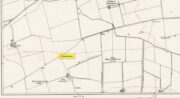
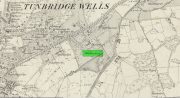
Cup-Marked Stone: OS Grid Reference – SE 12000 57932

Take the A59 road from Harrogate and Skipton and at the very top of the moors near the Gill Head Enclosures, take the small Kex Ghyll road up past the disused quarry works north for a mile or so. At the junction go left for about 1½ miles where, on your left, is Burnt House farm. A hundred yards past here is a small spot to park on the right-hand side of the road, opposite the gate to Rocking Hall House (make sure you leave enough room for tractors to pass you!). Across the road is the track to Rocking Hall and, 2 miles along the track, look out for the copse of trees ½-mile NE. Head towards it and, as you get close to the wall, walk slowly downhill towards the stream where a single block of stone lives. You’ll find it!
Archaeology & History

Rediscovered on Rocking Moor by Rod Chambers on August 15, 2023, this reasonably large sloping block of stone has between 21 and 24 cups cut quite deeply and scattered erratically into it, very similar to one some 200 yards to the northwest (Raven Stones carving 559). It seems pretty obvious that some of these cups were Nature’s handiwork, but have been modified by human hands. There’s nothing complex about it, but there may be a semi-circular arc around one of the cups, centre-left of the natural crack that cuts across the top of the stone, but this is very faint and could be just a trick of the eyes. Going there at sunrise and wetting the stone might tell us for sure.
Acknowledgements: Big thanks to Rod Chambers for use of his photo in this site profile.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian