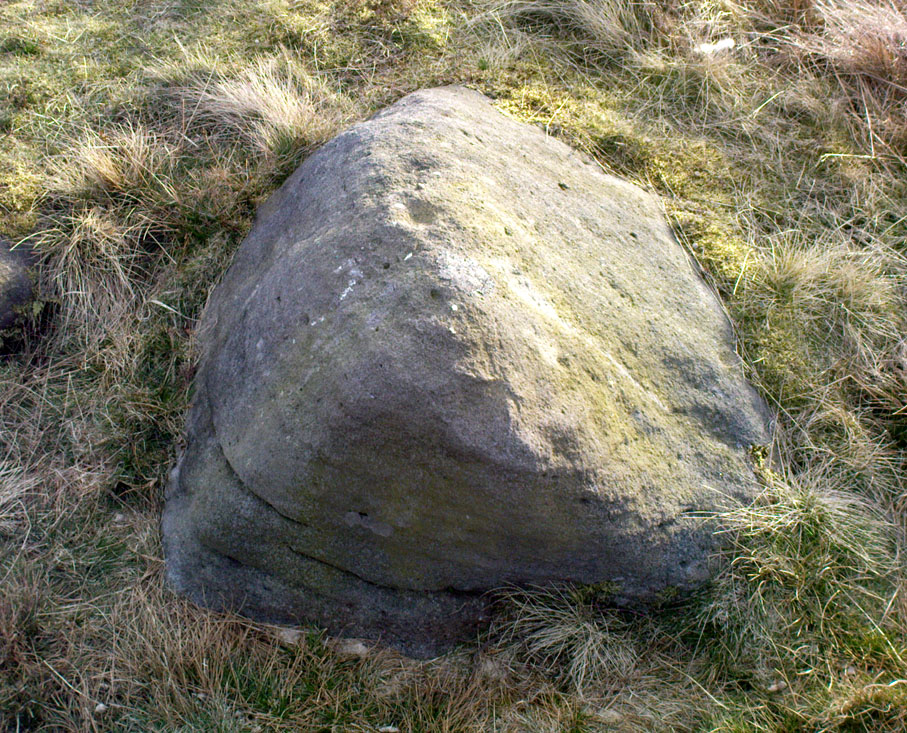
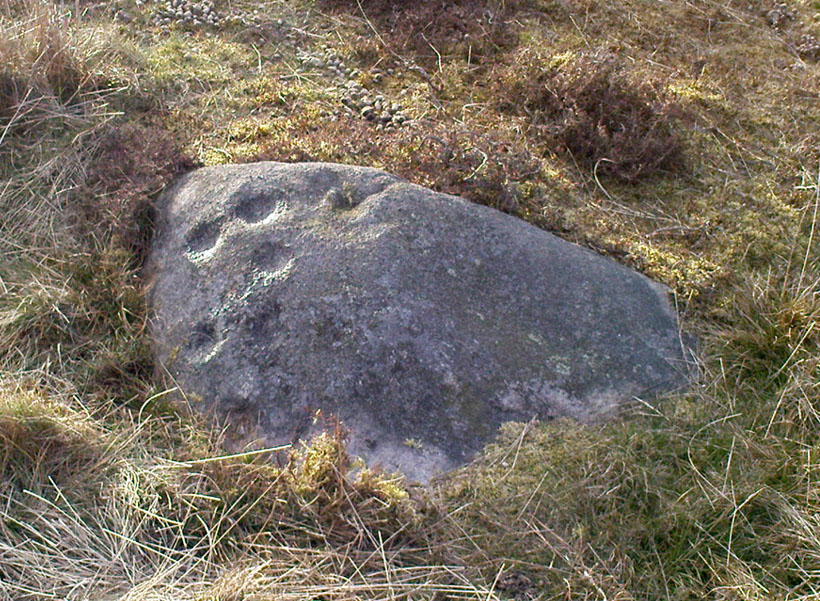
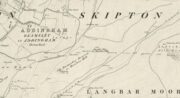
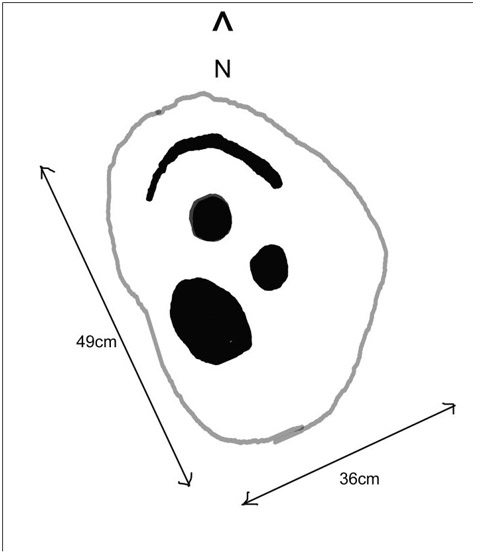
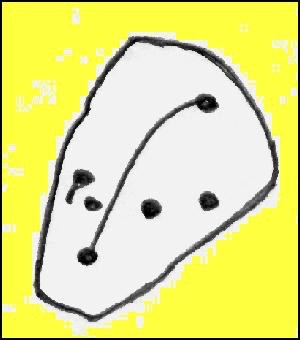
Cairn: OS Grid Reference – SE 09891 52435
Also Known as:
- Howber Hill

If you’re coming via Ilkley, cross the bridge to Middleton and turn left, following the long winding road for several miles until you hit Langbar village. If you’re coming via Bolton Bridge, go to Beamsley village and turn left up Lanshaw Bank until you hit Langbar village. Whichever of the two routes you use: on the north side of Langabr village is a distinct small rough car park. From here, cross the road where the footpath sign is and walk straight up the steep hill to Beamsley Beacon at the top. You can’t miss it!
Archaeology & History
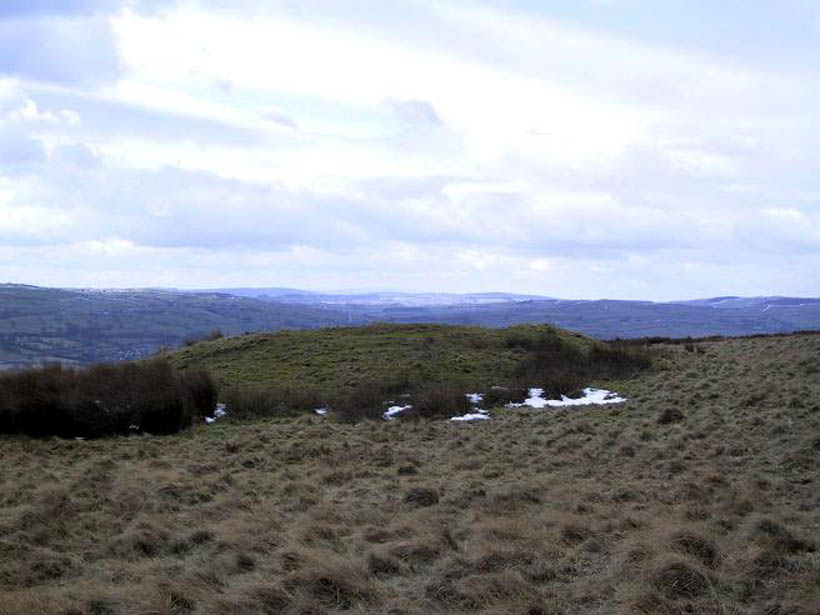
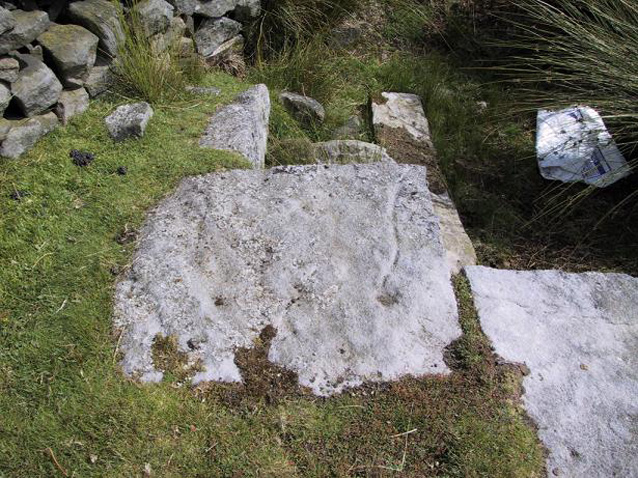
At the highest point on these hills, 1300 feet up, we come across this ancient prehistoric cairn. Its position in the landscape is impressive to say the least, being visible from nearly every direction on the moorland heights for many miles around, as well as being conspicuous from the riverlands below. A visit to the site nowadays shows it surmounted by a more recent mass of small stones turning it into a large walker’s cairn with only its compact base showing any real sign of antiquity.

Mentioned briefly in parish records from 1658 onwards, it was highlighted on the earliest OS-map as simply a Beacon hill, due to it being used for beacon fires. We’re not certain when its beaconesque function first came about; and, it’s possible, that its beacon element could have replaced a much earlier heathen fiery function, typical of many hilltop sites up and down this and other countries. But we do know that such fires were lit here at the beginning of the 19th century. The great Harry Speight (1900) told that of its
“use as a prospecting-point and beacon there is no doubt. In the Bolton Abbey registers, under date 1803, is this entry:
“Apprehensive of a French invasion, Beamsley Beacon was put in a state of repair, and four people appointed to watch it. About — of the inhabitants of this chapelry inrolled themselves as Volunteers, the whole number of whom in Craven amounted to 1,200 Infantry and 200 Cavalry. A Sergeant was appointed to drill the volunteers of this chapelry at Bolton.”
The beacon at this time received light from Pinhaw on Carlton Moor and sent it forward to Otley Chevin, as appears by an old chart at Wakefield, dated 1803.”

The beacon’s ancient name of Howber Hill is literally the Hill of Tombs, as derived from the Teutonic haugr, and Anglian how, being a burial mound; and berg is a hill, sometimes fortified. Whilst there seems to be no evidence of ancient fortification, compacted cairn material at the base seems to confirms the -how element. Yet despite Speight citing this etymology, he was was somewhat sceptical wondering, instead, if the site was merely a giant boundary marker—which it has been for centuries.
A short distance along the footpath to the east is the denuded old cairn known as The Old Pike. Further east still, along the same boundary line, there was once another old tomb, long since gone…
Folklore
I’m not sure whether this should gone in the folklore section or not. But, well, it’s here nonetheless! In Guy Phillips’s (1976) book on the mythic history of ancient Brigantia, he describes a number of alignments, or leys (not one of those stupid energy lines, which has nowt to do with leys)—one of which crosses Beamsley Beacon. It’s an west-east line that begins at Cockerham and from there goes,
“through Top of Blaze Moss SD 619525, Slaidburn (it is very clear here), Flambers Hill SD 877523, southern edge of Copy Hill 952523, Draughton (extremely clear), Beamsley Gibbeter and Beamsley Beacon, Heligar Pike, Scow Hall 203523, Little Almscliffe Crag, Tockwith church and on to the coast.”
I have to say that I’m sceptical of the veracity of this alignment.
References:
- Bogg, Edmund, Higher Wharfeland, James Miles: Leeds 1904.
- Cobley, Fred, On Foot through Wharfedale, William Walker: Otley 1880.
- Phillips, Guy Ragland, Brigantia – A Mysteriography, RKP: London 1976.
- Smith, A.H., English Place-Name Elements – volume 1, Cambridge University Press 1956.
- Smith, A.H., The Place-Names of the West Riding of Yorkshire – volume 5, Cambridge University Press 1963.
- Speight, Harry, Upper Wharfedale, Elliott Stock: London 1900.
Acknowledgements: Huge thanks to James Elkington for use of his photo on this site profile. Cheers mate. 
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian
The map could not be loaded. Please contact the site owner.