Enclosure (destroyed): OS Grid Reference – TQ 675 811
Archaeology & History

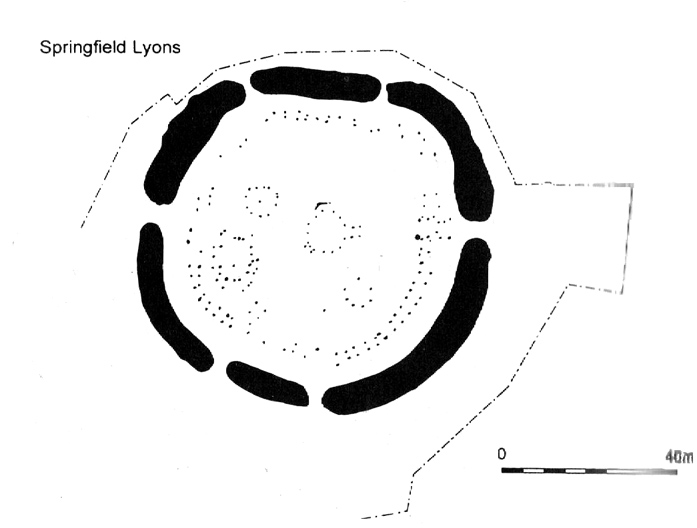
This large circular enclosure, measuring about 120 feet across, seemed to be a small settlement with several internal structures (fences, pits, cremations and a sunken-floored structure) that was first excavated in 1978 and described as a Bronze Age enclosure. Akin to a henge monument in some ways, this small settlement site had two entrances: one on the east and the other opposite on its west side. However, the main ‘entrance’ was on the eastern (sunrise) side, where post-holes laid a pathway over the ditch and into the structure itself.
The excavation on the eastern side of site revealed two periods of construction with associated structures, including three circular buildings. Some excavations to the east produced evidence for a range of contemporary activities. The assemblage of Late Bronze Age material included pottery, metalwork, cremation remains, sickle moulds and equipment for salt production. For further info and imagery, see the Link below.
References:
- Bond, Dermot, Excavation at the North Ring, Mucking, Essex, East Anglian Archaeology 1988.
- Brown, N., “The Late Bronze Age Enclosure at Springfield Lyons in its Landscape Context,” in Essex Archaeology & History, volume 32, 2001.
Links
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian
The map could not be loaded. Please contact the site owner.