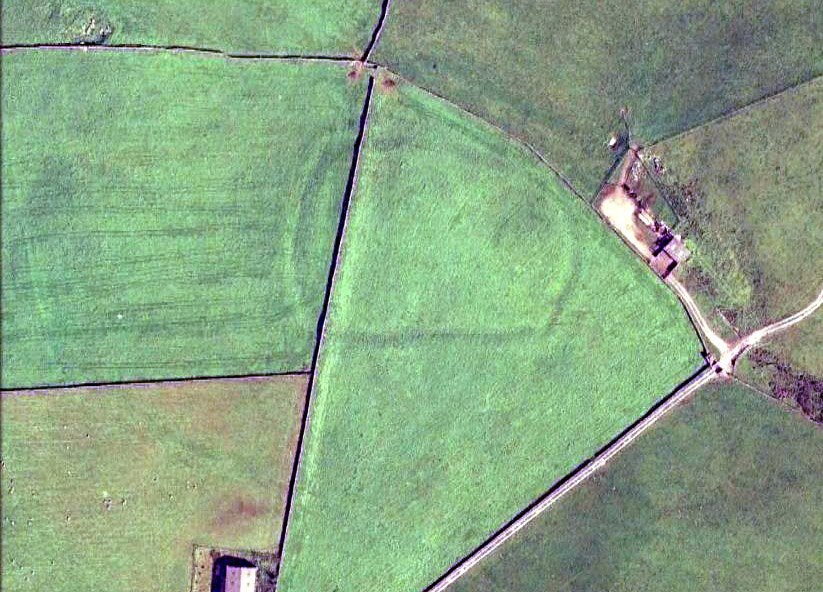
Enclosure: OS Grid Reference – SE 0874 1009
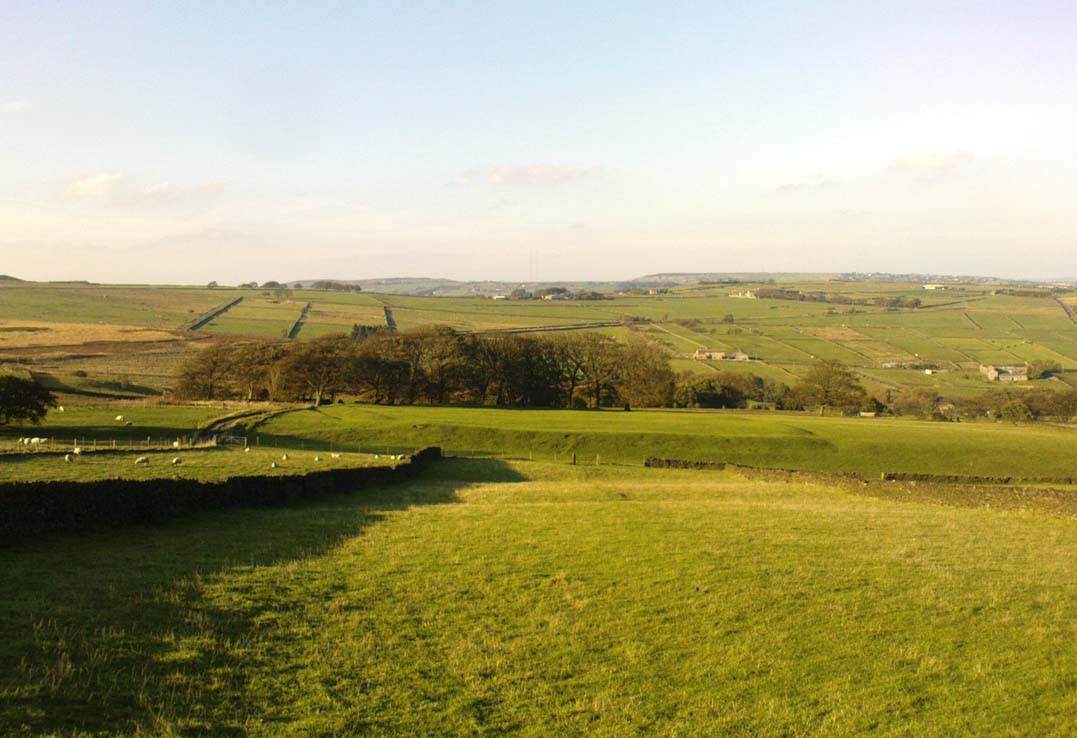

From the crossroads at the centre of Meltham, near the church, take the Wessenden Head Road up out of town for about a mile. Keep your eyes peeled to right (north) for the track leading downhill to Oldfield Hall or Farm. As you go down the track you’ll see a small cluster of hawthorns running along a small ridge 100 yards or so ahead, at the end of the field, with some line of embankment. This is on the right of the track and is the Oldfield enclosure!
Archaeology & History
The remains of this large quadrangular settlement were first described as of ‘Roman’ origin in Mr Morehouse’s History of Kirkburton (1861), where he told that,
“In the…township of Meltham are the remains of a Roman encampment, on the moor below West Nab, a short distance to the left of the road which leads thence to the village…forming nearly a square of about four chains. When I visited the place about twenty years since, in company with the owner and other friends, the whole was very distinct and perfect. This piece of ground has since been brought into cultivation, yet the trenches are still visible. This encampment would appear only to have been made to supply some temporary emergency.”
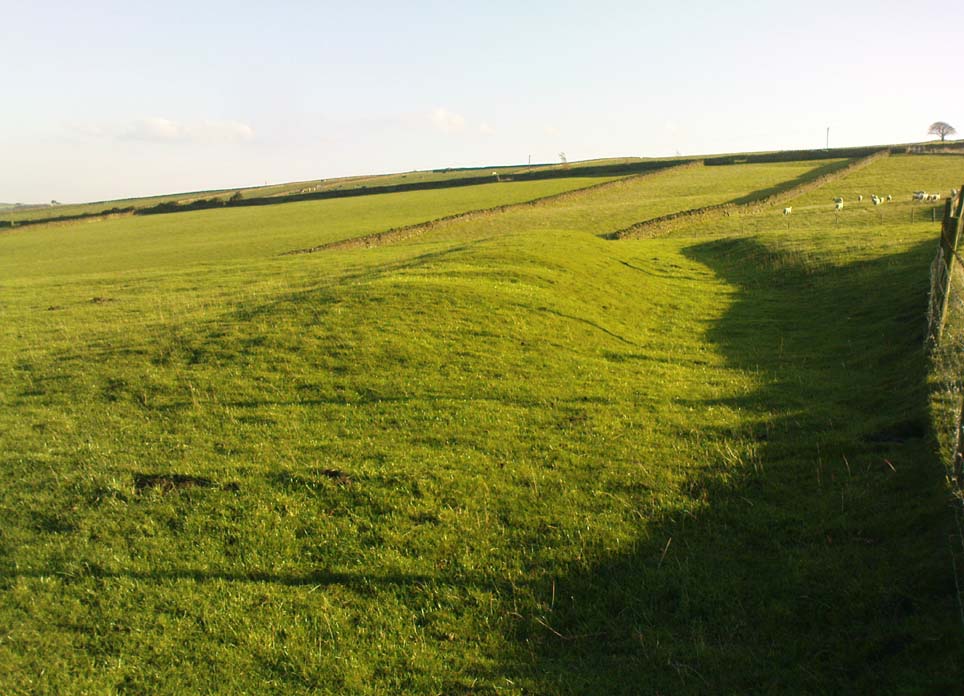


But Mr Morehouse’s speculation of its Roman origin and function are known to be untrue. The site is in fact of Iron Age origin and was probably in semi-permanent use for long periods between Spring and Autumn. But the ‘Roman’ nature of the site was echoed a few years later, albeit briefly, in Mr Hughes’ History of Meltham (1866), where he told that “querns or hand-mills for grinding corn were found” at the site.
In 1909, the Saddleworth antiquarian Ammon Wrigley excavated the site but found little that could enable a correct dating of the enclosure. It was explored again a few years later by Ian Richmond and then again by J.P. Toomey in the 1960s. Bernard Barnes (1982) summarised their respective findings, telling:
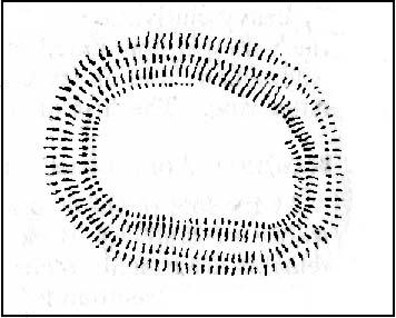
“Rampart of rubble and earth 7 feet wide faced with drystone walling; original height c.10 feet; V-shaped rock-cut ditch, 5½ feet deep and 6 feet wide, and a counterscarp bank similar to inner rampart with drystone revetment surviving to 4 courses. Northeast entrance had double timber gateway. Pre-rampart palisade trench on at least 2 sides of the enclosure with vertical posts 2 feet apart. Finds include 2 stone discs, rough out beehive quern, iron slag and very small fragments of pottery. Site dated to Iron Age.”
Another enclosure of similar period can be found a few hundred yards to the south.
…to be continued…
References:
- Abraham, John Harris, Hidden Prehistory around the North West, Kindle 2012.
- Barnes, Bernard, Man and the Changing Landscape, Eaton: Merseyside 1982.
- Bennett, Paul, The Old Stones of Elmet, Capall Bann: Milverton 2001.
- Hughes, Joseph, The History of the Township of Meltham, John Russell Smith: London 1866.
- Morehouse, Henry James, The History and Topography of the Parish of Kirkburton, H. Roebuck: Huddersfield 1861.
- Toomey, J.P., An Iron Age Enclosure at Oldfield Hill, Meltham, Brigantian: Huddersfield 1976.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian