Cup-and-Ring Stone: OS Grid-Reference – SE 18083 51229
Also Known as:
- Carving no.606 (Boughey & Vickerman)

If you’re coming up from Otley or Askwith, take the same directions as if you’re going to visit the impressive Naked Jogger Carving (stone 612), not far from the well-known Tree of Life Stone. From the Naked Jogger carving, walk up to the small outcrop of rocks that bends above you. There’s a small collapsed line of walling just behind the outcrop. Walk along this up the slope as if you’re heading for the Sunrise Stone carving, but only 30 yards along, low down and right into the edge of the wall itself, you’ll see this elongated piece of stone. That’s the spot!
Archaeology & History
If you’ve caught the petroglyph-bug, you’ll like this one! It received its name from the curious fusion of natural cracks with the man-made pecked lines that shows, quite distinctly when the light is right and the stone is wet, the outline of two humanesque forms joined to each other. Figurative rock engravings of ancestors in the UK are extremely rare and when we came across this example, we noticed how the design could be interpreted as two Askwith Moor ancestor figures. Figurative rock art images elsewhere in the world such as the magnificent Wandjina paintings and the extensive galleries of figures engraved at Murujuga (Burrup Peninsula) in Western Australia, might provide an initial comparison, though more specific work needs to be done to better understand this unique petroglyph.
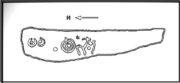
 You can almost make out the figures in the above photo: the upper torsos of two beings on the right-hand side of the rock, almost fused together. And the carved shapes of these “ancestral beings” are morphically similar to some elements in the Sunrise Stone just 50 yards away – which themselves remind me of a Northumbrian carving near Doddington known as West Horton 1a. (Beckensall 1991) But we should’t get too carried away by the idea because—as we can see here in the sketch of the carving—when looked at from a different angle above, we could infer the right-hand carved elements to be representative of an animal: a deer, perhaps. Rorscharch’s once more tickle the exploring mind….
You can almost make out the figures in the above photo: the upper torsos of two beings on the right-hand side of the rock, almost fused together. And the carved shapes of these “ancestral beings” are morphically similar to some elements in the Sunrise Stone just 50 yards away – which themselves remind me of a Northumbrian carving near Doddington known as West Horton 1a. (Beckensall 1991) But we should’t get too carried away by the idea because—as we can see here in the sketch of the carving—when looked at from a different angle above, we could infer the right-hand carved elements to be representative of an animal: a deer, perhaps. Rorscharch’s once more tickle the exploring mind….

 The rock has been quarried into at same time in the past (just like the nearby Sunrise Stone), leaving us to wonder what the complete carving might have looked like. No doubt some pieces of it will be in the collapsed walling either side of the stone. All we have left to see are the two unfinished cup-and-rings above the natural cracks that give rise to the “ancestral being” appearance. The faint double cup-and-ring has curious linear arcs to its side, with two well-defined cups enclosed by two of them. It’s a nice-looking carving when the light is good. The petroglyph was carved over a long period of time, as evidenced by the differing levels of erosion in different sections of the design. It’s a common attribute. The oldest section is the faint double cup-and-ring, whose mythic nature was added to / developed at a much later date, perhaps even centuries later.
The rock has been quarried into at same time in the past (just like the nearby Sunrise Stone), leaving us to wonder what the complete carving might have looked like. No doubt some pieces of it will be in the collapsed walling either side of the stone. All we have left to see are the two unfinished cup-and-rings above the natural cracks that give rise to the “ancestral being” appearance. The faint double cup-and-ring has curious linear arcs to its side, with two well-defined cups enclosed by two of them. It’s a nice-looking carving when the light is good. The petroglyph was carved over a long period of time, as evidenced by the differing levels of erosion in different sections of the design. It’s a common attribute. The oldest section is the faint double cup-and-ring, whose mythic nature was added to / developed at a much later date, perhaps even centuries later.
In the always-expressive archaeocentric description of Boughey & Vickerman’s (2003) otherwise valuable tome, they told this carving to be,
“Long, narrow, thick rock of medium grit. Six cups, one with a double ring with a tab out and two with at least partial single rings, grooves.”
Evocative stuff!
It’s very likely that this carving had some mythic relationship with its close neighbours either side of it, probably over a very long time period and I’m inclined to think it somehow related to the rising of the sun, just like its solar companion further up the slope. Please note how I emphasize this ingredient in the site profile of its neighbour, the Mixing Stone 10-15 yards away—roughly halfway between this and the Sunrise Stone. A distinct place of ritual was happening in this close-knit cluster of carvings…
References:
- Beckensall, Stan, Prehistoric Rock Motifs of Northumberland – volume 1, 1991.
- Boughey, Keith & Vickerman, E.A., Prehistoric Rock Art of the West Riding, WYAS: Leeds 2003.
- Reeder, Phil, “Snowden Carr Rock Carvings,” in Northern Earth Mysteries, no.40, 1990.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian