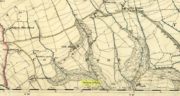
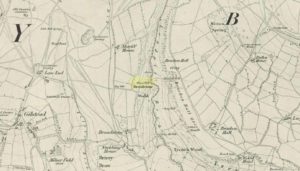
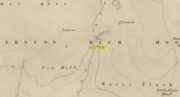
Sacred Well (destroyed): OS Grid Reference – SE 1589 3132
Archaeology & History
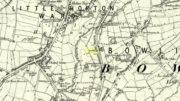
Along the now-lost Low Well Road between Little Horton and West Bowling, could once be found this innocuous-sounding water source. Shown on the 1st OS-map of the area in 1852, the site was deemed to be little other than a ‘public well’. At the end of the 19th century, a small well-house was built over the waters; and the years following that saw its complete demise. Its name you would think relates to a position in the land, but the dialect word low, or lowe can mean “a flame, blaze, light, glow”, it can also refer to a prehistoric tomb. However in this case it most likely derives from “a pond or standing pool”.
…And if some of you wonder why I have given this so-called Public Well the provenance of being a “sacred well”, please keep reading…
Folklore
Although it was deemed a simple ‘public well’ by historians and the public water authority, local folk knew there was much more to it than that! In the Bradford area, this innocuously-named Well is the most promiscuously supernatural of all water sources, with a hidden history of magickians, ghosts and black dogs haunting its once ancient flow. It was a site remembered as having oracular powers, where local people used it in scrying the future. For such powers to work here, one had to gaze into the waters as they stilled at 6 o’ clock in the morning – a common time used by ritual magickians for the invocations of spirits.
The Bradford historian William Scrotum (1889) told us that in the 1860s, local people reported that the phantom black dog—or Bharguest as it was known—with its glowing red eyes, was seen coming out of the well after dark and scaring people half out of their wits. Very soon people would not even venture out after dark for fear of encountering this great harbinger of Death. Several years passed before local people called upon the abilities of a ritual magickian in the hope that he could lay the ghostly hound and bring peace and stability back to the hearts and minds of those living hereabouts. Eventually, after much work, the magickian exorcised the waters and cast the black dog back into the depths of the Earth from whence it had come and, to this day, sightings of the spectral hound have stopped.
Water sources that possess ingredients of hauntings, magic and oracular properties are universally ascribed as ‘sacred’ in one way or the other. In pre-industrial times I have little doubt that, amongst the animistic pantheon of local Bradfordians, this was no exception.
References:
- Scruton, William, Pen and Pencil Pictures of Old Bradford, Thomas Brear: Bradford 1889.
- Wright, Joseph, The English Dialect Dictionary – volume 3, Henry Frowde: London 1902.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian