Sacred Well: OS Grid Reference – NS 66765 62063
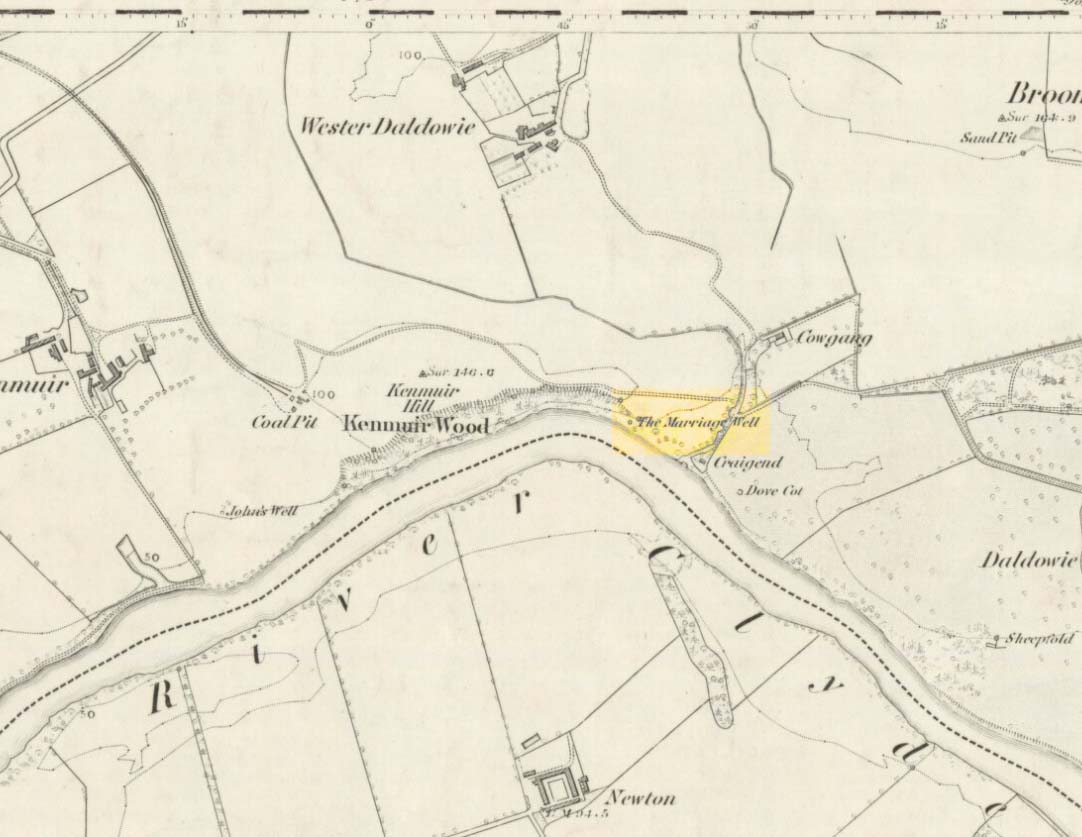
Get onto the A763 road several miles east of Glasgow city centre and go along Gardenside Avenue onto the Carmyle estate. A few hundred yards on, turn right down Carmyle Avenue, then left onto River Road. Follow the footpath along the edge of the River Clyde for nearly a mile—past the recently destroyed John’s Well—until you hit the remnants of Kenmuir Woods. You’ll reach some large polluted pools and when you reach the gap between the first and second pool, walk into the trees above the river and the Well is there.
Archaeology & History
The decaying remains of this old well can still be seen, incredibly, in the small copse of trees that are Kenmuir Woods, just a few yards above the River Clyde, 160 yards below the M8 and the same distance west of the Daldowie sewage treatment works, with polluted water treatment pools just yards away! Not the sort of place you’d take a partner for any sort of marriage ceremony whatsoever nowadays! But it wasn’t always like this of course. Only since the Industrialists stamped their mark…
When Hugh MacDonald (1860) wrote the finest narrative of this arena in the middle of the 19th century, his evocative words painted the entire landscape with a veil untouched since his days. Indeed, it is truly like another world compared to the sacrilege of what we see today:
“It is a wild and bosky scene, covered with a picturesque profusion of timber, and is the habitat of flowers innumerable. The weaver herbalists of Camlachie and Parkhead find it a perfect storehouse of medicinal rarities; and on Sundays they may be seen in sickly groups prying into every green recess in search of plants which old Culpepper would have loved for their rare qualities, or carrying them home in odorous bundles, confident of having obtained a mastery over “all the ills that flesh is heir to.” The botanist may also occasionally be seen lurking here, vasculum in hand, or on bended knee, examining the structure of some strange flower. But even the mere general lover of flowers will here find much to reward his attention. At present the May-flower (Caltha palustris), the wild hyacinth, the craw-flower of Tannahill, the red campion (Lychnis dioica), the odorous woodruff (Asperula oderata), the globe-flower or lucken gowan (Trollius europœus), and many others are in full bloom, and so thickly strewn that even as the poet says, “You cannot see the grass for flowers.”
“At the foot of the bank, near its upper extremity, there is a fine spring, which is known by the name of the ‘Marriage Well,’ from a couple of curiously united trees which rise at its side and fling their shadows over its breast. To this spot, in other days, came wedding parties, on the day after marriage, to drink of the crystal water, and, in a cup of the mountain-dew, to pledge long life and happiness to the loving pair whom, on the previous day, old Hymen had made one in the bands which death alone can sever. After imbibing a draught of the sacred fluid from the cup of Diogenes, we rest a brief space on the margin of the well.”
One wonders how far back in time the attribution of ‘Marriage Well’ from the animism of the trees went; and whether marriage ceremonies were performed here, quietly, away from the prying eyes of the Church and invading english in centuries much earlier under the guidance of the Moon. It’s probable…
Nature’s cloak was still intact here when, many years after Hugh MacDonald’s visit, the local writer Dan McAleer (1930) informed us that,
“Shy bridesmaids and their groomsmen used to visit after a wedding to drink the mystic waters of the Marriage Well. Certain places about the woods were well adapted for picnics, etc. After tea and refreshments the lads and lassies passed hours in amusement trying to step over the well and anyone soiling the water in any way while stepping across it would not get married that year.”
Much of the beauty of the landscape and Her waters, and the rich romance that arises from Her cyclical forms are long gone from here now… Cold ‘progress’ bereft of the necessity of Nature’s sanctity is no progress at all… Although the genius loci of the place may have long since gone, at the very least the regional council—or decent locals, if the council can’t be arsed—could erect some memorial and save the failing Marriage Well from what seems to be its close and final demise….
References:
- Carpenter, Edward, Civilization: Its Cause and Cure, George Allen & Unwin: New York 1914.
- McAleer, Dan, A Sketch of Shettleston, 1930.
- McDonald, Hugh, Rambles round Glasgow, John Cameron: Glasgow 1860.
- Michell, John, The Earth Spirit: Its Ways, Shrines and Mysteries, Thames & Hudson: London 1975.
- Michell, John, Simulacra, Thames & Hudson: London 1979.
- Morris, Ruth & Frank, Scottish Healing Wells, Alethea: Sandy 1982.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian
The map could not be loaded. Please contact the site owner.