Healing Well (destroyed): OS Grid Reference — TQ 3006 7734
Archaeology & History
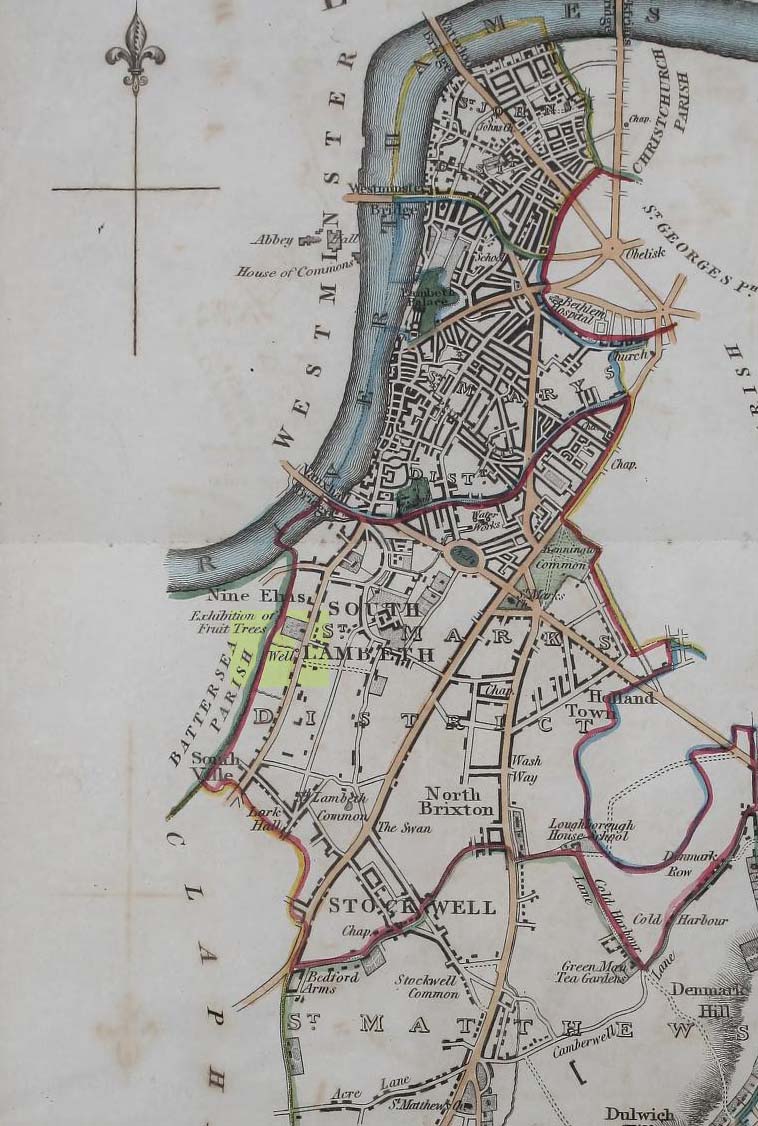
In Thomas Allen’s (1827) huge survey of Lambeth parish, he told that there was little of any interest along Wandsworth Road, apart from a good orchard, “and a fine spring called Vauxhall Well.” According to Daniel Lysons (1792), it was located “not far from the turnpike”; and according to Mr Sunderland’s (1915), was to be found “on the right-hand side of the Wandsworth Road” as you walked down it to the south. Thankfully its position was highlighted on the 1824 map of the parish (right) that accompanied Mr Allen’s work.
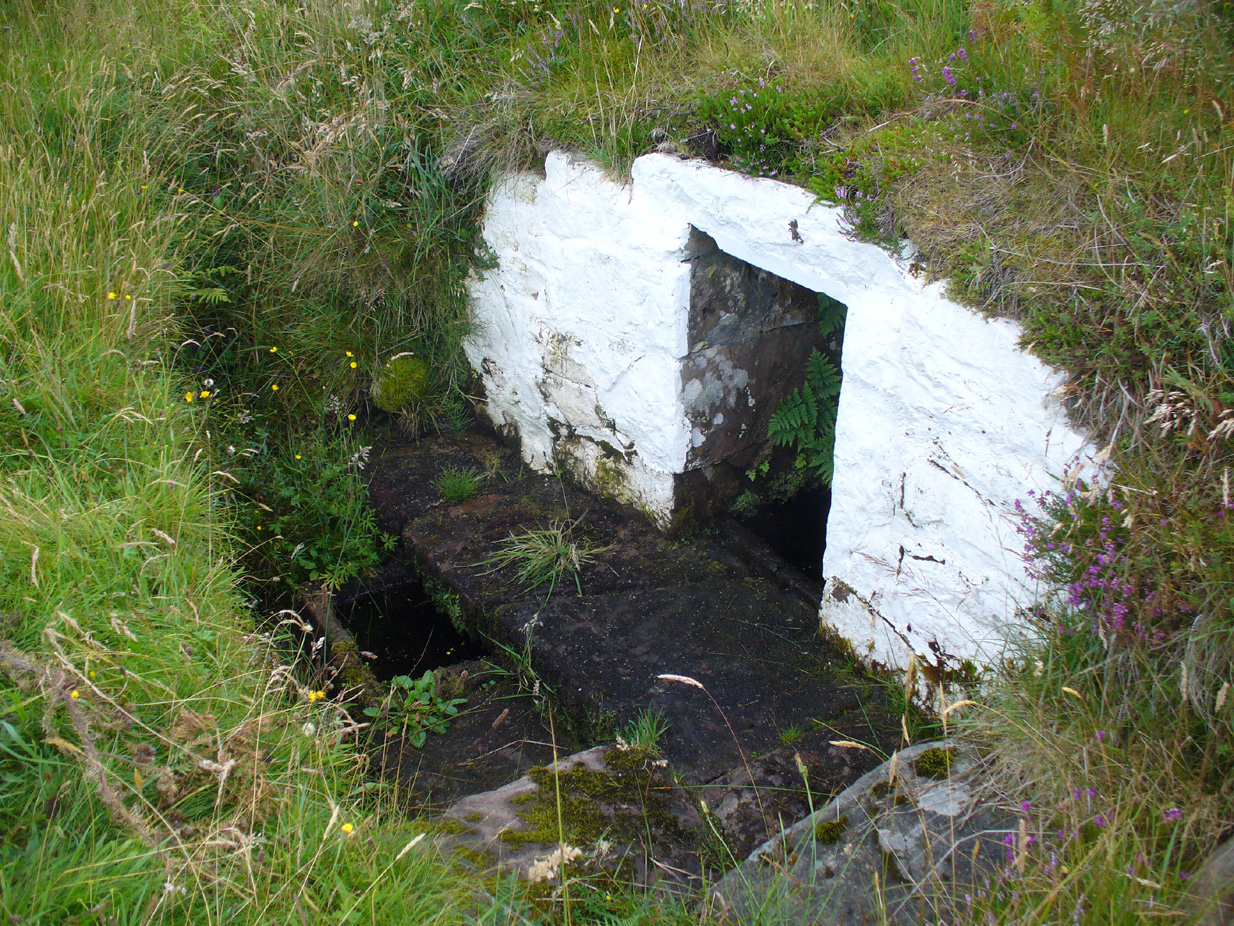
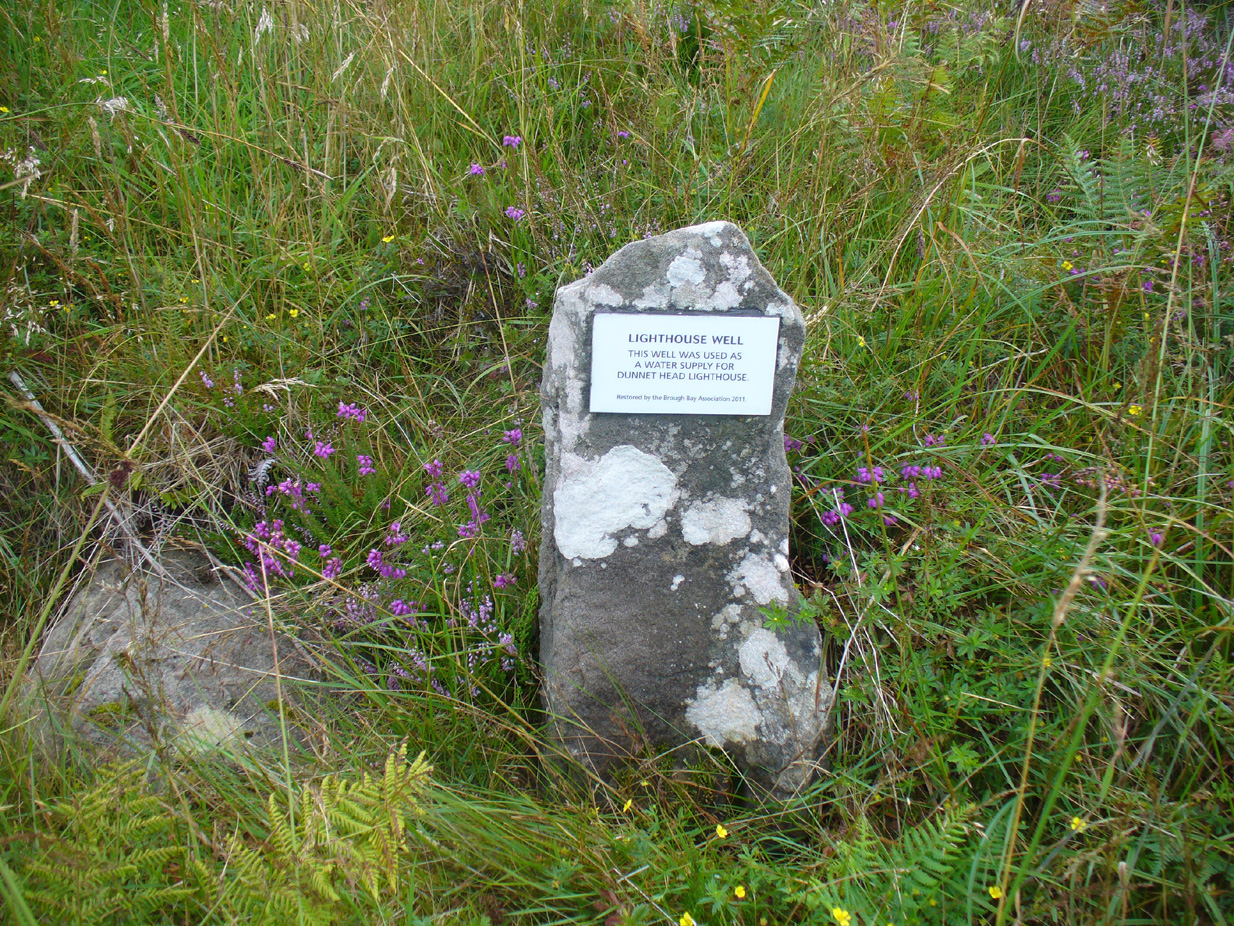
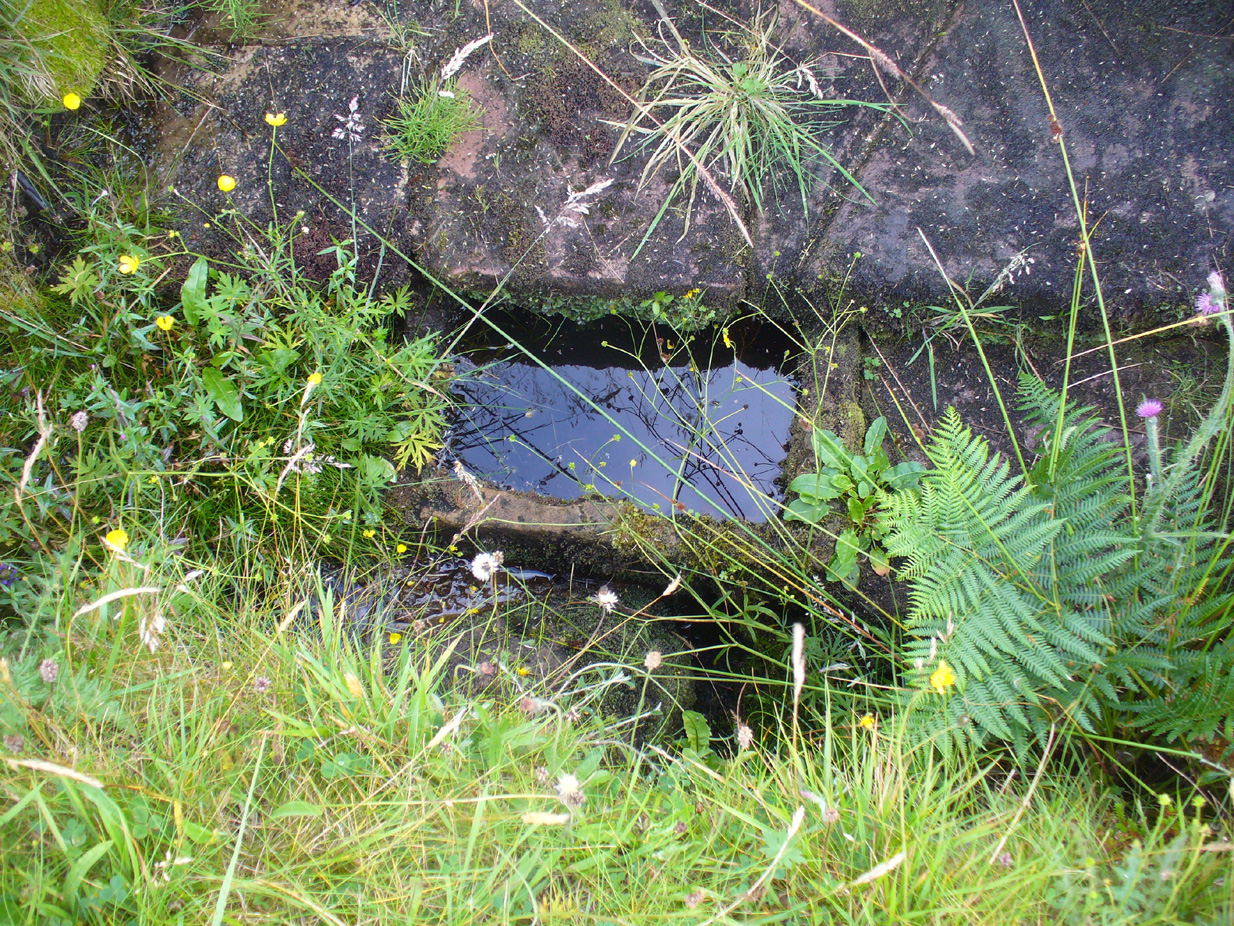
It appears to have been built over in the latter-half of the 19th century, soon after William Thornbury (1878) wrote that he thought the well was still visible, but vanished soon after.
The waters were universally ascribed by all historians, from Mr Allen onwards, as being,
“esteemed highly serviceable in many disorders of the eyes, and in the hardest winter it is never known to freeze.”
The name ‘Vauxhall’ derives from that brilliantly famous family name of ‘Fawkes’ (as in Guy Fawkes), being the ‘hall of Fawkes’. The name was first recorded here as early as 1241. (Gover et al, 1934)
References:
- Allen, Thomas, The History and Antiquities of the Parish of Lambeth, J. Allen: London 1827.
- Foord, Alfred Stanley, Springs, Streams and Spas of London: History and Association, T. Fisher Unwin: London 1910.
- Gover, J.E.B., Mawer, A. & Stenton, F.M., The Place-Names of Surrey, Cambridge University Press 1934.
- Lysons, Daniel, The Environs of London – volume 1, T. Cadell & W. Davies: London 1792.
- Sunderland, Septimus, Old London Spas, Baths and Wells, John Bale: London 1915.
- Thornbury, William, History of Old and New London – volume 6, Cassell, Petter & Galpin: London 1878.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian
The map could not be loaded. Please contact the site owner.
 This is the first detailed guide ever written on the holy wells and healing springs in and around the ancient city of Edinburgh, Scotland. Written in a simple A-Z gazetteer style, nearly 70 individual sites are described, each with their grid-reference location, history, folklore and medicinal properties where known. Although a number them have long since fallen prey to the expanse of Industrialism, many sites can still be visited by the modern historian, pilgrim, christian, pagan or tourist.
This is the first detailed guide ever written on the holy wells and healing springs in and around the ancient city of Edinburgh, Scotland. Written in a simple A-Z gazetteer style, nearly 70 individual sites are described, each with their grid-reference location, history, folklore and medicinal properties where known. Although a number them have long since fallen prey to the expanse of Industrialism, many sites can still be visited by the modern historian, pilgrim, christian, pagan or tourist.