Cup-and-Ring Stone: OS Grid Reference – SE 13027 46310
Also known as:
- Carving no.141 (Hedges 1986)
- Carving no.302 (Boughey & Vickerman 2003)
- Cottage Rock
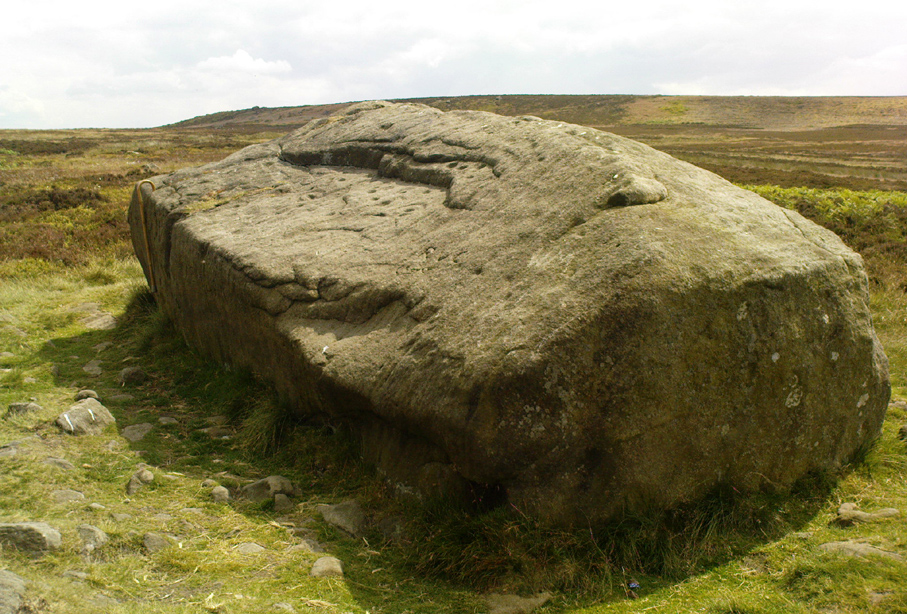

Dead easy to find this one! Get to the Cow & Calf Hotel and walk up the slope onto the moor ahead of you. If you want a direction-pointer, head for the large, seemingly overhanging rocks which are the Pancake Stone, at the top of the ridge, but a few hundred yards to the right (west). Once you reach the level on the moor proper, you’ll see this large haystack-shaped boulder close by. That’s it!
Archaeology & History
This tends to be one of the spots I stop at when doing my tourist walks, to i) let folk get their breath back after ambling from the car park, via Hanging Stones and Map Stone; ii) to drink in the view, and, iii) to begin acquainting themselves with the landscape as it was when this stone was carved (over many decades, perhaps longer), and the animistic cosmology underlying people’s notions of their land. It can be quite an education…
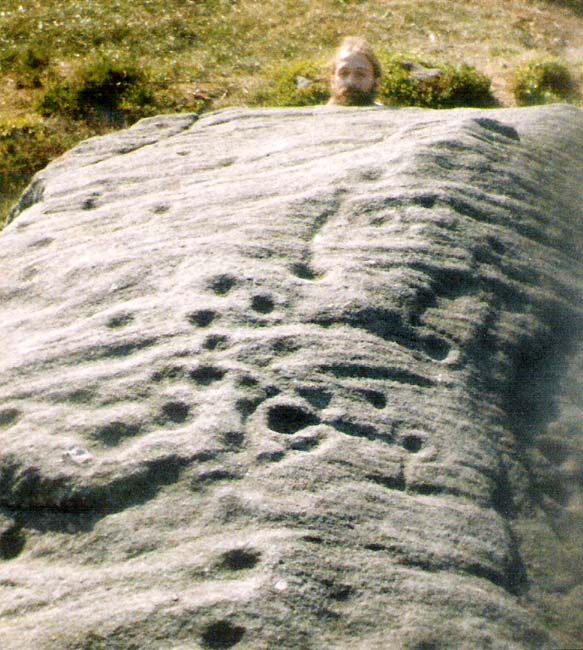


The Haystack Rock was a very important boulder in the mythic landscape on this plain. It stands near the western end of the Green Crag Necropolis: a huge area of land on these moors where, quite simply, the people of these hills laid their dead. Effectively, the Haystack Rock stands on the edge of Ilkley Moor’s “Land of the Dead”.*
Highlighting this quite firmly, we find that prehistoric walling ‘separates’ this great boulder from the other part of the Plain close to its east and southern sides (walling on its western side is as yet unproven). It was a boulder that was specifically sectioned-off, away from any tombs. All along this Plain are numerous small cairns, many with rock-art nearby, and certain parts of the Plain are split into sections by ancient walling (though a precise map of the walling, tombs and rock-art on this moorland ridge has yet to be done).
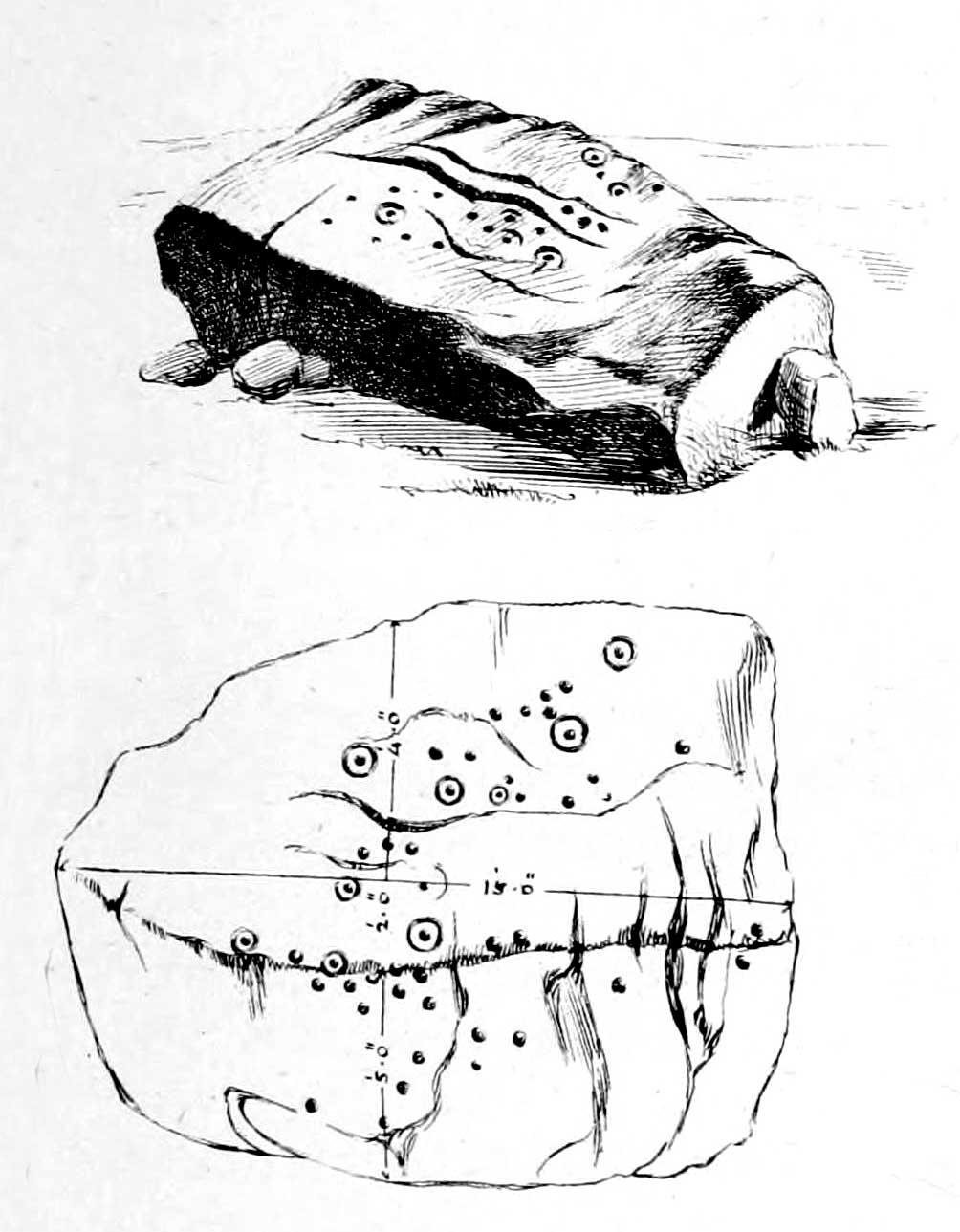
As far as the textbooks are concerned, we find the first mention of this great carved boulder came from J. Romilly Allen at the end of the 1870s. By 1900, a number of people had been here and written of its grandeur; but, as with cup-and-rings in general, its non-linear form and design elicited the usual notions of bewilderment, druids and puzzled ideas. Much like today really!
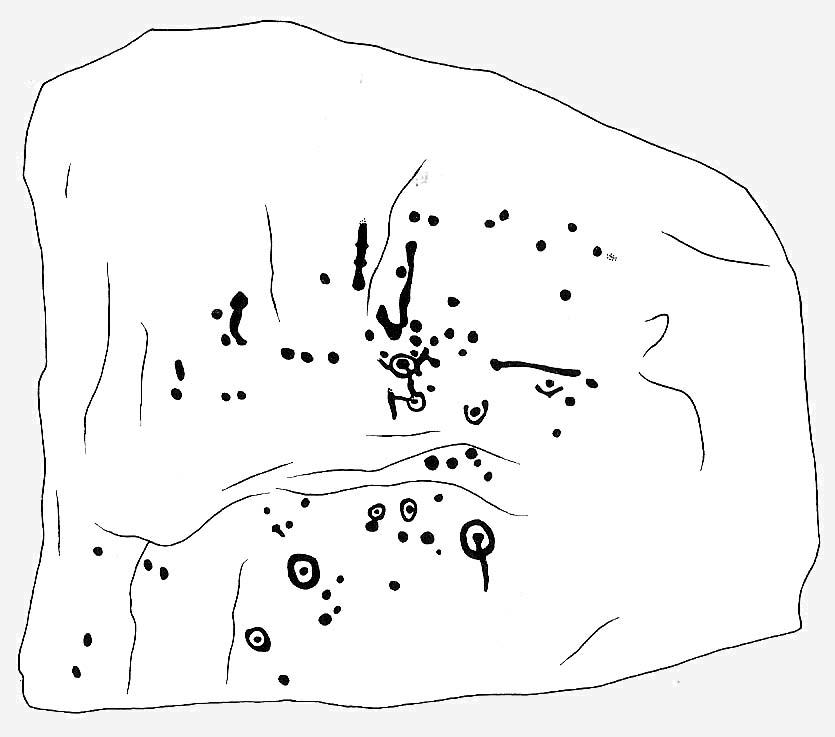
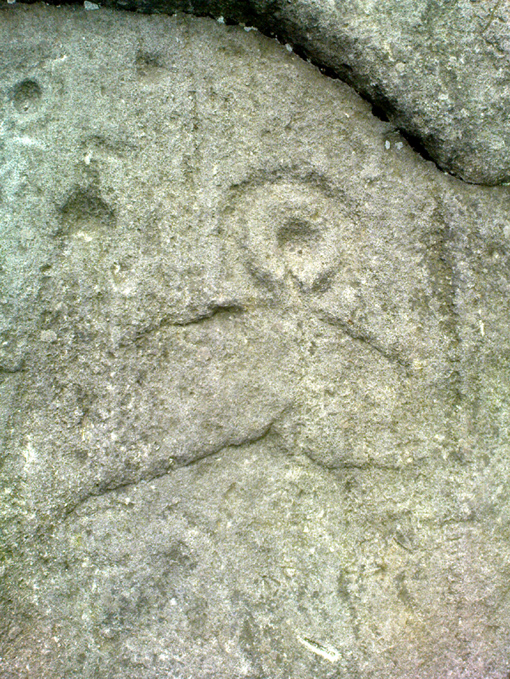
But this is a big and decent carving, with about 60 single cup-markings, 10 cup-and-rings, and various twizzly grooves and lines linking cups to others, and others going to seemingly nowhere. Some of these lines, of course, may be weathering, or weathered channels emerging from once shorter lines. We might never really know for sure what the original carving actually looked like. On the north-facing side is what looks like a decidedly human figurine etched onto this great boulder, in good old cup-and-ring style. I’ve shown this to a few hundred people and they all seem to make the same remark: it’s a woman with her legs wide open — an early form of sheela-na-gig on Ilkley Moor no less! But whether this was intentional (many folk think so), or just us seeing something we want to see (men in particular!), we might never know.


The black-and-white illustration above that shows what seems to be just about all elements of the carving in considerable detail, may well be accurate, but it’s nothing compared to seeing the carving first-hand. When it comes to ancient rock-art, detailed drawings are one thing, but the real thing is altogether much much better! Check it out and see for yourself…
Folklore
I’m not too sure what credibility we should give to Nicholas Size’s (1934) extravagant claims, but this was one of the sites he alleged to have seen visions of druidic rites and ghostly figures!
References:
- Allen, J. Romilly, ‘The Prehistoric Rock Sculptures of Ilkley,’ in Journal of the British Archaeological Association, 35, 1879.
- Bennett, Paul, The Old Stones of Elmet, Capall Bann: Chieveley 2001.
- Boughey, Keith & Vickerman, E.A., Prehistoric Rock art of the West Riding, WYAS: Wakefield 2003.
- Forrest,C. & Grainge, William, A Ramble on Rumbald’s Moor, part 3, Wakefield 1869.
- Hedges, John, The Carved Rocks on Rombalds Moor, WYMCC: Wakefield 1986.
- Size, Nicholas, The Haunted Moor, William Walker: Otley 1934.
* It’s gotta be pointed out that Ilkley Moor’s ‘Land of the Dead’ extends much further than just the Green Crag. Much of the extended land above here to the south was an important area, where at some places rites of the dead were performed. The supposed ‘settlement’ nearby (as well as the lesser known one on the moor west of here, on the moor above Ilkley Crags, near Cranshaw Thorn Hill) was likely to be a place where the dead were rested for a period. But more about that in the section on the Green Crag Settlement…
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian
The map could not be loaded. Please contact the site owner.