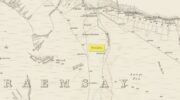
Stone Circle (destroyed): OS Grid Reference – NT 474 548
Archaeology & History
Included in Aubrey Burl’s (1976) first gazetteer, without comment, the site was subsequently added to John Barnatt’s (1989) magnum opus. He tells that in the 19th century, “early Ordnance Survey records…note a destroyed stone circle” here, but draws a somewhat sceptical opinion of its very existence as “the Ordnance Survey frequently made mistaken interpretations in the 19th century and hence this should be treated with caution.”
Despite this, early local historians refer to the site, albeit in the past tense. The first would seem to have been Walter Elliot (1869) in his address to the respected Berwickshire Naturalists Club. Some members of this group had visited a number of ancient sites the previous year:
“A camp above Channel Kirk was also indicated, near which a stone circle formerly existed, but it has been destroyed and the materials used for building dykes within the last five or six years.”
The “camp” was an old Roman one which has itself been almost completely destroyed, despite it still being shown on modern OS-maps.
The circle was mentioned in passing in Mr Thomson’s (1902) huge work on his descriptions of the many local hillforts. Close to one at Kirktonhill known as the Roman or Agricola’s Camp, “forty years ago, there was said to have been a stone circle.” This was reiterated in Craw’s (1920) survey of prehistoric monuments in Berwickshire.
Perhaps the most curious omission is in Mr Allan’s (1900) huge survey on Channelkirk parish. His description of the Roman camp was considerable, but he made no mention of an adjoining circle. The best we got from him was a vague allusion about some ancient pre-christian site not far from the church, when he wrote:
“Whether or not some rude form of a place of worship might then exist on the spot where now a church has stood for so long it were rash to assert, but there are certain indications that some particular place, specially marked as consecrated to religious rites, was then a local possession.”
(it should be noted that the Canmore entry for this site has its location at the prehistoric camp due west of Kirktonhill, which is incorrect)
References:
- Allan, Archibald, History of Channelkirk, J. Thin: Edinburgh 1900.
- Barnatt, John, Stone Circles of Britain – volume 2, BAR: Oxford 1989.
- Burl, Aubrey, The Stone Circles of British Isles, Yale University Press 1976.
- Burl, Aubrey, The Stone Circles of Britain, Ireland and Brittany, Yale University Press 2000.
- Craw, J H., “Early types of burial in Berwickshire“, in History Berwickshire Naturalists Club, volume 24, 1920.
- Elliot, Walter, “Anniversary Address Delivered at Berwick on the 30th of September, 1869,” in History Berwickshire Naturalists Club, volume 6, 1869-72.
- Thomson, A., Lauder and Lauderdale, Craighead Brothers: Galashiels 1902.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian
The map could not be loaded. Please contact the site owner.