Cup-and-Ring Stone (lost): OS Grid Reference – Q 53 03?
Archaeology & History

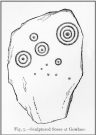
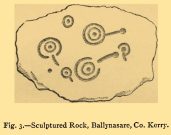
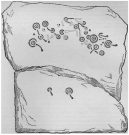
First discovered by Richard Hitchcock in 1848, this petroglyph (along with the Gowlane East (2) carving) was one of two missing stones in the area that James Graves (1877) thought were seemingly “fragments of a large monument,” although he said nothing more about it and, sadly, Mr Hitchcock’s sketch here is all that we have left to guide us. The carving may have come from one of the nearby raths, souterrains, or have been part of a circle or cairn. The stone looks to have been reasonably small in size and, hopefully, is residing in a wall somewhere or is just buried in a field.
There are several Gowlane place-names in the area, but Judith Cuppage (1986) told that the great 19th century artist and antiquarian George du Noyer “identified the townland as Gowlane East”, although the closest “neighbouring townland” would be Gowlin (Gualainn). If any local folk know where this might be hiding, please let us know. (the grid reference cited here is a very vague guess!)
References:
- Cuppage, Judith, Archaeological Survey of the Dingle Peninsula, Oidhreacht Chorca Dhuibhne: Ballyferriter 1986.
- Graves, James, “On Cup and Circle Sculptures as Occurring in Ireland,” in Journal Royal Society Antiquaries, Ireland, volume 4 (4th series), April 1877.
Acknowledgements: Huge thanks for use of the Ordnance Survey map in this site profile, reproduced with the kind permission of the National Library of Scotland.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian
The map could not be loaded. Please contact the site owner.