Sacred Well: OS Grid Reference – NS 72919 98903
Also Known as:
- Canmore ID 46067
- Fountain Head
Getting Here

Christ’s Well (allegedly…)
Along the A84 Stirling-Doune road, watch out for the minor Cuthill Brae road to the caravan park. Go past the caravan place (ignore the grumpy fella there who tells you “this is private”) over the cattle grid and walk immediately to your right, along the top of the field, going through the first rickety gate 150 yards along. Follow the overgrown circular woodland path around, and as you see the Safari Park and Blair Drummond House ahead of you, walk just another 100 yards or so along the path until you reach a boggy hollow in the ground with an old small building inside it. That’s it!
Archaeology & History
For a variety of reasons, this little known site hiding away and all but lost in the mythic lives of homo-profanus, is one of the most important sites in the Stirlingshire region due to it being a site where animistic rites and practices were regularly enacted by local people in the 15th century—and before, no doubt! We know this because we have a veritable list of, albeit, ranting christian accounts from some early church records, that were thankfully transcribed at the end of the 19th century by local writer R.F. Menzies. (1899) Despite the seemingly “christian” title given to this old well, the local people used it extensively for their magick, their traditions, their healing, their solace and their spirituality.

The waters within…
Before we start, it’s important to note that the geographical position stated here, in the trees at Blair Drummond, is taken from the reference at Canmore, who do not cite a literary source or oral account which affirms this to be the exact spot. I mention this as there has been a problem regarding its exact location, not only by Mr Menzies, but also in the texts by MacKinlay (1893) and Morris (1982), each of whom said that the well was in the parish of Menteith, several miles to the west. In Menzies (1905) history of Logie parish, a footnote is added in relation to the position of the site:
“Mr W.B. Cook considers that ‘there is no authority for saying the well was in Kincardine-in-Menteith. An exhaustive enquiry by me has narrowed its locality down to two possible places, viz. Walton (i.e., well-town) and Bridge of Teith, both sites of pre-Reformation chapels, in the parish of Kilmadock. It is as nearly certain as can be that Christ’s Well in Menteith was near the ancient chapel at Bridge of Teith, the remains of which—along with the well itself—are still to be seen.’”
This would therefore differ from the position presently cited by Canmore and the official records. The ruins of the chapel described by Mr Cook were noted by the Ordnance Survey team at the Bridge of Teith when they visited in 1862 and it was highlighted on their maps four years later. No “well” was noted however—and although we have Mr Menzies (1899) to thank for the presently accepted spot for this Christ’s Well, we don’t know for certain that this is the correct place. The situation is made more troublesome if we refer to Moray Mackay’s (1984) definitive history of the adjacent parish of Doune. Mr Mackay wrote his work in the early 1950s and, like other local historians, was both fascinated and puzzled about this well. He wrote:
“Many writers in the past have been content with placing this well “in Mentieth” and leaving it at that, but my curiosity was aroused by the fact that more than one reference indicated that it was ‘near to Doune,’ and I set about locating it. It was a somewhat involved process, but I give here a resume of my findings which I published in the Stirling Observer of April 22, 1954.
“Firstly I was led to a paper of modern origin in Blair Drummond Estate Office which gave the site of Christ’s Well as ‘in the fernery at Blair Drummond.’ I found the fernery and also a rather fine well, over which a stone covering has been raised at an unknown date, and thought my quest ended. Later however…a reference in the Register of the Secret Seal, dated 1519, very strongly indicated Bridge of Teith as the site of Christ’s Well, and I was led to a very old well between the back door of the church there and the brink of the river.
“Still later I came across a pencilled note on a map in Doune Lodge Estate Office which read ‘Walton or Christwell unentailed’ as applying to a piece of ground immediately east of the Walton or Welltown site…
“There were, therefore, three alternative sites for Christ’s Well, only one of which had all the qualifications implied in the records as being (1) near Doune; (2) associated with a chapel; (3) in Kilmadock parish. Consequently, I am convinced that the very old, dry-stone well at Bridge of Teith is, in fact, the once-famous Christ’s Well in Menteith.”

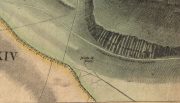
Christ’s Well (as ‘Fountain Head’) on 1866 map

Cook & Mackay’s site of Christ’s Well, by the chapel
The site that Mr Mackay and W.B. Cook believe to be the Christ’s Well is 1.5 miles (2.43km) north of the position cited by Canmore (at NN 7221 0121). As if to make things even more complicated, if we travel exactly 5 miles (8.05km) southeast to Cambusbarron, anothersite of the same name (later to be called the Chapel Well and associated with ancient ruins) is found! J.S. Fleming (1898) describes it in some detail.

Carved stone dated 1690

Carved stone dated 1678
However, for the time being at least, if we assume that the Canmore entry is the real Christ’s Well, if you visit the place you will find an old well-house that has been built over a redirected spring of water which seems to have originally rose just a few yards to the rear of the structure. Above the open front of the well-house—also constructed only a few hundred years ago—are placed two separate inscribed stones: one with the letters “CD ER” and the year 1690 beneath them; and above this an older stone, with the date 1678 etched on it. These may be the dates when an earlier stone structure, whose scattered rocky edges are visible beneath the vegetation around and behind the present well-house, were demolished and then rebuilt. But this is guesswork on my behalf!

‘Standing Stone’ to the rear
The entire structure is built inside a deep hollow which has no doubt been created and eroded into being by the spring of water itself. On the rise at the back of this hollow is a curious standing stone which, as Penny Sinclair pointed out when we visited here a few days ago, was made out of a fossilized tree. This standing stone is only a few centuries old and either marks the original rise of the spring, or was erected at the same time of the well-house.
Less confusing were the activities performed here by local people in the 16th century—and way before that no doubt. We have a lengthy set of accounts that describe how local people visited the Christ’s Well at the traditional dates of Beltane, Midsummer, etc, performing a variety of rites typical of those found in animistic cultures the world over. Sadly, it was the activities of the incoming christian cult that put an end to such ancient traditions by persecuting local people, as we know it has done everywhere that its virulent tendrils have infested. Anyway, I hope that readers will forgive me citing the entire length of the accounts described by Mr Menzies (1899) about this well; but I think they give us vital insights into traditional healing practices that were just about destroyed by that corrupt institution that is the Church (for ease of reading, I’ve edited and modernized to some degree the repetitive and fragmentary language of the early written accounts):
“The brethren of the Presbytery of Stirling and various Kirk Sessions within the bounds were much exercised and troubled by frequent pilgrimages to a holy well, called Christ’s Well, situated somewhere in the neighbourhood of Ochtertyre, in the parish of Kincardine. For at least thirty years after 1581, pilgrimages were undertaken by certain people, who imagined they could obtain cures for certain diseases at this well. The wonderful thing is that tradition is dumb regarding the exact site of the holy spring. There is a fine spring situated within the grounds of Blairdrummond, which may have been the Christ’s Well, the supposed virtue of which was, on the one hand, so consequential to the public health, and on the other, so troublesome to the Kirk.
“On 20th August, 1581, the Presbytery Record runs: ‘The brethren understands that a papist pilgrimage began of late at the Christ’s Well, and ordains every minister within their own bounds to try those persons who resort to it, and to call them before the particular Sessions that they can be convicted…’
“Two years later the evil crops up again, and on 7th May, 1583, ‘The brethren understand that a great abuse by the rascal sorts of people that pass in pilgrimage to Christ’s Well and use it for great Idolatry and superstition that are expressedly against God’s law; and because the Kings Majesty with advice of his three estates of parliament, (there shall be) certain punishments as well as corporal pains as pecuniary sums of money to be executed against such persons; and for execution of which against persons passed and to the said Well, the brethren understands my Lord of Doune Stewart of Menteith has commission given to him to that effect to see that punishment is executed in conformity with the said Act. Therefore the brethren ordains and gives commission to Mr. Andro Zung (Minister at Dunblane), Mr. William Stirling (at Kilmadock), and Michael Lermonthe (at Kilbryde) to pass to my Lord of Doune to treat with him for execution of punishment against the persons according to the said Act and his commission.” On 4th May, 1583, “The brethren ordains and gives commission to the brothers dwelling in Dunblane or any three of them to pass to Christ’s Well this next Saturday evening, accompanied with such persons as you may have to espy which persons comes to the said Well and report the names of such persons you can get to the brethren.’
“On 28th May, 1583, “On which day the brethren understanding that a great number of people have resorted to, and resorts in pilgrimage to Christ’s Well, using yet superstition and Idolatry expressedly against God’s law and the acts of parliament. Therefore…the brethren ordains summons to be directed to charging of such the said persons, whose names shall be given in writing to the clerk to appear before the brethren to answer therefore, to the effect that orders may be taken with them that have been there, to the glory of God and execution of the Kings Majesty’s laws and in example of others to do the same.’
“On 4th June, 1583, “Margaret Wright in Cambus, Janet Kidstoun in Cambus, and Thomas Patersone in Black Grainge” did not appear in courtto answer “for passings in pilgrimage to Christs Well,” and were summoned the second time under pain of excommunication. On 11th June, “Janet Tailzor (spouse to Robert Cowane) in Touch, Marione Watsone in Touch, Marjorie Fargusson in Touch, Margaret Downy in Polmais,” also for the same “compeared not.” (i.e., did not appear in court, as ordered – PB)
“The depositions given in excuse referred to some disease or ailment: One, “confessed she passed there to get help for a soreness in her side and confessed she passed about the well and prayed to Christ’s Well on Sunday and drank of the Well and washed her side with the water thereof and left behind her a sown thread” (as offering). Another, “passed….because she was sick in her heart and in her head and lipnit (trusted) that the Well would have helped her sicknesses…and she passed about the Well and cast the water over her shoulder and drank of it and left one piece of silver behind her.”
Ten years later several cases of pilgrimage to Christ’s Well come before the Presbytery. 22nd May, 1593, “On which day the brethren are credibly informed that Malcolme Alexander in Menstrie, James Baird at Muckart mill, and Jonet Mairschell, his spouse, passed in pilgrimage to Christ’s Well and visit superstition and Idolatry thereat. Therefore the brethren ordains them and such others who have done such like within their bounds to be summoned to answer for the same and unduly discipline them therefore under the pain of disobedience; and ordains each Minister to travel with one or two gentlemen in his parish to pass to the said Well on Saturday evening and espy what persons come there and what they do and relate the information to the minister, and see that each minister take Inquisition in his own Eldership what passes at the said Well and relate them to the presbytery.”
29th May, 1593, *On which day the summoned James Baird…to answer for passing in pilgrimage to Christ’s Well appeared in court, the said James, and confessed that through earnest persuasion of his wife (who was also moved to be there by other people), he passed with her to Christ’s Well on Saturday the 12th day of May instant, and that she two hours before the sun went down on Saturday evening drank of the said well and washed her legs and arms in it and did no fairer; he did nothing with the water, for his errand there was only with his wife who was persuaded to go there for her healing by Issobel Scotland. He confessed that there was at the said Well this year Ewffam Wilsone in Blairhill. Alaster Leany who was some time servant to Alexander Ezat in Culross. He confesses that David More is he whom bears aqua-vitae and being oft times in David Fargus house in Alva, said to his wife that there was money brought to that Well…; and that Crystie cadzear in Alva confessed to him when he and his wife came home from the well, that he was three or four times at Christ’s Well and was the better, he confesses that his wife is sick and cannot come to court this day and obey the summons and therefore desires that his excuse for her may be admitted. The brethren having considered the said James Baird’s fault, ordains him to make repentance therefore in Dollar kirk as it is adjacent to him the next Sunday in secclayth (???), and that the plaintiff above written be summoned to answer for the said offence under the pain of disobedience.”
Another case falls to the ground for want of proof. On 5th June, 1593, “One summons upon Malcolme Alschunder in Menstrie…to answer for passing to Christ’s Well and using superstition and Idolatry there at, but there is no appearance in court. He appears on 12th June, “And denies that he passed to Christ’s Well or was bewast (to the west of – PB) Teith at any time in May, and therefore the said matter remains to be proven.” On 3rd July, “Inquisition being taken, asks if there be any witnesses that can prove Malcolme Alexander was at Christ’s Well, there is none found, and therefore it is thought good to proceed no farther against him for the said offence.”
On 14th May, 1595, James Duncansone in Fossoway, and Helen Jameson, his spouse, are charged to answer “For superstition and Idolatry in passing to Christ’s Well in pilgrimage… The said Helen confesses she passed to Christ’s Well through the year to get her bairns eye healed which was blind a month before. She washed his eye thrice with the water thereof, and alleged that the bairn saw or he come home; and confesses that she passed there this year also to give thanks for the benefit she received the year preceding, and left a shirt of the bairns behind her, which was on the first Sunday of May… The said James Duncansone denies that he passed to the said well with her, but only to Ochtertyre, where he was all night—well the morning that she come to him, and then they passed together to Dunblane. The brethren finds him also culpable as his wife in her said fault, seeing he has known thereof and past with her to Ochtertyre, which is the most part of the way, where he ought and should have stopped her, and therefore they are ordained to make public repentance in linen clothes the next three sabbath days bare-footed.”
James Duncansone’s wife appears to have refused to obey the Presbytery, and on 16th July, 1595, she is summoned to appear in court, “beand chair- git as said is to heir and sie hir self decernit to be excommunicated for not completing the injunctions to her for passing in pilgrimage to Christ’s Well two different times, who being oft times called, appeared not. Therefore the brethren ordains her to be summoned de novo to the effect aforesaid with certification.”
“As no further mention is made of this woman’s case, she must ultimately have satisfied (them). The resorting to this well comes before the Presbytery (again) on 23rd April, 1600: ‘The brethren being credibly informed of the great abuse and superstitions of visits by many people at Christs Well, namely in the night immediately preceding the Sabbaths in the month of May; for remaid thereof the brother of the Ministry within their boundaries are ordained that publicly in their kirks the next Sabbath inhibit and forbid in the name of God and his kirk that no persons shall pass to the said Well… And to the end that such abusers that go there may be stopped from their superstition. The brethren ordains the ministers of Kilmadock and Kincardine with the special gentlemen of their flocks, to await vicissim (in return) at the said well on the night preceding the Sabbath during all the month of May; and to that effect the brethren ordains the clerk to write in the names (of visitors) to the gentlemen of the said parishes.’
“The members of Presbytery were determined to put a stop to such superstitious practices, and ere long, their efforts met with success. In the meanwhile however, isolated cases came before them for judgment . Thus on 29th July, 1601, “Jonet Rob in Pendreich” is summoned to appear to answer “for disobedience to the elders of her parish church of Logie, conjoined with slandering the kirk by passing in pilgrimage to Christ’s Well.” She does not appear, and is summoned pro tertio, but apparently having satisfied the “eldership” of Logie, the matter is not again referred to.
“The last mention of Christ’s Well is at the meeting held on 1st July, 1607, when a batch of nine penitents from the parishes of Airth and Bothkennar, “Compare and confess they were at Christ’s Well to heal their diseases, and took some of the water and left something behind, every one of them, at the well. The brethren finds that they have committed superstition and have dedicated to Satan that thing they have left behind them (at the well), and are therefore ordained to make public repentance at the next adjacent kirks of Airth and Bothkennar.”
Menzies noted another mention of people using the waters here a few years later, telling:
“As late at June 6, 1630, the Kirk Session Records of Stirling contain an entry, where five women and two men, “confesses passing in pilgrimage to Christ’s Well in May, and therefore they are ordained to make public repentance at the next sabbath, in their own habit, under pain of disobedience.”
In these records we can clearly see that a bunch of incoming religious fanatics have arrived and set themselves up to engage with the Scottish people so as to undermine and destroy the indigenous traditions and practices prevalent at that time, by imposing laws against them which were not for the benefit of the local people. Indeed, the laws were preposterous! The initial description that the rituals performed by the local people were ‘papist’ in nature is, of course, a cover—as was the name, Christ’s Well—in an attempt to avert the christian cult from attacking their traditional places of healing and rites. This failed—but at least we have the accounts describing the outlandish presbyterian impositions.

Penny sits guarding the well
However, even with these accounts it is difficult to say with any certainty where the original Christ’s Well emerged. The position Penny Sinclair and I visited, as marked on the modern OS-maps, is congruous for rites of solitude as described in the church accounts; and a distinct genius loci feels to be just beneath the surface. However, it is difficult to see how people visiting here would have been noticed by the christian enforcers, as it is away from prying eyes. However, if the well was at the Bridge of Teith, it would explain how so many people were “caught in the act” of performing their rites, as an old chapel was adjacent to the well. More research is required, obviously…
In the meantime, I truly recommend visiting this place to those who enjoy the quietude of sacred sites. Tis a fine secluded place—although it could do with a good tidying-up to free its fresh waters once again…
References:
- Bennett, Paul, Holy Wells and Healing Springs of Stirling and District, forthcoming
- Bradley, Ian, Water—A Spritual History, Bloomsbury: London 2012.
- Edensor, Tim, “Watery Traces and Absences: Sensations and Speculative Histories of an Ancient Well and a Carse Landscape,” in Cultural Geographies, October 2024.
- Eliade, Mircea, Patterns in Comparative Religion, Sheed & Ward: London 1958.
- Eliade, Mircea, The Sacred and the Profane, Harcourt: New York 1959.
- Fergusson, R. Menzies, Alexander Hume: An Early Poet-Pastor of Logie, Alexander Gardner: Paisley 1899.
- Fergusson, R. Menzies, Logie: A Parish History – volume 1, Alexander Gardner: Paisley 1905.
- Fleming, J.S., Old Nooks of Stirling, Delineated and Described, Munro & Jamieson: Stirling 1898.
- Grant, William (ed.), The Scottish National Dictionary – volumes 1-10, SNDA: Edinburgh 1931-1976.
- Mackay, Moray S., Doune – Historical Notes, Forth Naturalist: Stirling 1984.
- MacKinlay, James M., Folklore of Scottish Lochs and Springs, William Hodge: Glasgow 1893.
- Morris, Ruth & Frank, Scottish Healing Wells, Alethea: Sandy 1982.
- Wright, Joseph (ed.), English Dialect Dictionary – volumes 1-6, Henry Frowde: London 1898-1905.
Acknowledgements: Huge thanks to Penny Sinclair for the venture over and help to locate this fascinating site.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian
The map could not be loaded. Please contact the site owner.