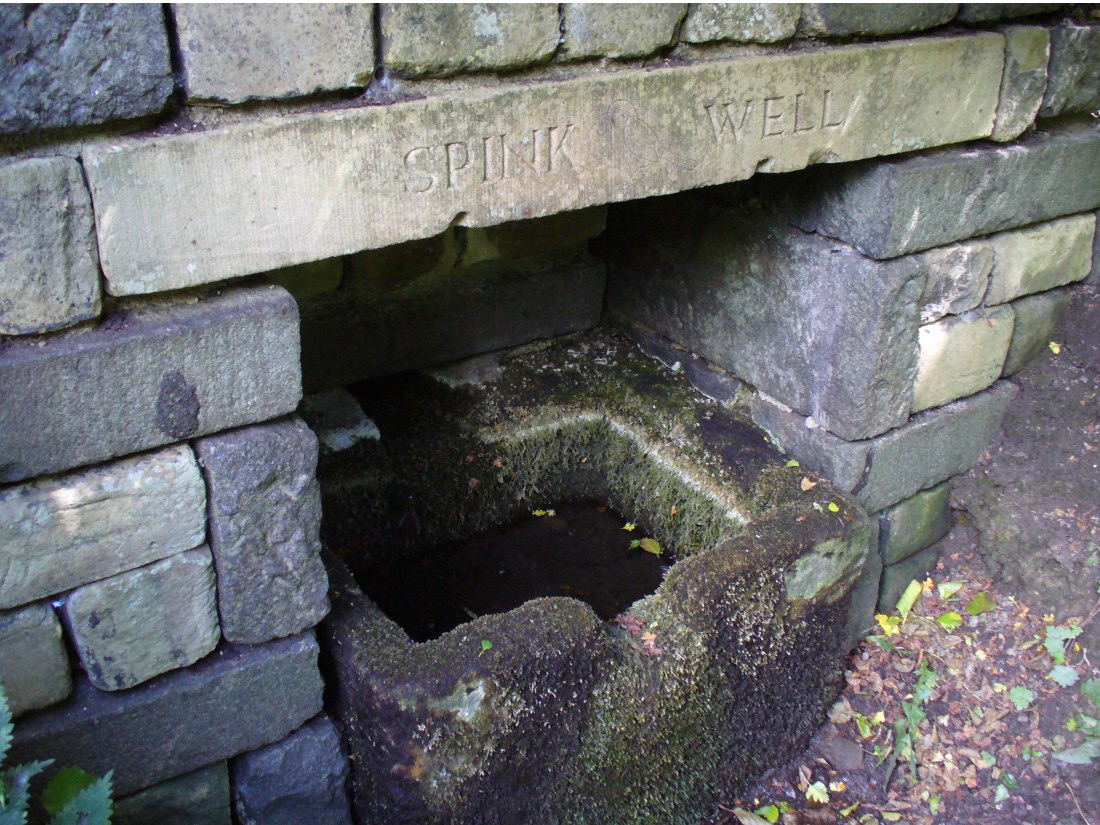
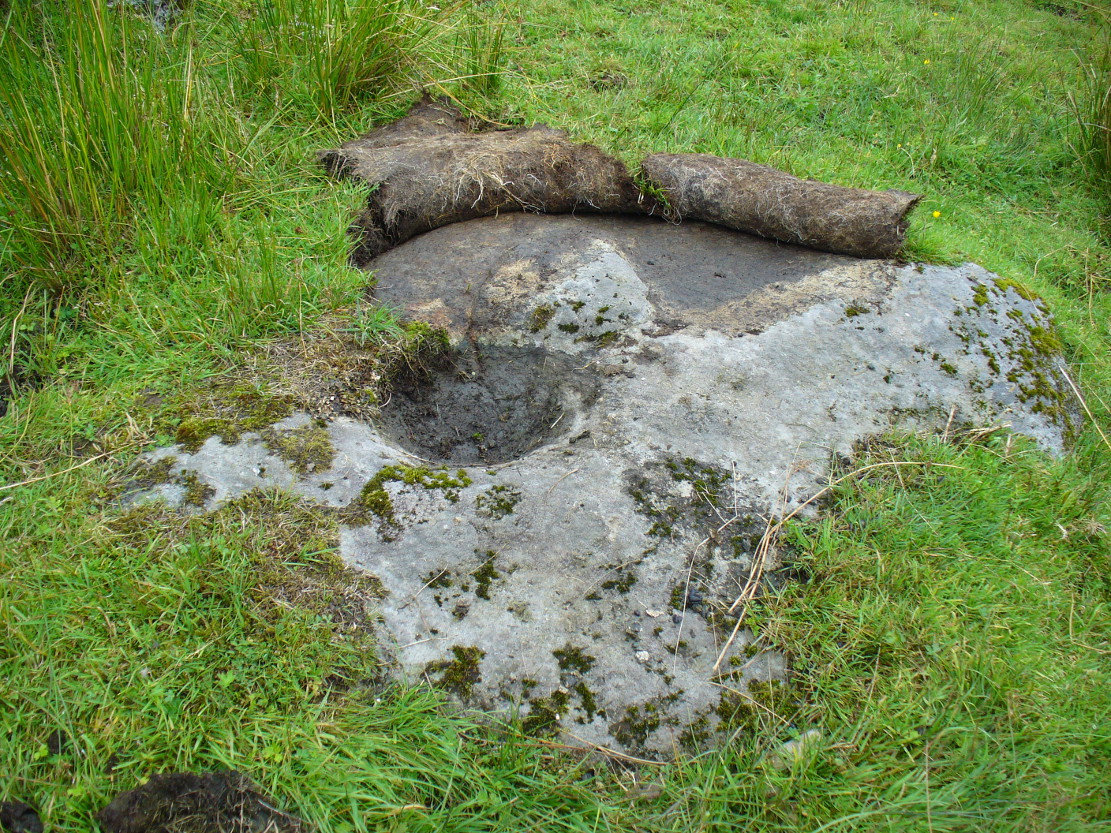
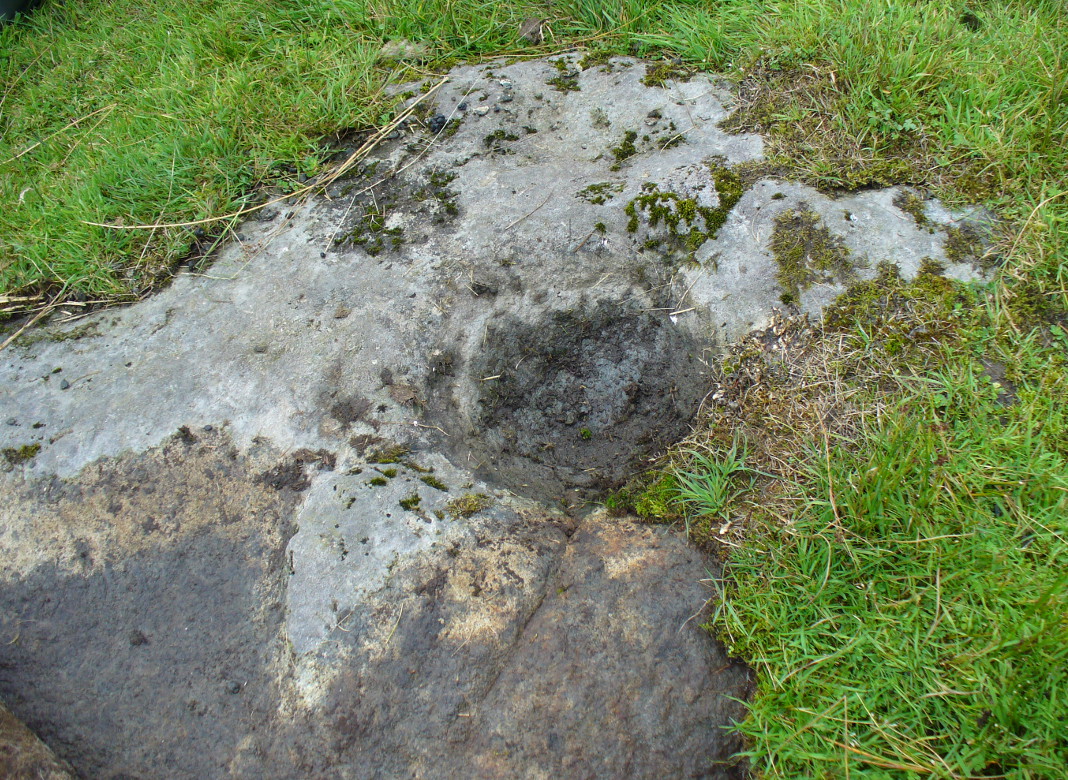
Holy Well: OS Grid Reference – SE 785 021
Also Known as:
- Alley Well
Often noted under Lower Burnham, although this is a hamlet and not strictly the parish, is in Haxey. The spring can be found by taking the footpath after Starkey’s farm, top of Holy Well lane, with Holy Well House the nearest dwelling.
Archaeology & History

Potentially if Hunt (1923) quoted in Hills (1967) is to be believed, this is the most famed holy well in the county, as he believes that this was the site where King Oswald—later St Oswald—was slain and here the well was St Oswald’s Well rather than at Oswestry. He notes that:
“The Holy Well at Lower Burnham in the parish of Haxey is supposed to mark the site where King Oswald fell. People took away the soil until a deep hole was formed which filled with water…It has been known for 1300 years as the Holy Well, and annual feasts were held near it until recent years. This confirms the Ven. Bede’s statement about the sanctity of the soil in the eyes of the people.”
According to Garner (1991) by the early 19th century the well’s popularity had waned and the spring fell into private ownership and the water was used to run two water mills, and as such a gully of considerable depth constructed. However the spring did not produce enough continuous water and the scheme failed. A similar attempt was made by Rev. Thomas Skipworth Rector of Belton was more successful but only because a dam was constructed although still the power was not great enough. Interest in the well had not completely disappeared, and an announcement in 1875, in the Epworth Bells stated:
“Firmly believing in the efficacy of the Burnham water in the cure of some outward bodily complaints, we sometime since urged the importance of making that water once more available to the public, and at the same time we urged the desirability of the public availing themselves of the water.”
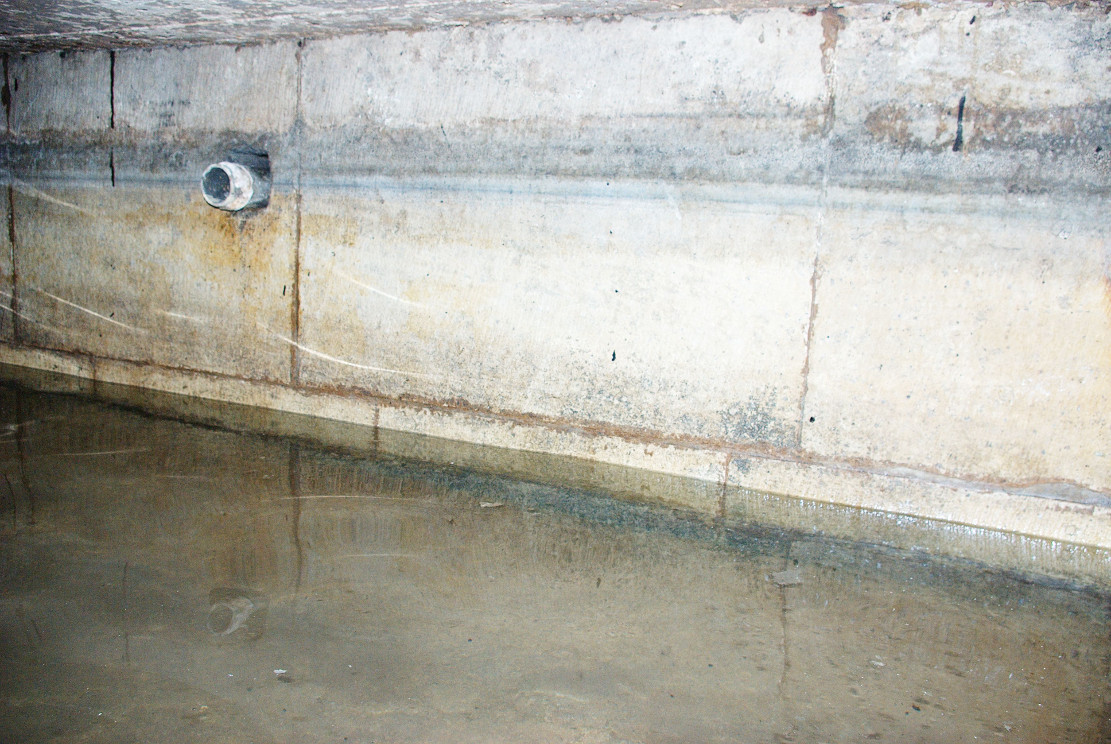
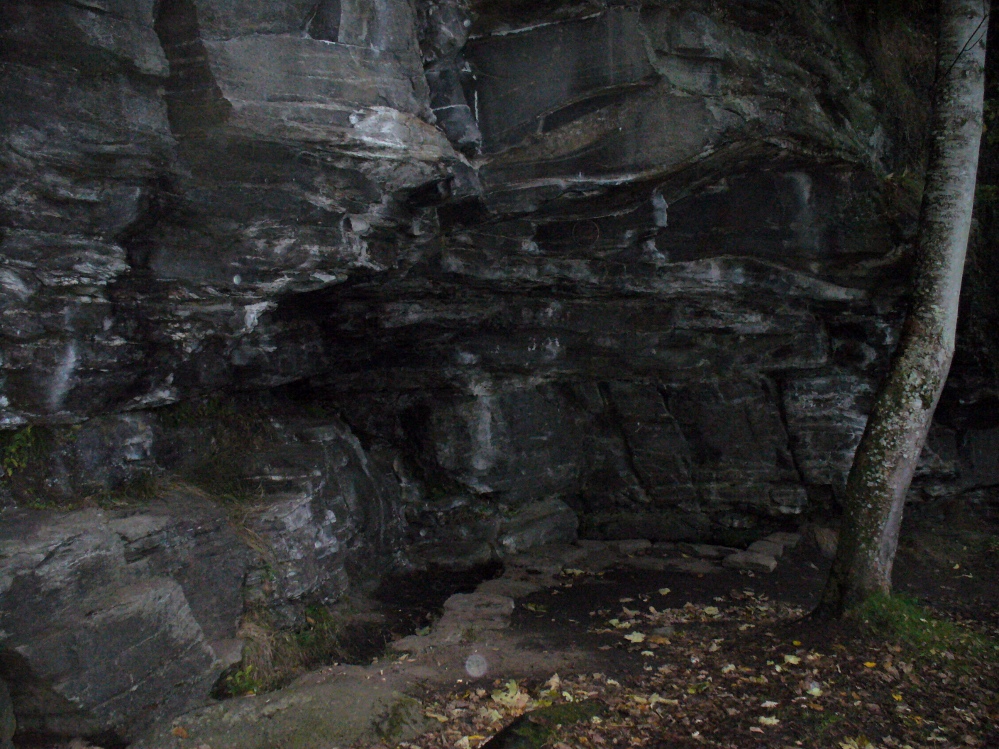
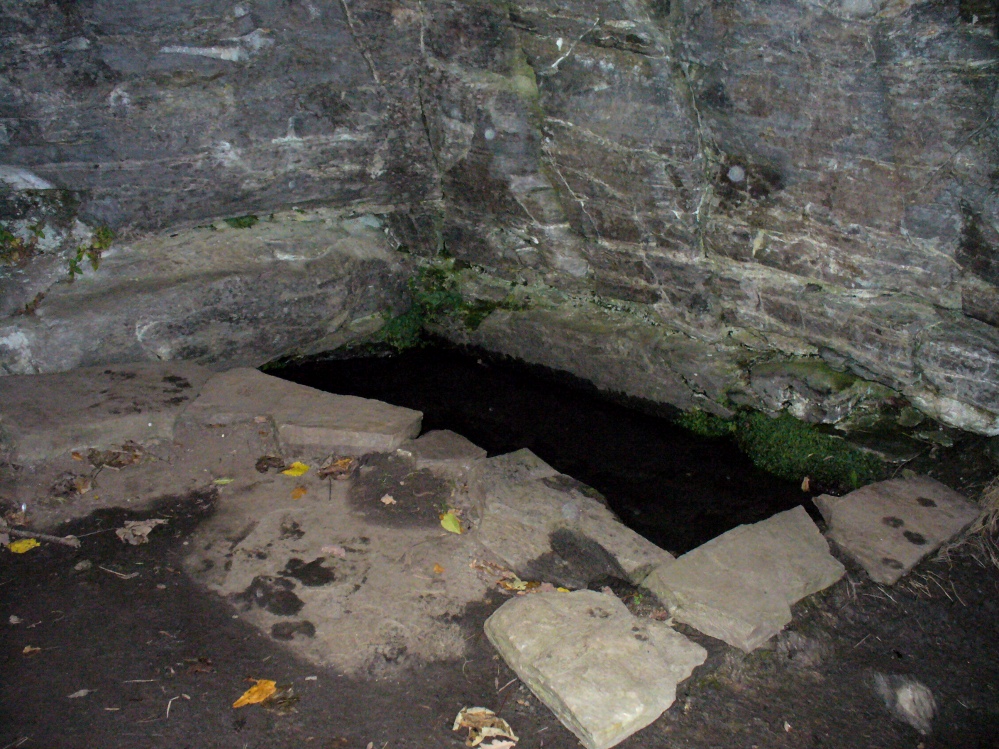
Responding to this plea, a group of local men, Cooper, Starkey, Ducker, Skelton, Meggitt and Templerton came together to ‘re-open the well’ It had been for years only a dry, roughly rectangular, hollow but ‘within minutes of digging, water gushed out, and the hollow filled.’ No evidence of constructional material was seen but the landowner, Mr. Lockwood, agreed to allow the well to be kept open and the water to be freely available when he did not have cattle in the field, as such the well was fenced in probably as local people reported in the Crowle Advertiser (1960) with white railings. Indeed, up until the 1940s the well remained fenced off with barbed wire as a cattle water place and at some point it was filled in.
This meant that the well had again fallen into disused and its exact location was perhaps becoming unclear, when in the 1960s when three Epworth men, Frank and David Lindley with Jack Warriner. A report in the Crowle Advertiser of 1960 noted that:
“At a spit depth, what seem to be known locally as water stones began to be turned up; at about two feet six there was a promising slab, followed by another, at a little deeper level; and after discovery of several hand-made bricks had dispirited the diggers somewhat, three more irregular shaped stones of considerable size were scraped clean of the mud that overlaid them. By now there was bared to view what could have been the stepped entrance to the well which from visual testimony of old residents, the explorers hoped to find.”
This stepped entrance consisted of eight steps according to local people. The group then discovered at about four feet timber was found and on this two corner stones were found rested. This was thought to have been the remains of the enclosure which went around the well.
In March 1961 another attempt was made to open the well in view of a pilgrimage by the Lincoln Diocesan Youth Pilgrimage, this time the excavators had gone twice as deep and the strata of waterstone was hit, but no evidence of a constructed well. This was not a concern of the Vicar of Owston Ferry, Canon L. D. Ravins who was of the opinion that an actual construction would have been unlikely if the above description by Hunt was to have happened. This time according to the Crowle Advertiser:
“Both he and Canon Ravins feel that the water may well have medicinal qualities (they noticed they say an unmistakably sulphurous smell from it during the excavations) and they are intending to have the chemical analysis made.”
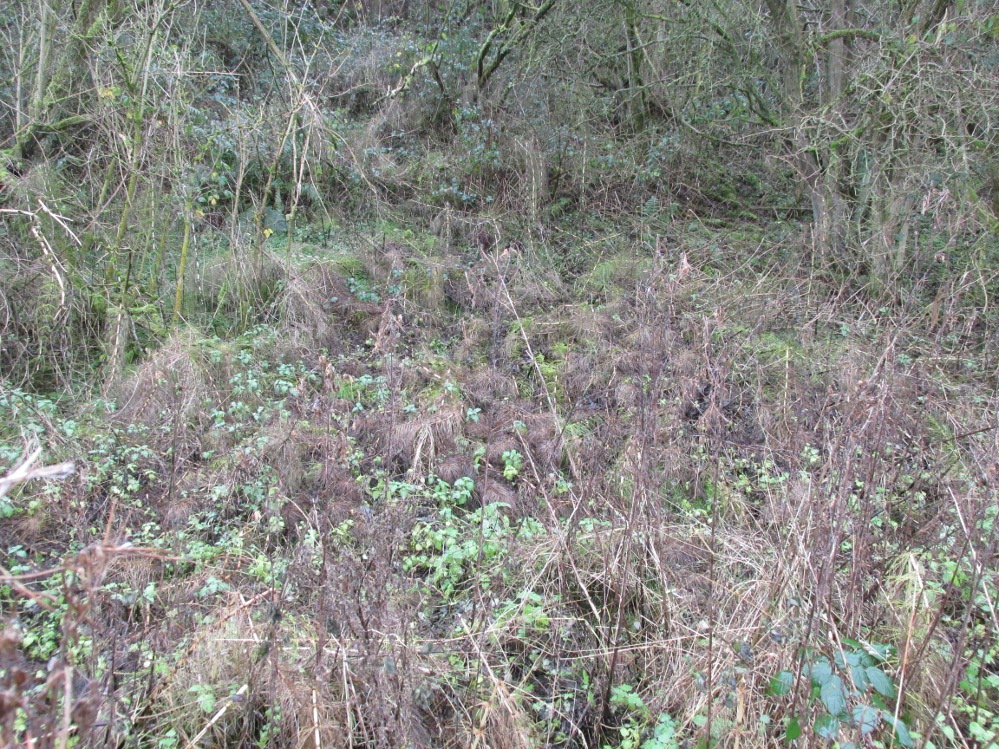
However, the analysis did not reveal any sulphur but it did have Magnesium and Calcium sulphates and Calcium bicarbonate all linked to spa waters and hence verifying its medicinal role. The well was visited by the pilgrimage and Garner (1991) recollects that a white timber enclosure was placed around the site with a sign proclaiming ‘The Holy Well’ according to him the ‘whole site now barely discernible save for a lone willow sentinel-like over the place revered by myriad generations in days long since past.’
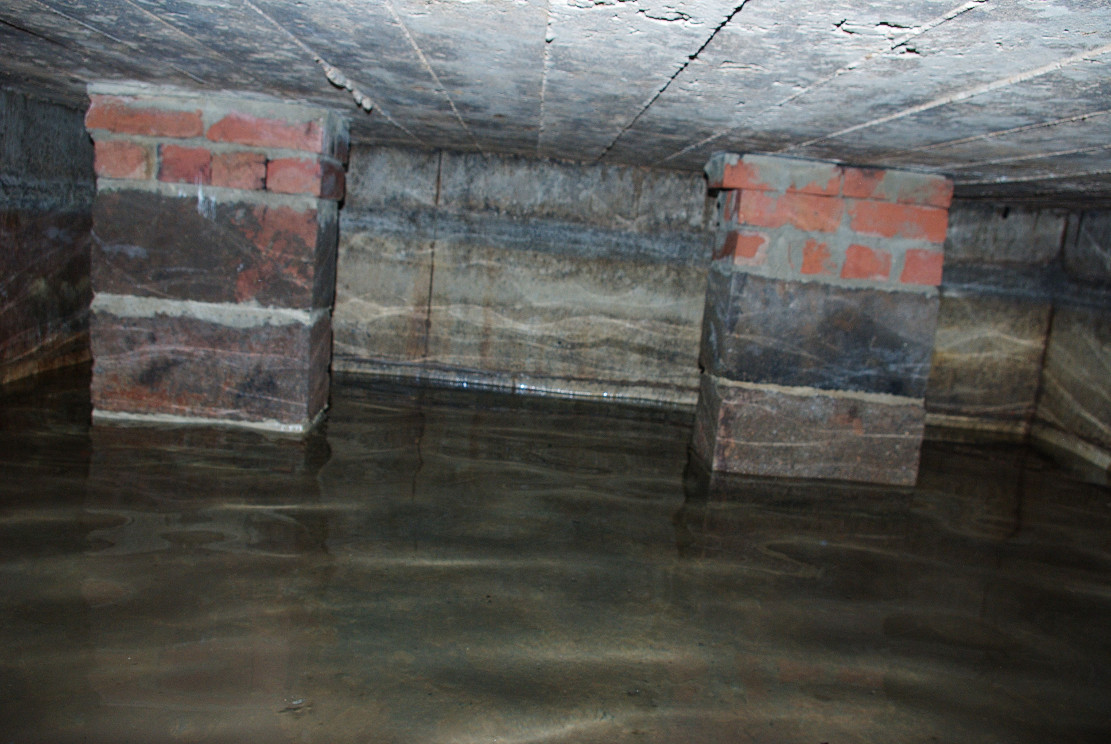
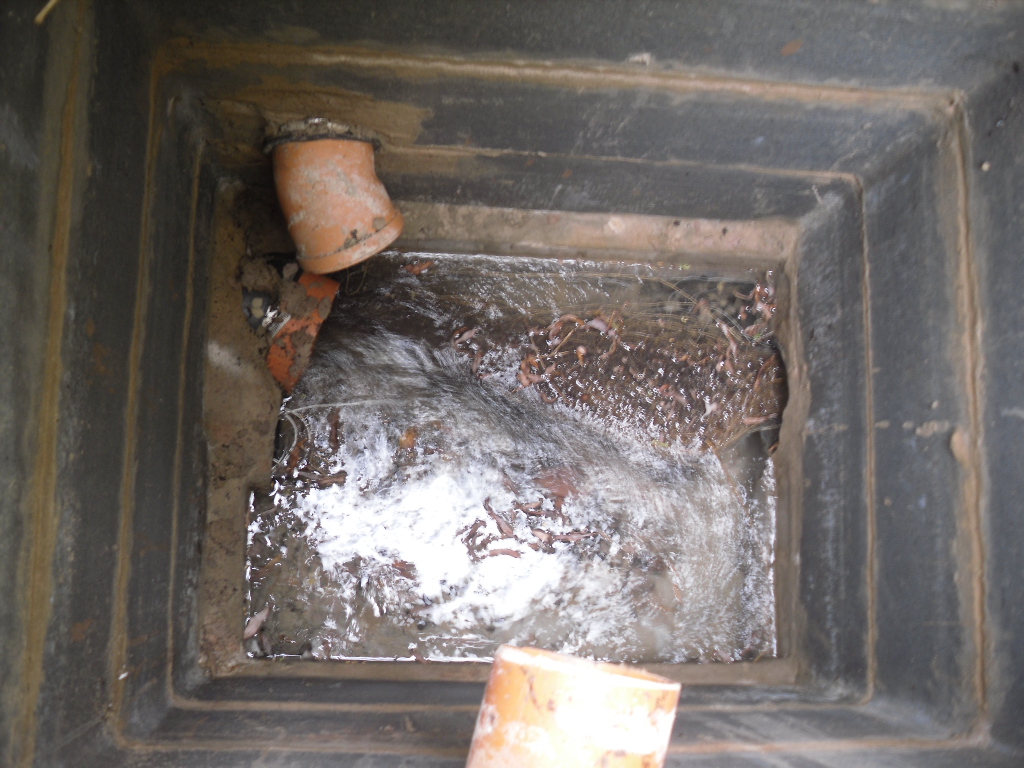
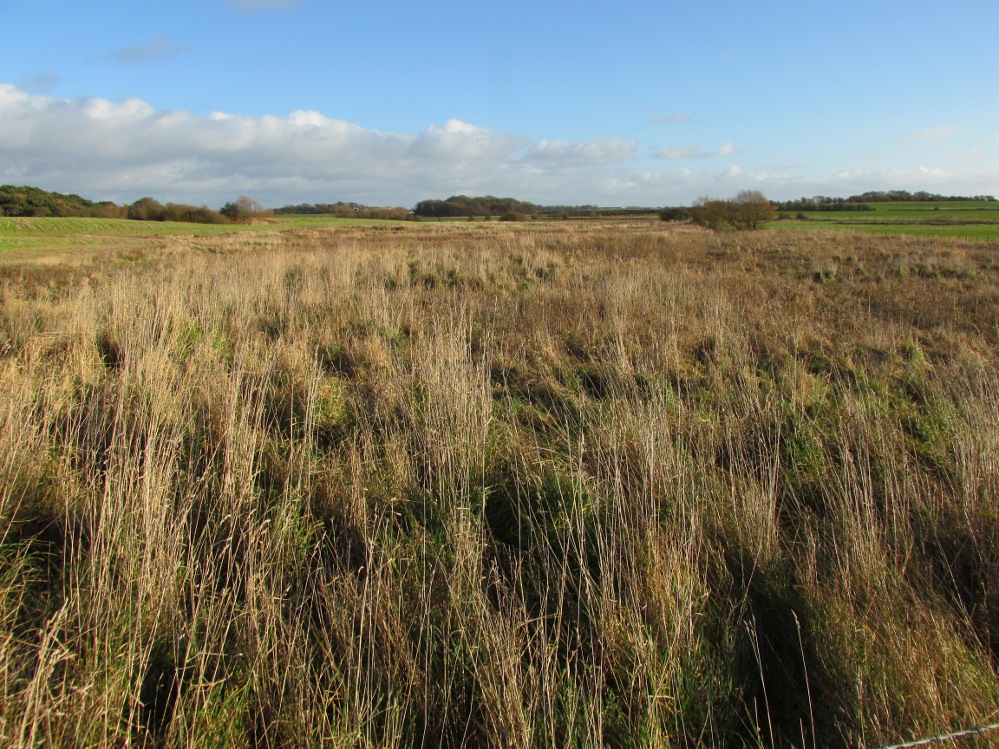
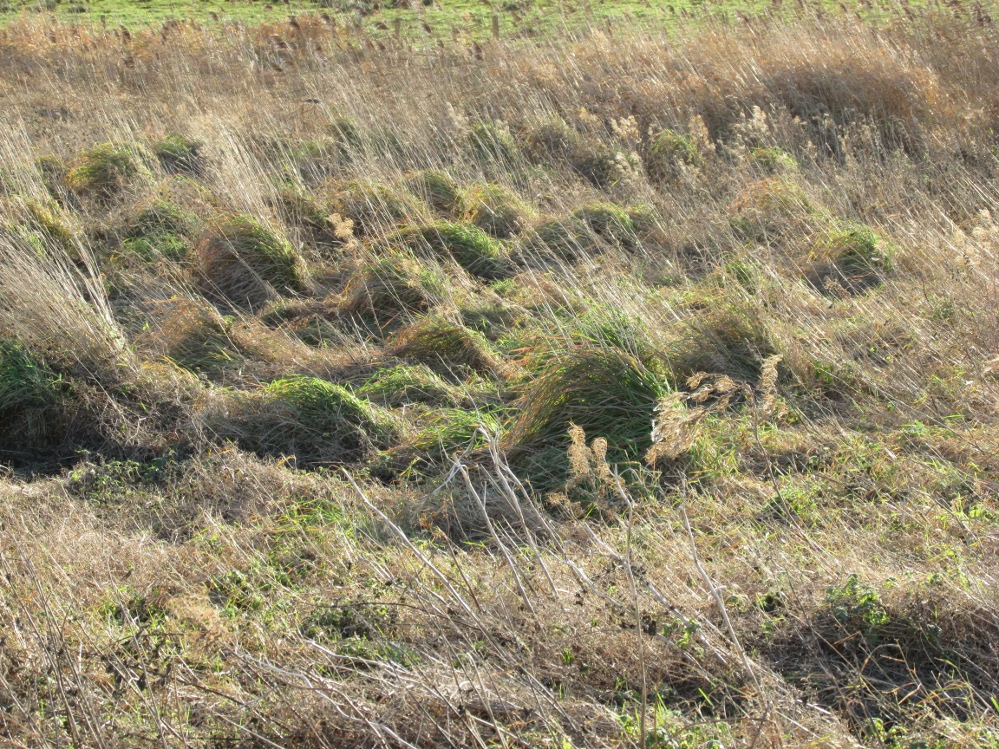
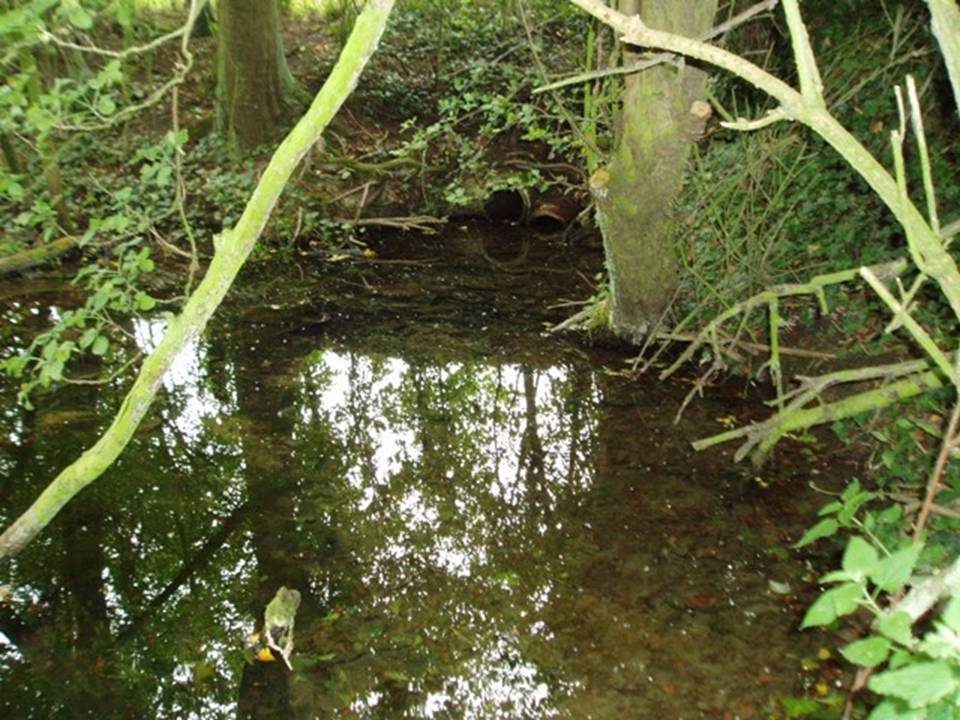
However, this was not the case when I visited the site and found a large pool with a pipe at one end, from which a channel appeared to flow. Although Garner (1991) noted a ‘few elder citizens of Burnham strongly favour its position a few metres south of the spot popularly referred to”.
Folklore
However this name has not been recorded and the site is best known simply as the holy well. This site was, according to Gutch & Peacock (1908),
“ …dedicated to the ever-blessed Redeemer, and on the festival of His Ascension was supposed to possess the power of healing all sorts of deformities, weaknesses, and cutaneous diseases in children, numbers of which were brought from all parts to be dipped in it on that day.”
The earliest mention appears to be Peck (1809) who stated:
“a Spring called the Alley Well of very cold water which was very much resorted to by the people in their neighbourhood, being very proper for those of a weakly habit.”
Stonehouse (1839) notes:
“about one hundred and twenty years ago, the concourse of visitors was so great that a Village Feast was held at the same time… and at a much later period conveniences were annually made for the use of the bathers, and gingerbread-stalls and other slight reflections were provided on the spot. This practice has, however, of late years fallen altogether into disuse… The spring now appears in a dirty and neglected state.”
The fame of the spring led to it being immortalised in Hamilton’s novel Captain John Lister where the titular hero watches during the early morning of Haxey Fair, a melancholy procession through the main street of women, accompanied by diseased and deformed children. In the book, the innkeeper explains by saying:
‘They are going to the Holy Well at Nether Burnham. ‘Tis a famous spring, and has been many ages, and on this day there is virtue in the water to cure almost any disease or sickness in a child, if be dipped before noon…out of Nottinghamshire and Yorkshire and I don’t know where all.’
(Essay taken from R.B. Parish Holy Wells and healing springs of Lincolnshire)
References:
- Garner, J. R. (1991) Burnham – the story of an Axholme village.
- Gutch, E. & Peacock, M. (1908) Country Folklore Vol. VI: Folklore of Lincolnshire
- Hills, P.J. (1967) The Holy Well of Burnham the site of the Battle of Maserfield-the identification re-examined.
- Stonehouse, W.B. (1839), The History and Topography of the Isle of Axholme.
- Various anonymous cuttings from Crowle Advertiser (1960)
Links:
Copyright © Pixyledpublications
The map could not be loaded. Please contact the site owner.
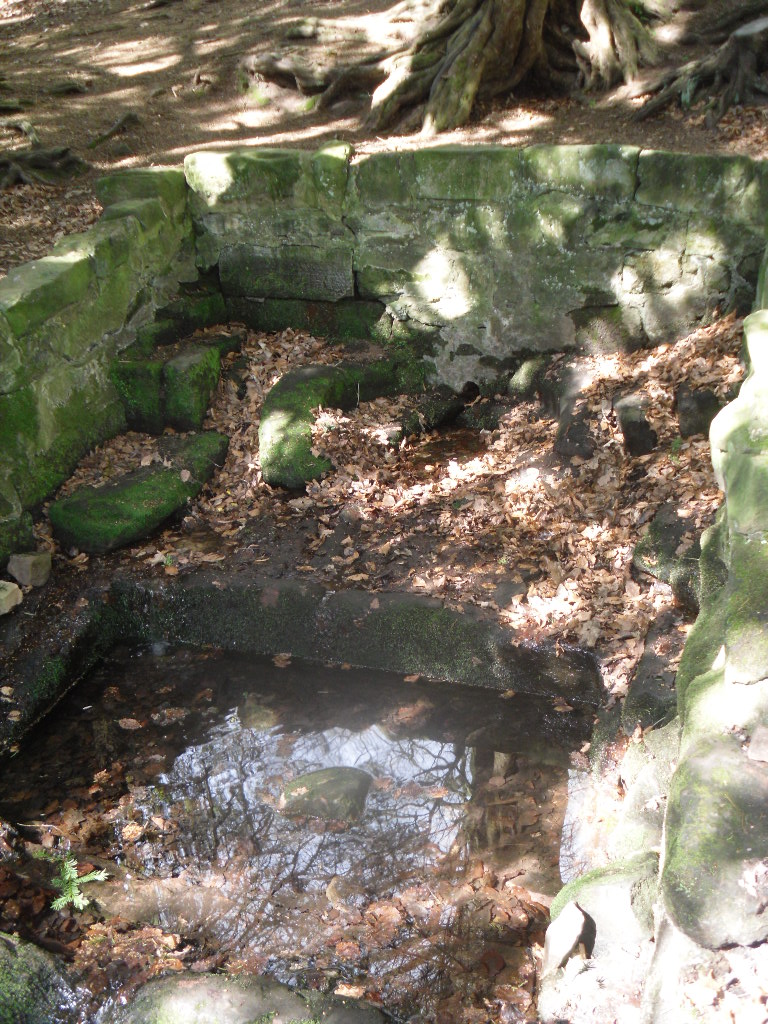

 Perhaps what makes this well one of the most evocative and interesting is the fact that it arises in an oval grove of yew trees. Some folklorists and New age Antiquarians have seen this as being evidence of some pagan origin of the well and although it is interesting that the site is unconverted to the Christian faith. However, one must be careful. Firstly the trees do not look that old and secondly the presence of a nearby Warden’s Tower, a folly, suggests that this is perhaps a 18th century piece of antiquarianism. I have been unable to find much more of its history.
Perhaps what makes this well one of the most evocative and interesting is the fact that it arises in an oval grove of yew trees. Some folklorists and New age Antiquarians have seen this as being evidence of some pagan origin of the well and although it is interesting that the site is unconverted to the Christian faith. However, one must be careful. Firstly the trees do not look that old and secondly the presence of a nearby Warden’s Tower, a folly, suggests that this is perhaps a 18th century piece of antiquarianism. I have been unable to find much more of its history.