Tumulus: OS Grid Reference – SE 0322 1039
Getting Here

From Marsden itself, take the A62 road west and where the road bends round, the large hill rising on your left is where you’re heading. There’s a parking spot near the bottom of the highest part of the hill. From here, walk right to the top, up whichever route you feel comfortable with. At the very top is an intrusive modern monolith (dedicated to somebody-or-other, which the fella wouldn’t approve of if he really loved these hills*). About 10 yards east of the stone is a small grassy mound with a bittova dip in the middle. That’s it!
Archaeology & History
This is a little-known prehistoric site, whose remains sit upon a very well-known and impressive hill on the western edges of Marsden. Described in Roy Brook’s (1968) excellent survey on the history of Huddersfield as “the most important site” from the Bronze Age in this region, it seems curious that the attention given to it has been relatively sparse and scattered. The tops and edges of the hill have been cut into and worked upon by the uncaring spade of industrialism (of which there is much evidence), aswell as much of the peat being used for fuel over countless centuries — some of which appears to have been cut close to the all-but-lost remains of this once-important burial site.
The first description of the hill itself seems to be in 1426, where it was named in the Ramsden Documents, “past’ voc’ le Pole.” (Smith 1961) It wasn’t until appearing as Puil Hill on the 1771 Greenwood map that the title we know of it today began to take form. Local people would alternately call it both Pule and Pole Hill. But its name is somewhat curious, as the word appears to derive from the variant Celtic and old English words, peol, pul and pol,
“meaning a pool or marsh, especially one that was dry in the summer. Pole Moor therefore means Pool or Marsh Moor…and Pule Hill = the hill in the marsh.” (Dyson 1944)


However, in Smith’s English Place-Name Elements, he gives an additional piece of word-lore which seems equally tenable, saying the word may be “possibly also ‘a creek'”, which could be applied to the water-courses immediately below the west side of the hill. We might never know for sure. But the archaeological remains on top of Pule Hill have a more certain history about them…
The burial site first appears to have been mentioned in a short article by Henry Fishwick (1897), who wrote:
“Whilst searching for…flints on the summit of Pule Hill a few weeks ago a discovery was made which is of considerable antiquarian interest. On the highest point of the hill, and from 12 to 18 inches below the surface, were found two human skeletons lying on their sides almost directly east and west, the knees of both being drawn up. Near to them were two small circular urns measuring 4¾ inches high, 5 inches across the top, and 6 inches in diameter at the widest part, the base being 3 inches across. These are made of native clay very slightly burnt, and are ornamented with short lines (apparently cut with some sharp instrument) which forms a rough herring-bone pattern. On the centre band are four ears or small handles which are pierced so as to admit a small cord. The urns contained animal matter and a few calcined human bones.
“Since the discovery of these two urns another has been exhumed from the same place. It measures 3½ inches in height and 7 inches in diameter at the widest part, which is just below the rim of the mouth. Its ornamentation is similar to the others, but quite so elaborately executed; the base is made with four feet or claws. On one side of the urn is an ear or handle pierced with a small hole in the direction of a double-groove, in which it is placed; there is a second double-groove near the bottom. When found this urn only contained sand. Fragments of a fourth urn were discovered on the same spot… The discoverers of these were Mr G. Marsden and Mr F. Fell.”
As a consequence of this, a couple of years later members of the Yorkshire Archaeology Society took it upon themselves to have a closer look at the place — and they weren’t to be disappointed. They cut a large trench across the top of the site from east to west, digging down until they hit the bedrock of the very hill; then dug an equal trench as much as 30 yards to the north, and on the southern side to the edge of the hill near where it drops. They came across,
“In three places were found distinct cavities…driven into the rock to a depth of about eighteen inches, the dimensions of which…averaged three feet long by two feet wide.”

Within these rock cavities they found small portions of bone, charcoal and flint. It was also found that the urns which were described earlier by Mr Fishwick, had been found laid on their sides “at the places where the cavities were subsequently discovered.” Inside the urns, the remains of various human bones were discovered and reported on by Mr Boyd Dawkins: a craniologist of some repute in his time.
The discoveries were remarked upon a few years later — albeit briefly — in D.F.E. Sykes (1906) excellent history work of the area, where he told us that it was one of his esteemed friends, “George Marsden of Marsden…who was fortunate enough in August, 1896, to find” the ancient remains. But perhaps the most eloquent description of the Pule Hill remains was done by James Petch (1924) of the once-fine Tolson Museum archaeology bunch in Huddersfield (still open to the public and very helpful indeed). Mr Petch wrote:
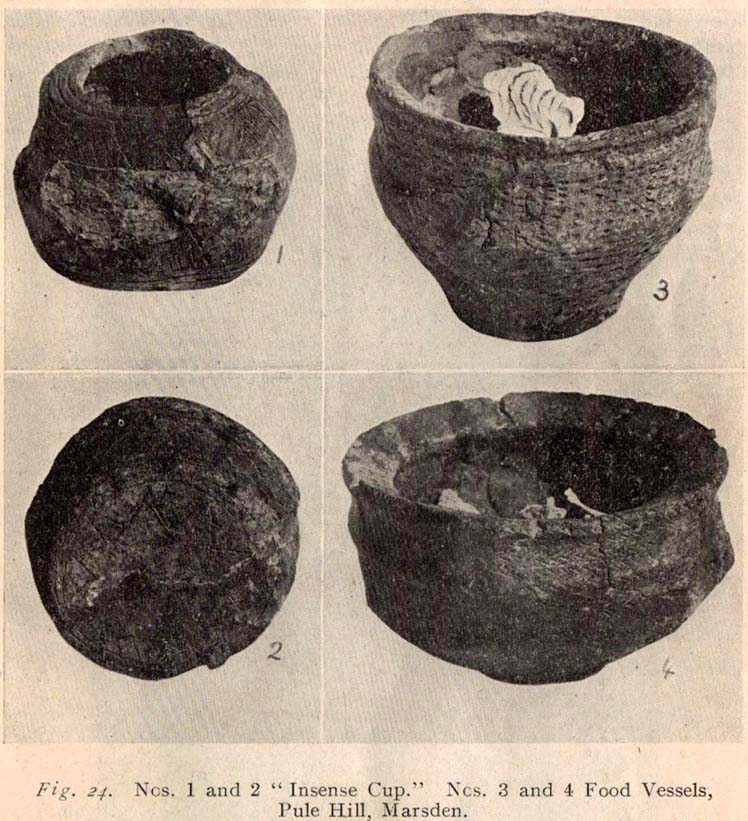
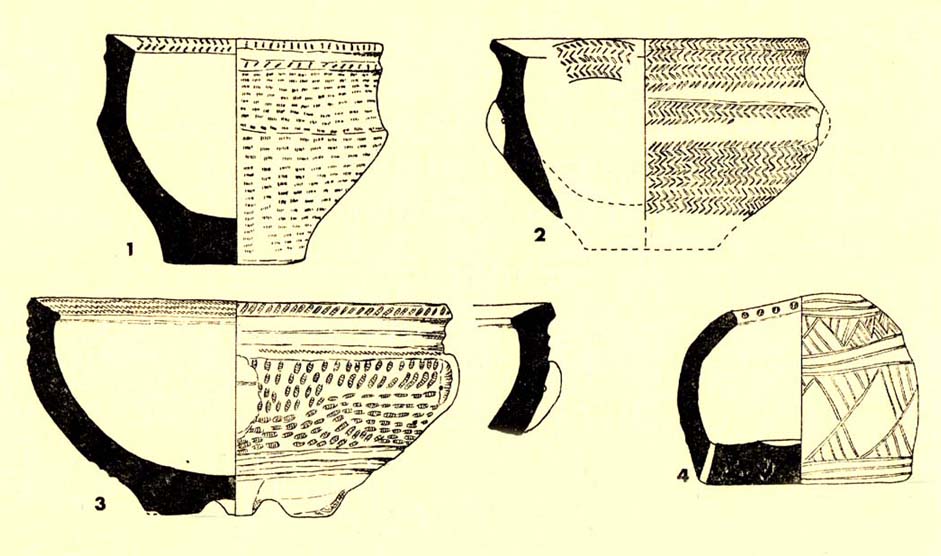
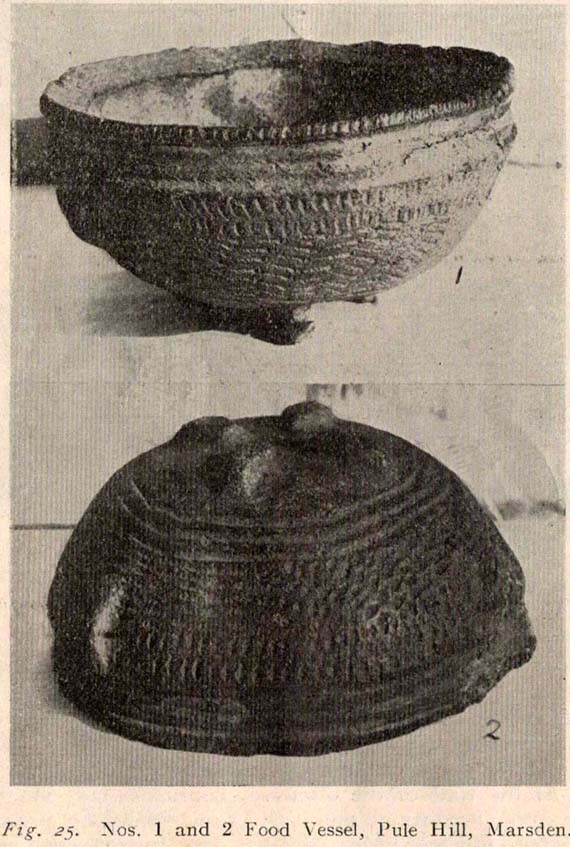
“Several Bronze Age interments have been found in the locality. Of these the most important is that discovered on the summit of Pule Hill and excavated in 1896 by the late Mr. George Marsden. The finding of an arrowhead led to digging and four urns containing burnt human remains, and so-called “incense cup” were uncovered and removed (Figures 24, above, and 25, below) . In 1899 the site was again opened up for further examination. It was then noted that the urns had been set in cavities dug into the rock to a depth of about 18 inches. The type of the urn fixes the interment as belonging to the Bronze Age, and characteristic of such interments are the rock-cavities. The site is however somewhat exceptional in that no trace was found of the mound which was usually heaped over an interment. As the site is very exposed, the mound may have been weathered away, leaving no traces visible to-day. Along with the urns were found an arrowhead, one or two scrapers, a disc, a few pygmies and a number of flakes and chippings. It is important to note that these flints are mostly the relics of a Mas d’Azil Tardenois workshop which existed long before the interment was made on the summit of Pule Hill, and that they have no necessary connection with the Bronze Age burial…
“Owing to the generosity of the late Mr. George Marsden, the discoverer, and his family, the urns are now in the Museum. They form one of the most striking exhibits in the Prehistoric section. They are illustrated in Figures 24 and 25, above.
“The smallest of the group (Figure 24, 1 and 2, above) belongs to the type known as “incense-cups,” this name being the result of a somewhat fanciful attempt to account for the perforations the examples always show. It is quite evident and widely recognized now that this explanation – that they were in fact censers – is unsatisfactory, and that the use of this peculiar type of vessel is a problem as yet unsolved. Nos. 3 and 4 and Fig 25, 1 and 2 (above), are styled “food vessels,” such as may have been their ordinary use.
“No. 3 is ornamented with slight indentations, and without lugs; it has two strongly marked beads around the mouth, with a distinct groove between them. No. 4 has two slight lugs opposite to one another, which appear to have been pinched up from the body of the vessel; they were perforated but the holes have been broken out. Fig. 25, Nos 1 and 2 (above), is the best of the series, it is ornamented with small cone-shaped indentations and shows several unusual features; the width is great in proportion to the height; the lugs are not opposite and were attached to the vessel after it was made; the one on the left is seen to be perforated, and the position of the second is above the figure 2 in the illustration. The four feet were attached in a similar manner, and are not solid with the body of the vessel. All the vessels are hand made and show no indication of the potter’s wheel.”

The site has subsequently been listed in a number of archaeology works, but there’s been no additional information of any worth added. Manby (1969) noted that of the four vessels from this prehistoric ‘cemetery’, one bowl was of a type more commonly found in East Yorkshire — though whether we should give importance to that single similarity, is questionable.
One thing of considerable note that seems to have been overlooked by the archaeological fraternity (perhaps not too surprising!) is the position of these burial deposits in the landscape. To those people who’ve visited this hill, the superb 360° view is instantly notable and would have been of considerable importance in the placement and nature of this site. The hill itself was probably sacred (in the animistic sense of things) and is ideal for shamanistic magickal practices. The communion this peak has with other impressive landscape forms nearby – such as the legendary West Nab — would also have been important.
For heathens and explorers amongst you, this is a truly impressive place indeed…
References:
- Abraham, John Harris, Hidden Prehistory around the North West, Kindle 2012.
- Barnes, Bernard, Man and the Changing Landscape, Eaton: Merseyside 1982.
- Brook, Roy, The Story of Huddersfield, MacGibbon & Kee: London 1968.
- Clark, E. Kitson, “Excavation at Pule Hill, near Marsden,” in Yorkshire Archaeological Journal, volume 16, 1902.
- Cowling, Eric T., Rombald’s Way, William Walker: Otley 1946.
- Dyson, Taylor, Place Names and Surnames – Their Origin and Meaning, with Speicla Reference to the West Riding of Yorkshire, Alfred Jubb: Huddersfield 1944.
- Elgee, Frank & Harriet, The Archaeology of Yorkshire, Methuen: London 1933.
- Faull, M.L. & Moorhouse, S.A. (eds.), West Yorkshire: An Archaeological Guide to AD 1500 – volume 1, WYMCC: Wakefield 1981.
- Fishwick, Henry, “Sepulchral Urns on Pule Hill, Yorkshire,” in Proceedings of the Society of Antiquaries, volume 16, 1897.
- Manby, T.G., “Bronze Age Pottery from Pule Hill, Marsden,” in Yorkshire Archaeological Journal, volume 42, part 167, 1969.
- Petch, James A., Early Man in the District of Huddersfield, Tolson Memorial Museum: Huddersfield 1924.
- Smith, A.H., The Place-Names of the West Riding of Yorkshire – volume 2, Cambridge University Press 1961.
- Sykes, D.F.E., The History of the Colne Valley, F. Walker: Slaithwaite 1906.
- Watson, Geoffrey G., Early Man in the Halifax District, HSS: Halifax 1952.
Acknowledgements: Huge thanks to Ben Blackshaw, for guiding us to this and other sites in the region!
* To be honest, I think it’s about time that these increasing pieces of modern detritus that keep appearing in our hills, dedicated to whoever, should be removed to more appropriate venues, off the hills, keeping our diminishing wilderness protected from them in ways that real lovers of the hills deem necessary. Such modern impositions are encroaching more and more and intruding upon the places where they simply don’t belong. I’ve come across many hill walkers who find them unnecessary and intrusive on the natural environment, so they should be discouraged. There is a small minority of sanctimonious individuals who seems to think it good to put their clutter onto the landscape, or want to turn our hills into parks – but these personal touches should be kept in parks, instead of adding personal touches where they’re not needed. Or even better, put such money into things like schools, hospitals or communal green energy devices. People would much prefer to be remembered by giving the grant-money to the well-being of others, instead of being stuck on a stone on a hill (and if not, well they definitely don’t belong to be remembered in the hills!). What if everyone wanted to do this?! Or is it only for the ‘special’ people. Please – keep such things off our hills!
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian
The map could not be loaded. Please contact the site owner.
