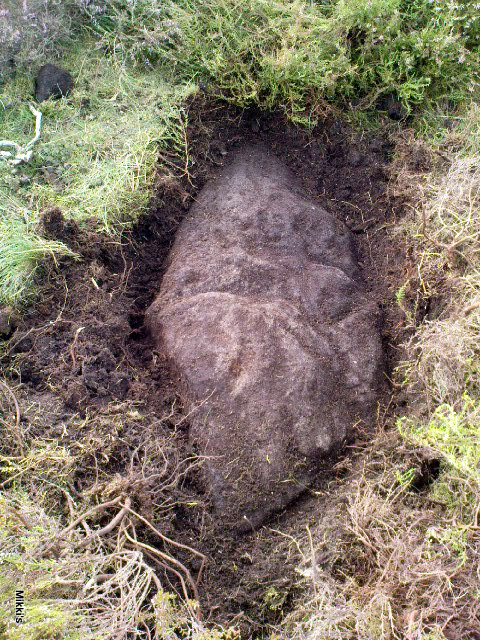
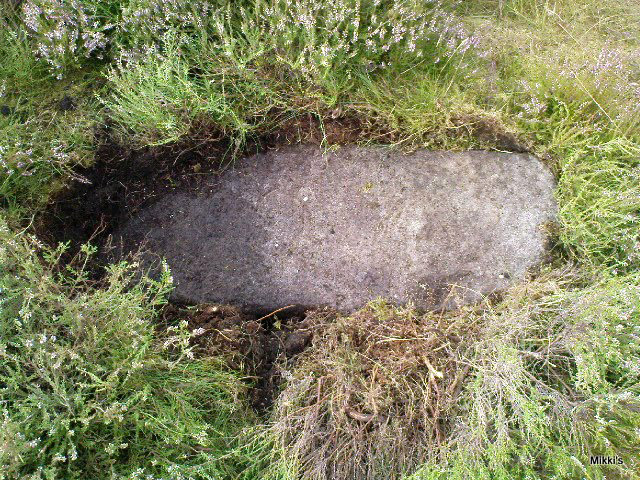
Stone Circle: OS Grid Reference – SE 06432 63048
Also Known as:
- Appletreewick Stone Circle
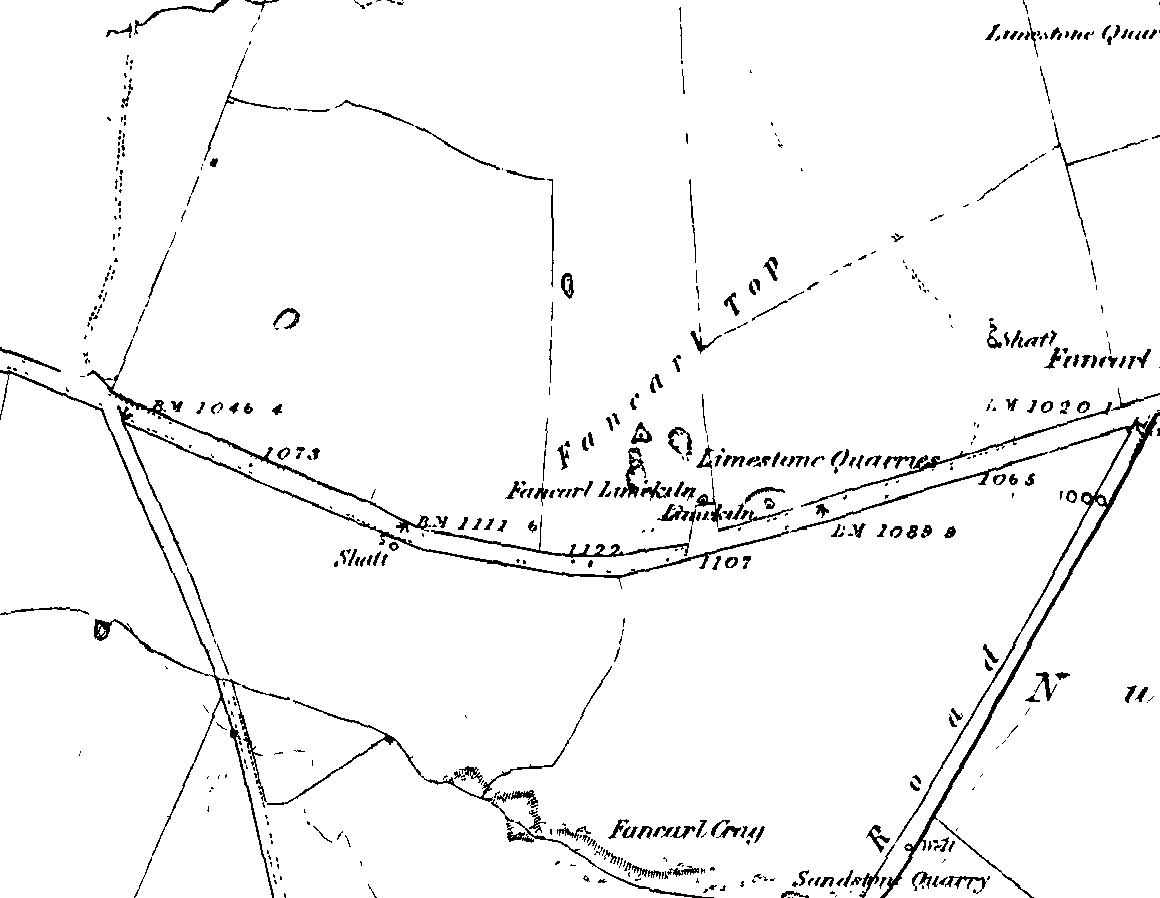
Along the B6265 road between Grassington and Pateley bridge, heading east, past the hamlet of Hebden, a mile or so on where the road goes uphill, stop where it levels out a bit (before it goes further uphill to Stump Cross), a half-mile before the rocky outcrop of Nursery Knott on the left (north) side of the road. A gate into the field on the same side is what yer after, with a small disused quarry therein. Go up here to the quarry-top and then walk uphill for literally 100 yards and the curious small ring is right there.
Archaeology & History

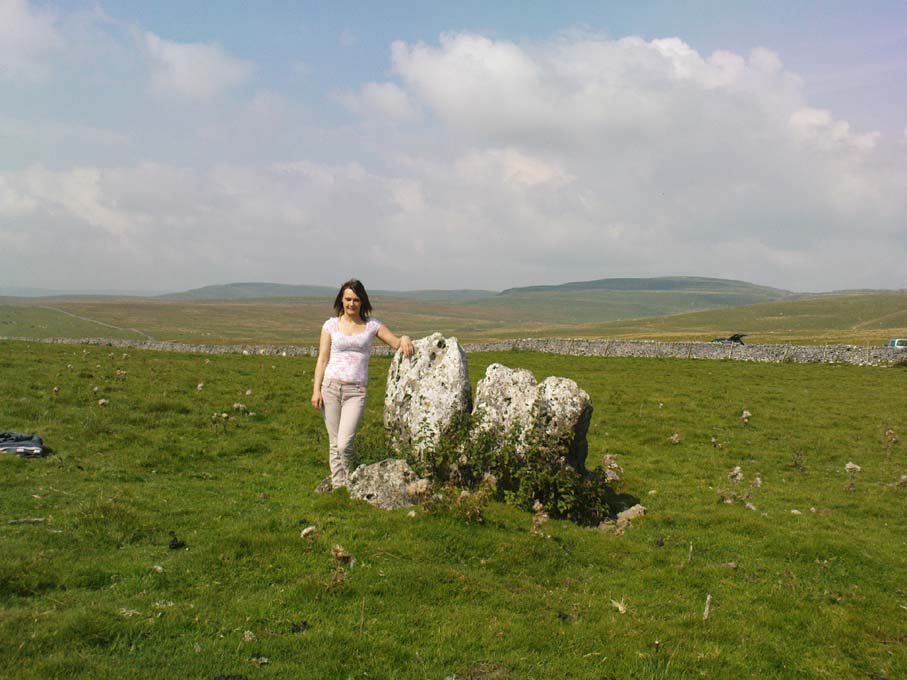
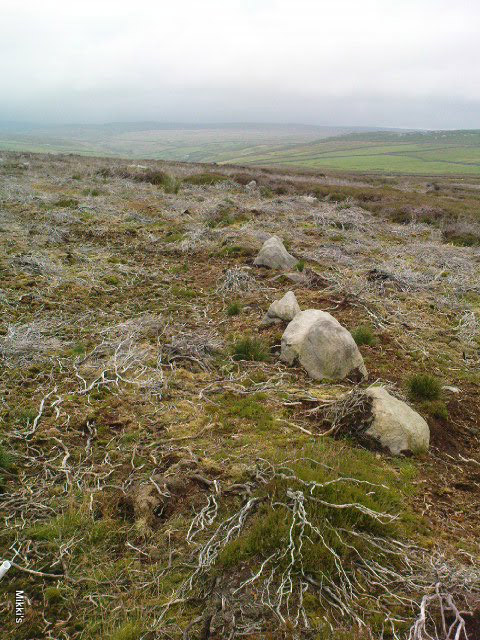
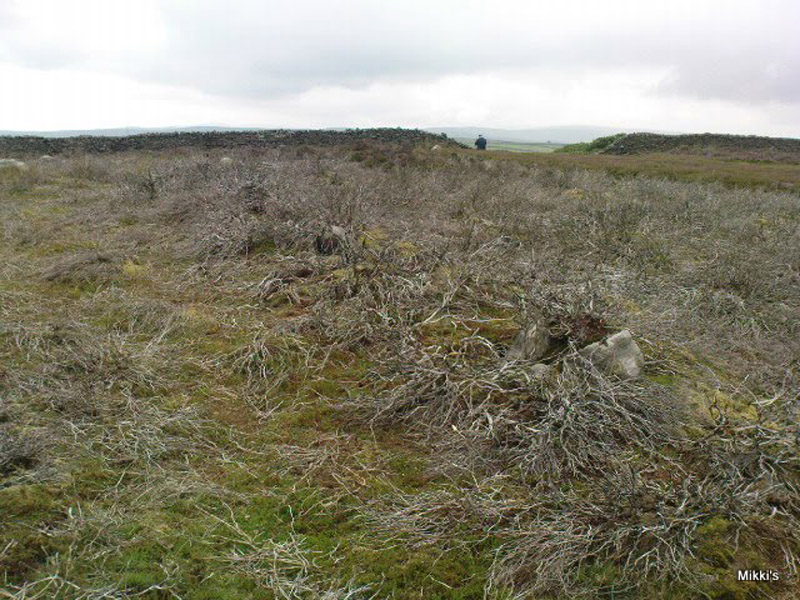
This small stone circle sitting on the grassy ridge overlooking the ritual rocks of Simon’s Seat and central Wharfedale to the south and the Yorkshire heathlands east and west, is probably not what it once was. Overcome by the excess of industrial workings in the fields and moors all round here, it is probable that its present condition is far from its original state. Indeed, if we move back to the 18th century, we find that place-name and map evidences tell us the site was a tomb. The 1771 Greenwood map names the site as the Fancairn — an etymological curiosity in itself, possibly deriving from the ‘Windy Cairn’, which makes sense. The place-name fell into its present title of ‘Fancarl’ after the great Ordnance Survey chaps came, heard dialect and went on their way…

The circle doesn’t appear to have been noted by the great Yorkshire historians Harry Speight and Edmund Bogg in their literary rambles here (rather odd), but was brought to our attention first of all (in a literary sense anyway) by Arthur Raistrick. (1965) He first “surveyed” the site in 1950, but said little until a short remark was printed in the Yorkshire Archaeological Journal, where the notes told it to be one of “two stone circles, one with clear standing stones, 30ft in diameter, and the other a double circle of small recumbent stones, 12ft in diameter.”
The second, smaller double circle he mentions is probably a hut circle or cairn, faint traces of which are seen in the adjacent field. Remains of a prehistoric enclosure were also once evident in the same field; and thankfully to the south (across the road) we can still find many examples of cup-and-rings at Skyreholme.
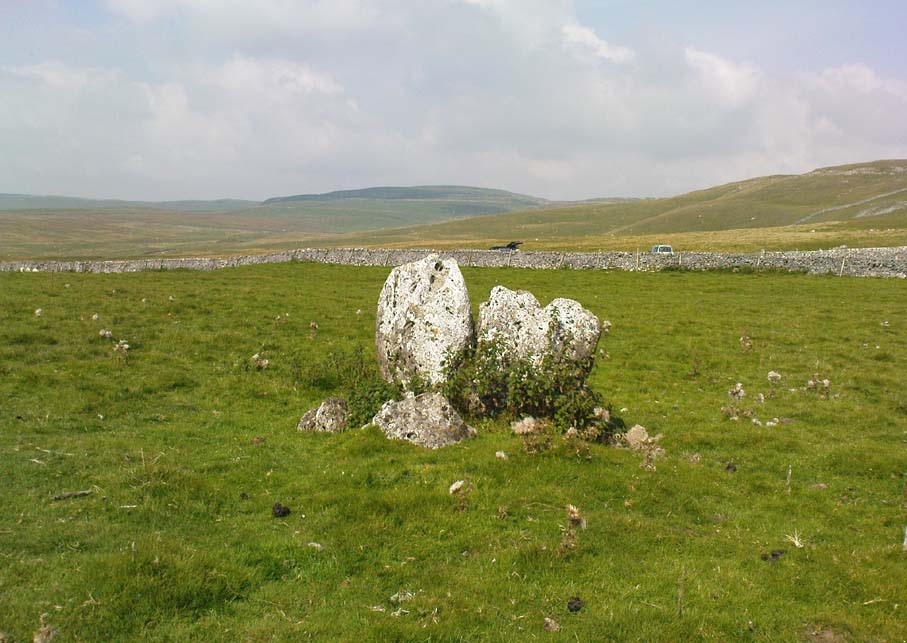
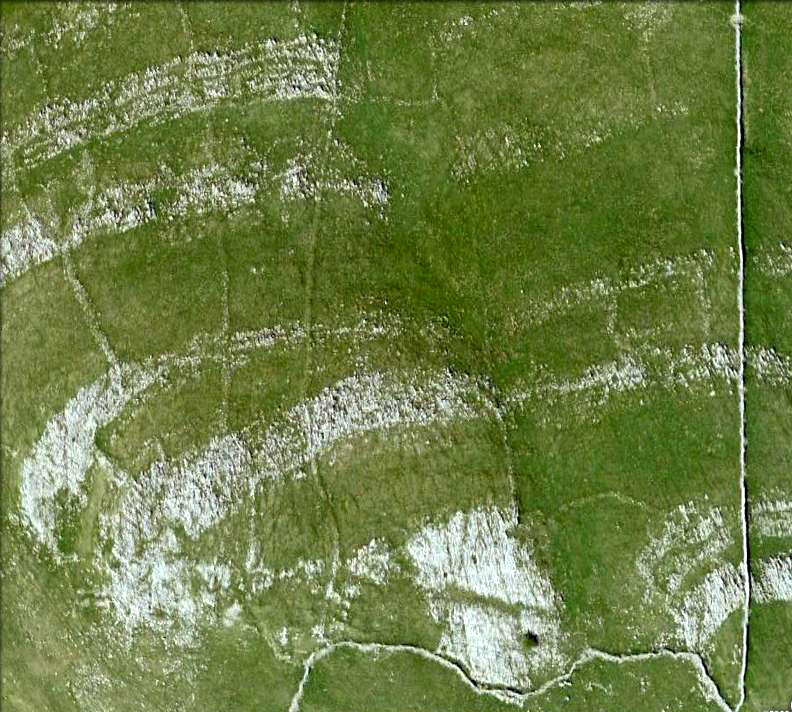
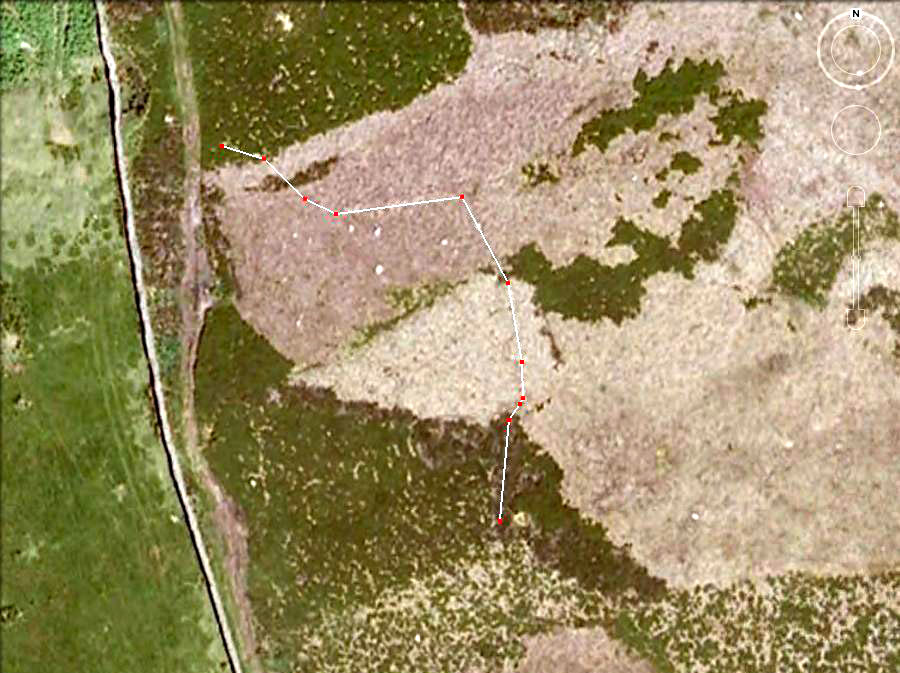
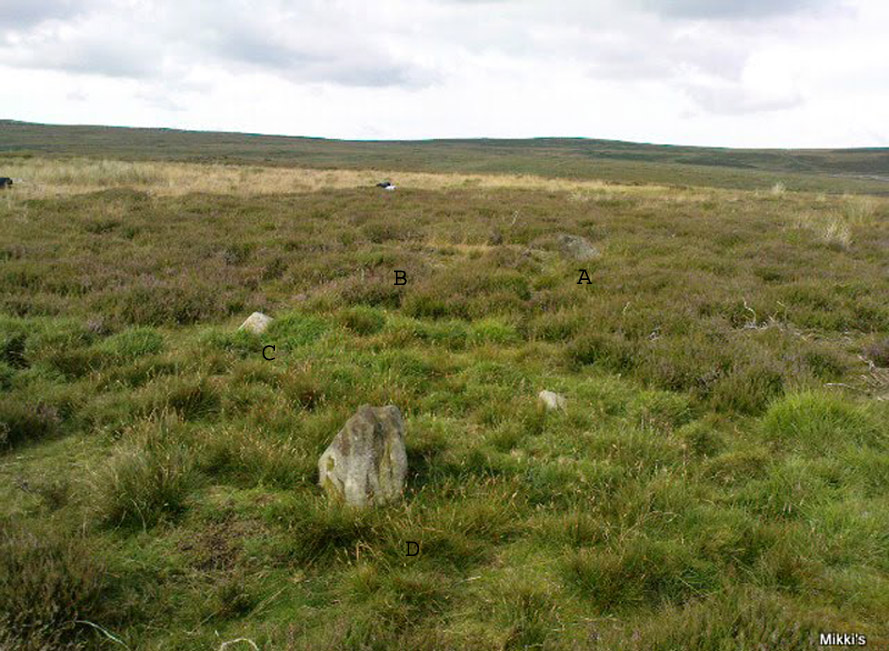
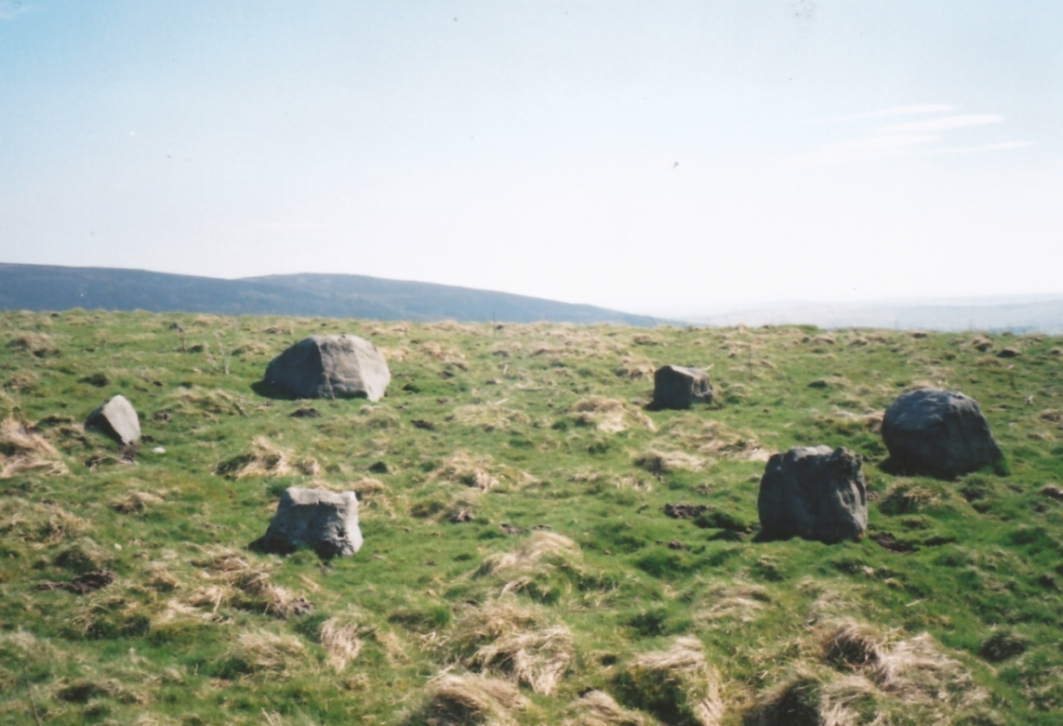
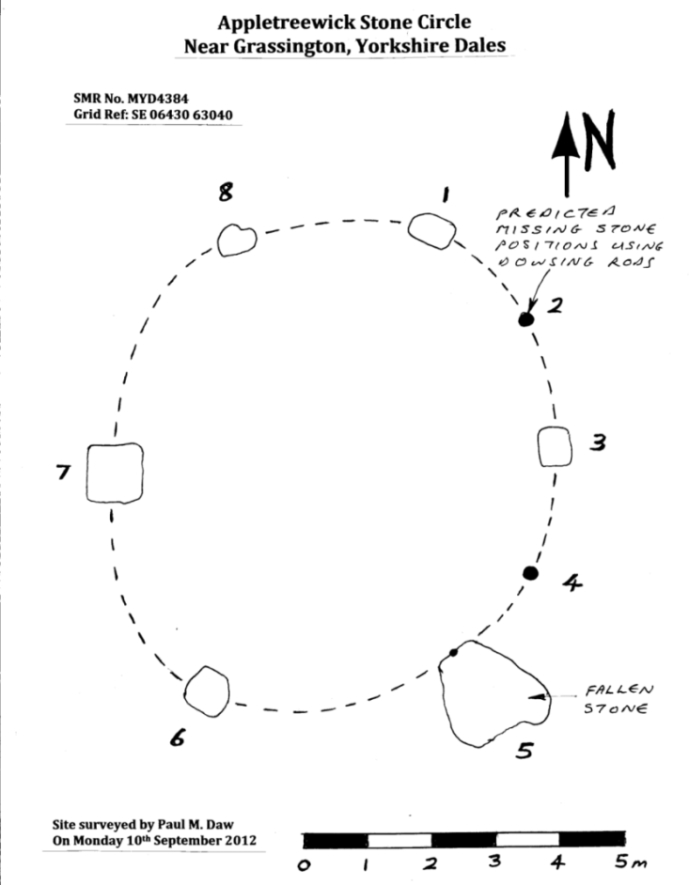
John Barnatt (1989) and Aubrey Burl (2000) include the site in their relative major surveys, with both of them citing the circle, of six small stones, to measure 8.5m by 7.5m. The survey shown of this small stone ring was done by Paul Daw following his visit to the site on Monday 10th September 2012.
Folklore
Although we can only see six stones in this ring today, when the surveyor Paul Daw (2012) did a ground-plan of the place, he also did a dowsing survey of the site and found there were originally two extra stones on the eastern side of the circle. An archaeological dig would be interesting to see if post-holes or the remains of these two additional stones are under the turf. He wrote:
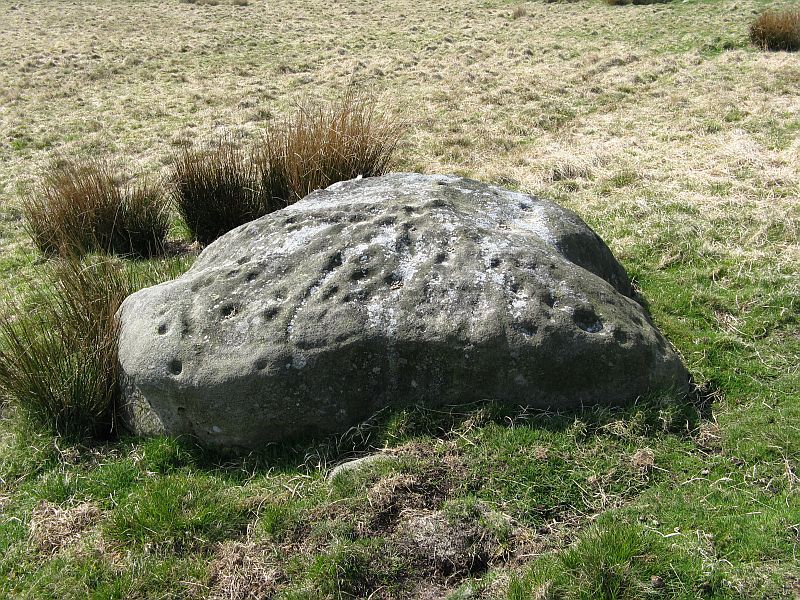
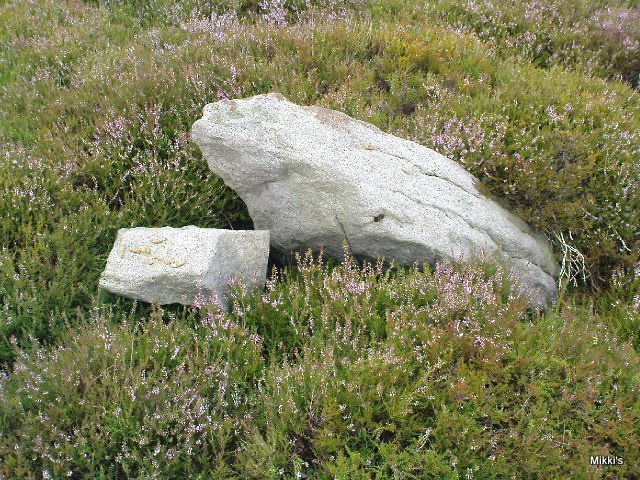
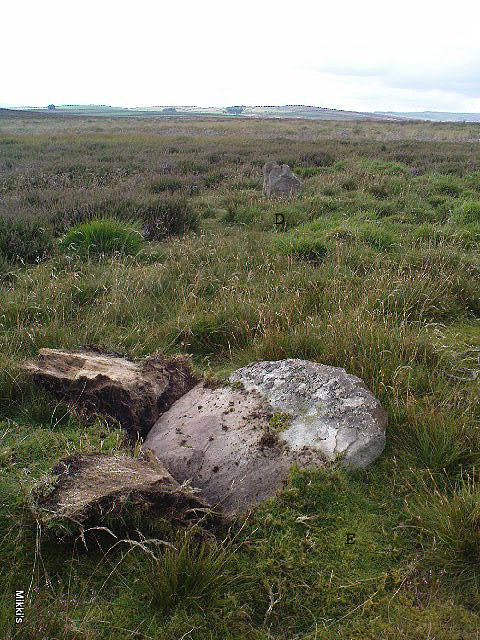
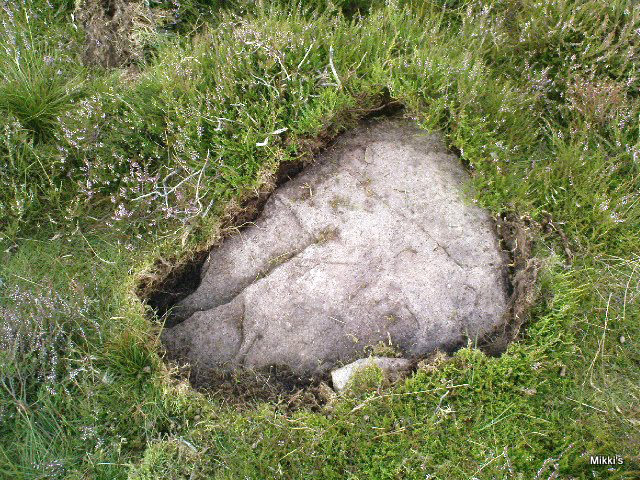
My dowsing survey revealed that the stone circle measured 7.7 metres diameter (N-S) and 7.0 metres (E-W). A reaction was received over the centres of stones 1, 3, 6, 7 and 8 indicating that they are still standing in their original positions, but stone number 5 to the south-south-east of the circle had a reaction at its northern end, which indicates that it was once standing but had fallen outwards. It is not therefore an earthfast stone, as speculated by A. Raistrick, when he visited the site. The stone measures 1.65 m x 1.65 m x 800 mm and fans out like a shell from bottom to top. It would have been an impressive stone when standing, but was top heavy, and the most likely stone to fall.
Stones 1, 3, 6, and 8 are all of a similar size, are much more stable, and stand at about 500 mm high. Stone 7 in the western sector is 800 mm high, and measures 950 mm x 850 mm, and looks like a rectangular block, with slightly rounded edges.
I also obtained a reaction at positions 2 and 4, indicating that there were once stones standing in these positions. To the north of the stone circle there are a number of stones lying on the surface. A. Raistrick suggested that there may have been another small stone circle in this area, but my dowsing rods did not detect anything, and it is probable that these are random stones lying on the surface.
This entire region is bedevilled with faerie, goblin and giant lore, plus creation myths of our peasant ancestors (Sutcliffe 1929) — some still living if you’re lucky enough to talk with the old folk, who might tell you a thing or two, or might not, depending on how you smell.
References:
- Barnatt, John, The Stone Circles of Britain – 2 volumes, BAR: Oxford 1989.
- Burl, Aubrey, The Stone Circles of Britain, Ireland and Brittany, Yale University Press 2000.
- Daw, Paul M., “Appletreewick Stone Circle, Yorkshire Dales,” unpublished survey report 2012.
- Raistrick, Arthur, ‘Yorkshire Archaeological Register 1964: Appletreewick, W.R.,’ in Yorkshire Archaeology Journal, volume 41, 1965.
- Smith, A.H., The Place-Names of the West Riding of Yorkshire – volume 6, Cambridge University Press 1963.
- Sutcliffe, Halliwell, The Striding Dales, Frederick Warne: London 1929.
Acknowledgements: Huge thanks to Paul Daw for his photos and survey of the site, and for sharing details of his dowsing results here.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian
The map could not be loaded. Please contact the site owner.