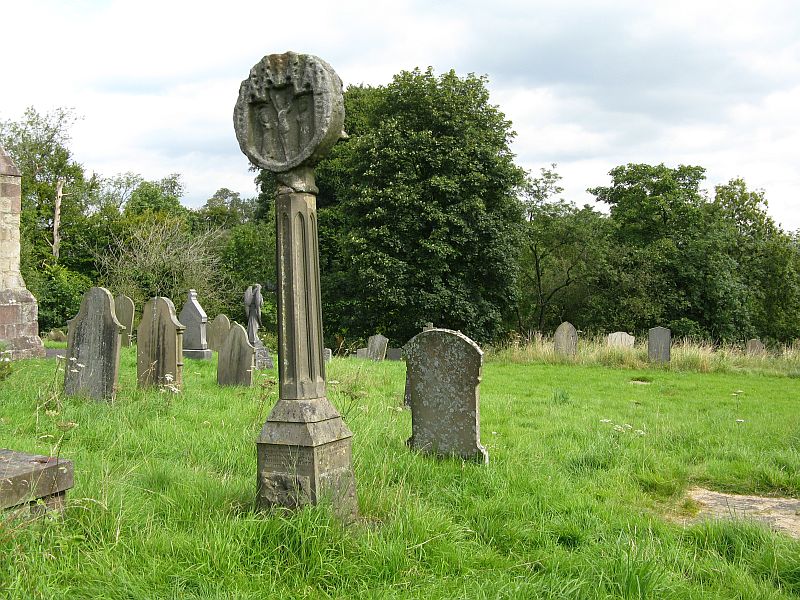
Found in the middle of a beautiful nowhere not far from the prehistoric standing stone on Standing Stone Hill, this old tall monolith was said to have stood as a marker beside the old road which ran from Halifax over the moors to Colne, until the more recent Widdop Road became the more preferred route. Known locally as the Long Stoop, in 1900 George Tyack said of it,
“This stone, which is composed of millstone grit, lay for a long tine broken and overthrown, but has in recent years been replaced on its original site and restored. It is a simple Latin cross standing twelve feet high amidst the heather of the Yorkshire moors.”
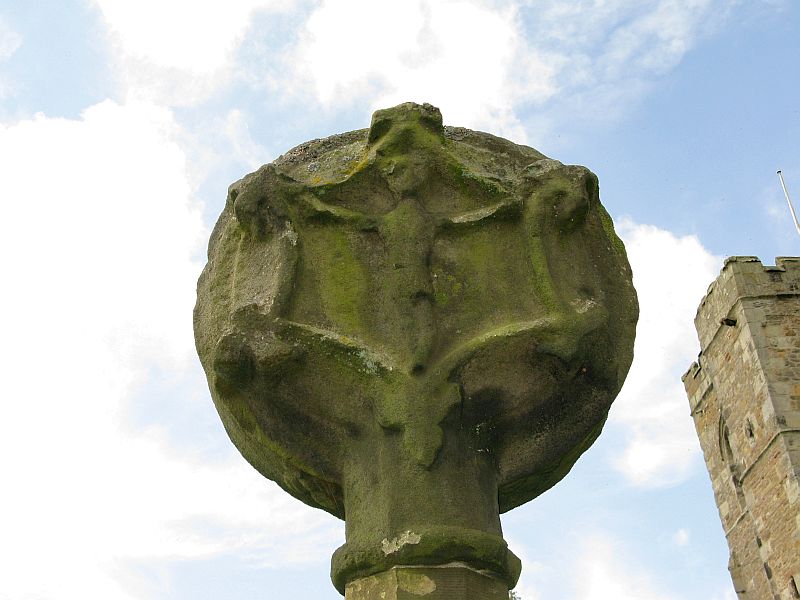
Shortly before Tyack’s description, the local historian John Longbottom (1897) wrote a series of articles on the old stone crosses of the region and gave us this old sketch of the site (right). Even in his day the cross had been “wilfully thrown down” (probably by the screwy Puritans at that time), but a short time later it had been “repaired and restored to its original position.” In Longbottom’s day there were short ‘arms’ extending outwards from near the top of the obelisk, defining it as a distinct ‘cross’, but these have subsequently been lost following further local demolition attempts. He told how,
“Reaps Cross is known locally to shepherds, gamekeepers and farmers at ‘T’ Long Stoop’, and…apart from its religious associations, it forms an important landmark, now as in ancient times, to many a poor weary traveller crossing the dreary and lonesome hills between Lancashire and Yorkshire.”
The cross keeps getting knocked over, by both lightning and idiots of various persuasions; but thankfully the old fella keeps getting resurrected and put back in its place. It’s history is a curious one. When Clifford Byrne (1974) wrote about the site in his unpublished survey, he told how
“This cross appears to be of medieval origin and…in 1973 the monolith lay broken, one section lying in the grass, whilst the other section still stood in the pedestal. It is seen to have been broken once before, for the remains of iron clamps are seen on both sections. The arms have been broken off in some age… A local farmer insisted that the correct name was Ralphs Cross not Reaps Cross, and it should be noted that a section of moor at Widdop (the valley with the high cliffs) is named after a Ralph.”
Standing some 12 feet tall, this is the highest of all the crosses in West Yorkshire and obviously some considerable work went into its creation all those centuries ago. Nobody is sure when it was first made, but the educated guess is 12th century. Why it was erected here, way off from anywhere in the middle of the wild moors, is equally puzzling. It may have had something to do with the nearby medicinal springs; it may have been as a guide-post to travellers—”to Rastric Greave”, according to Waddington (1884); it may have marked an ancient religious route; or it may have distracted people away from the prehistoric upright that gave its name to Standing Stone Hill, a short distance to the west We simply don’t know. It’s well worth visiting though, as the moorland landscape up here is truly expansive and civilization seems thankfully centuries away…
Folklore
Local tradition told that the cross marked an old corpse route, along which the dead were carried before being buried at Heptonstall. Here at Reaps Cross, the bodies were rested by the weary travellers. If this is true, it is probable that the ancient standing stone more than half-a-mile to the west once had something to do with such old rites and routes.
References:
- Bennett, Paul, The Old Stones of Elmet, Capall Bann: Milverton 2001.
- Byrne, Clifford, A Survey of the Ancient Wayside Crosses in North-East Lancashire, unpublished MS, 1974.
- Longbottom, John, “Ancient Crosses in Halifax Parish – Part 2,” in Halifax Naturalist, 2:8, June 1897.
- Taylor, Henry, The Ancient Crosses and Holy Wells of Lancashire, Sherratt & Hughes: Manchester 1906.
- Tyack, George, The Cross in Ritual, Architecture and Art, William Andrews: London 1900.
- Waddington, J. Arthur, “The Crosses in and Around Burnley,” in Transactions of the Burnley Literary & Scientific Club, volume 1, 1884.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian