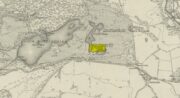
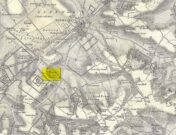
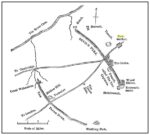
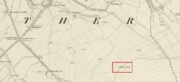
Cist: OS Grid Reference – NN 8488 2344
Also Known as:
Archaeology & History
Were it not for the valuable records in the Scottish Statistical Accounts, we’d have lost all knowledge of this site. It was described in notes by by Colin Baxter (1793), where he told us:
“About 200 yards west from the church of Monivaird, a barrow was opened some years ago, in which two urns were found, each containing a stone of a bluish colour, very hard about four inches long, and of a triangular shape, somewhat resembling the head of an axe.”
The site was subsequently mentioned in the Ordnance Survey Name Book of the parish, with some additional bits of information:
“In the year 17–, there was found, about one hundred yards to the westward of the old church of Monzievaird, a barrow containing a stone-coffin, in which were inclosed two coarse earthen urns, the one filled with burnt bones, the other containing the bones of the head. Of these, the under jawbone and the teeth were very entire. In the stone coffin was also found a stone hatchet, bluish-coloured, very hard, about four inches long, and of a triangular shape, a remain which proves the barrow of very remote antiquity – prior to the use of iron. The stone hatchet is preserved at Ochtertyre.”
No traces remain of the site; and although the stone axes came to be in the possession of Sir William Murray of Ochtertyre, the urns and other remains have long since been lost.
Folklore
The name of ‘St Serf’s Water’ derives from it this area being dedicated to St Servanus in early times; the holy well of St Serf could be found a short distance south from where this tomb was built.
References:
- Baxter, Colin, “United Parishes of Monivaird and Strowan,” in Statistical Account of Scotland – volume 8, William Creech: Edinburgh 1793.
- Porteous, A., “Extracts from a History of the Parishes of Monivaird and Strowan“, in Archaeologia Scotica, volume 2, 1822.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian
The map could not be loaded. Please contact the site owner.