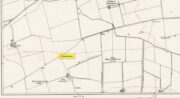
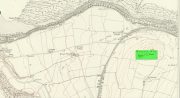
Settlement: OS Grid Reference – NO 3661 7044

From Kirriemuir town centre up the B956 Kinnordy Road, turn left where it goes along the B955 road for several miles towards Cortachy, following the same route as if you’re going to the curious Whitehillocks stone circle. Literally two miles (3.2km) along the road past Whitehillocks farmhouse, a large “parking” spot is at the right-hand side of the road. From here, walk along the road for 230 yards and go thru the gate on your left. The first low-rise hut circle is to your immediate right; and from here, meander along the track ahead of you, keeping your eyes peeled…
Archaeology & History
Despite being initially difficult to make out (as the photos here indicate), once your eyes have adjusted to the landscape morphology, you realise what an impressive prehistoric complex you’re wandering through. Saying that, it’s primarily a site that’s gonna be of interest to antiquarians, archaeologists and historians, as this is a settlement you’re looking at, lacking in megaliths, petroglyphs and similar ritual sites.


The first site that you’ll probably notice is visible from the road—but it’s not the first part of the settlement that you’ll pass. Immediately through the gate (as I’ve said) is the embanked rise of earth—only one or two feet high—making up the first notable hut circle (NO 36612 70453), measuring roughly 15 yards across. The shape and form of this circle typifies the others in the arena ahead of you, so that once you’ve made yourself aware of what this one looks like, you’ll be able to see the others with greater ease. Another low embanked circle of roughly the same size is just a few yards away at NO 36605 70439.
Straight back onto the track you’ll notice another larger D-shaped enclosure immediately on your left (NO 36622 70406), about 17 yards across; this is accompanied by what looks like a cairn immediately right of the track (NO 36609 70413), but this is actually a much smaller D-shaped enclosure, just right for one or two people.
The small rounded hill in front of you has what may be a circular enclosure on its top, but I wasn’t too sure about it. But looking down from this hill is the most visible of all the structures in the settlement (NO 36580 70307)—and the one I mentioned as being visible from the road. At first it’s a little deceptive in appearance, as you get the impression that the oval of stones (top photo) is what constitutes this hut circle, when in fact this element may be mediaeval in nature as it’s been built on top of an earlier Iron Age (?) enclosure. You can barely see this earlier form at ground level, so it’s best to walk back up the rounded hillock and cast your gaze back and forth and round the side of the ring of stones. You’ll see, eventually, the shallow overgrown walling of a larger oval-shaped enclosure, measuring eighteen yards across, whose edges start from the bottom of the hillock and arc around to the outer edges of the stone construction.

Back onto the track and further into the meadows, the next hut circle you’ll meet is (keep your eyes peeled) right by the track-side (NO 36573 70230). It has wide embanked walls that are low to the ground and completely overgrown, measuring 15 yards (E-W) by 18 yards (N-S), with what looks to be the original entrance or door on its south-side. A similar large circle exists on the other side of the track a little bit further along (NO 36499 70138).
There’s much more to this settlement, including lengths of walling in the grasslands below the last two circles and where, if you look carefully, you’ll see one of at least two cairns in this area. On the other side of the road are one or two other small hut circles and a much larger construction in the field further down the road, measuring 25 yards in length (NO 36569 70481). This would seem to be the largest of the lot.
The age of this settlement probably covers a considerable period of time: beginning perhaps in the Bronze Age, certainly in the Iron Age and all the way through into the mediaeval period where, all down Glen Clova, remnants of such hamlets still live beneath the soil. This entire arena is bathed in silence, save the wind and call of the birds. Tis a beautiful space to spend a few endless hours…
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian