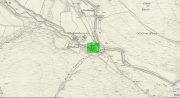
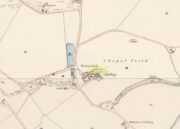
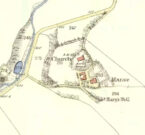
Stone Circle (destroyed): OS Grid Reference – NO 5414 6935
Archaeology & History

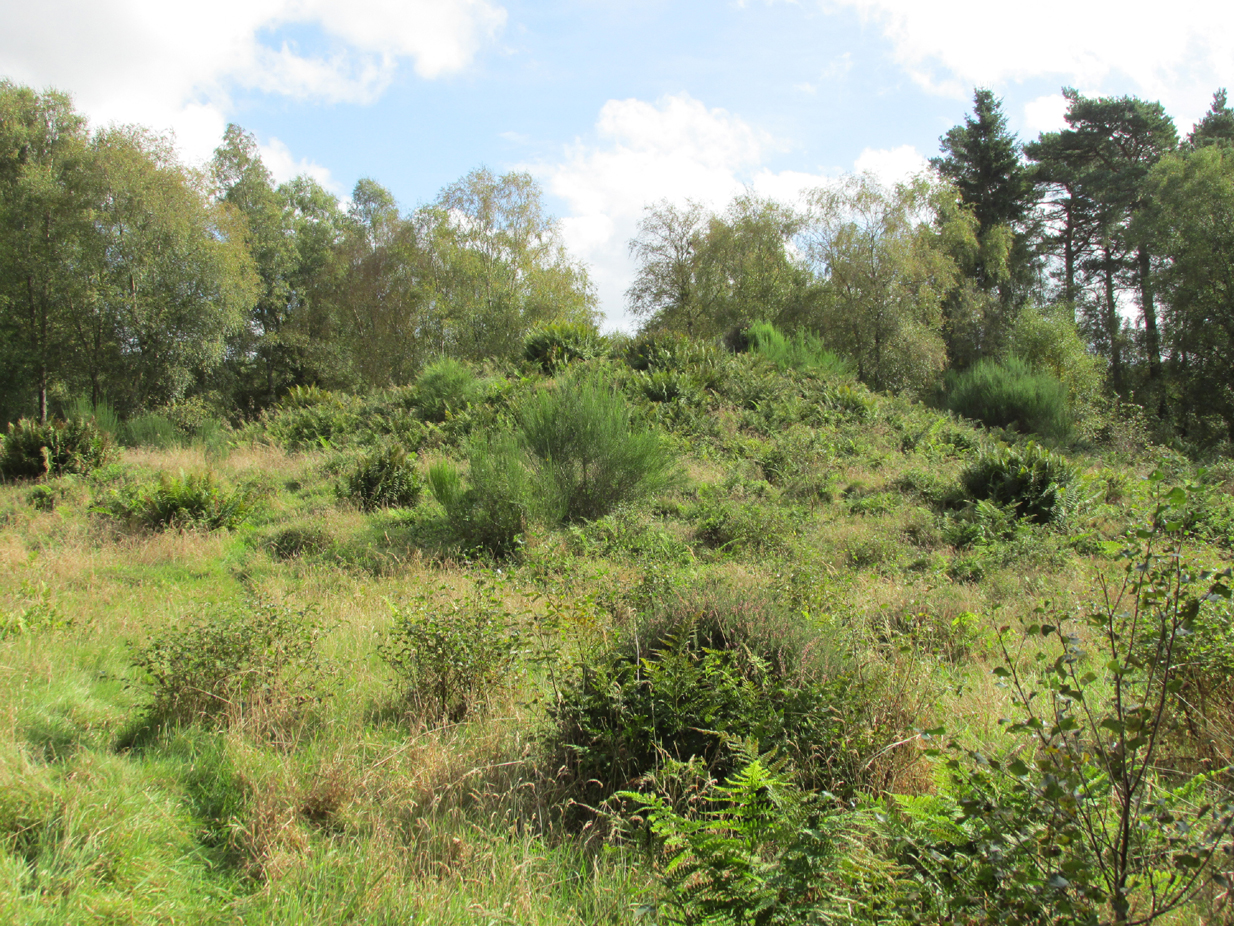
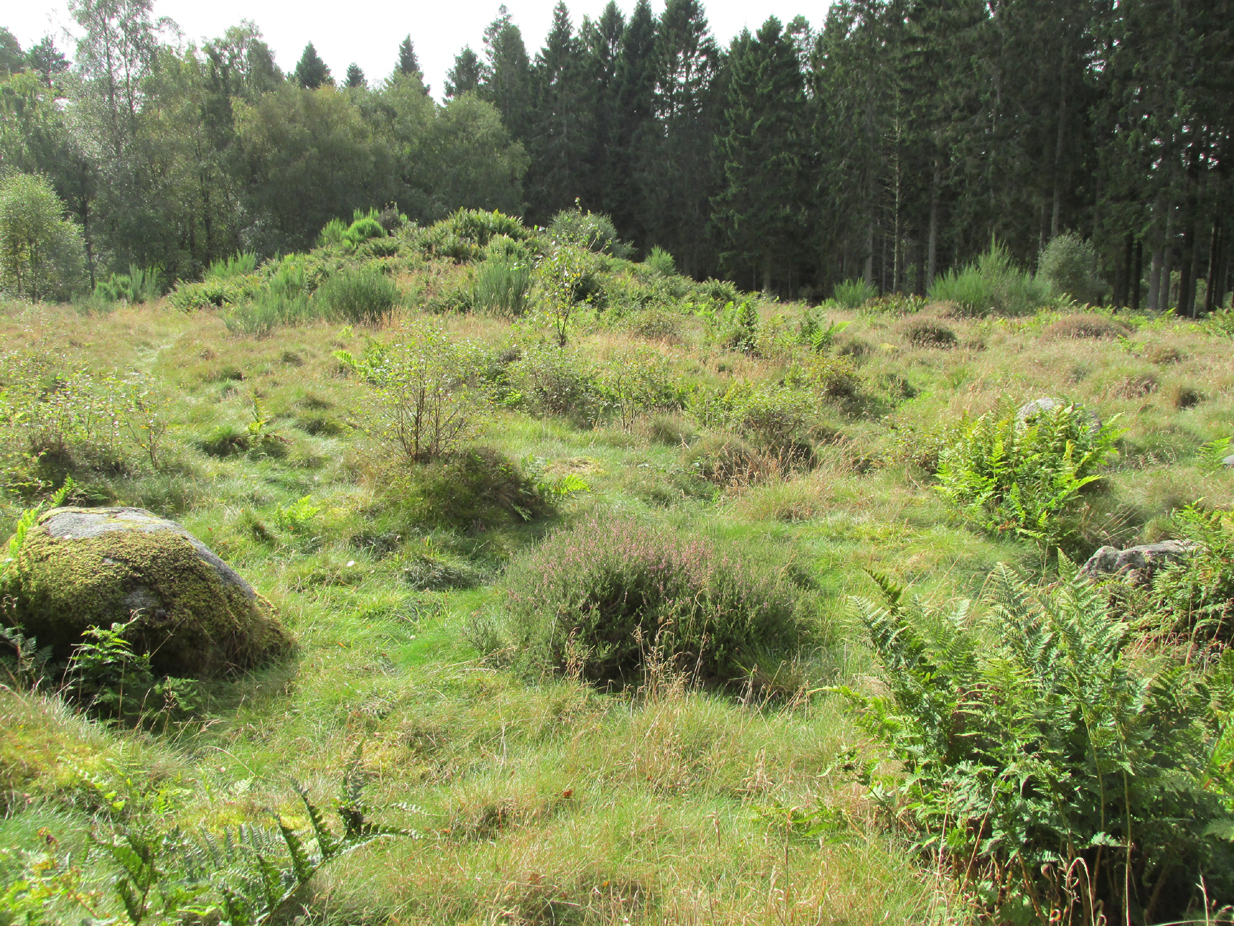
Entered in Aubrey Burl’s (2000) magnum opus as a stone circle, the site has also been reclassified as a ring cairn or cairn circle, for obvious reasons. We can haggle about definitions if we wanna get a bit anal about it, but even from what little we know, this was an impressive looking site to say the least! Burl (1976) originally suggested that it may have been a recumbent stone circle: an Aberdeenshire outlier, so to speak—and he may have been right. Sadly the place has been destroyed, like so many megalithic rings in this neck o’ the woods.
It was first mentioned, albeit briefly, by Alexander Gardner in his 1843 summary of the parish in the New Statistical Account where he told that, “there are the remains of a Druidical Temple at Newbigging near the remains of an ancient Castle or Tower called Dennyfern.” Our main source of information comes via the early Ordnance Survey lads after they’d visited the place in 1861. They wrote:
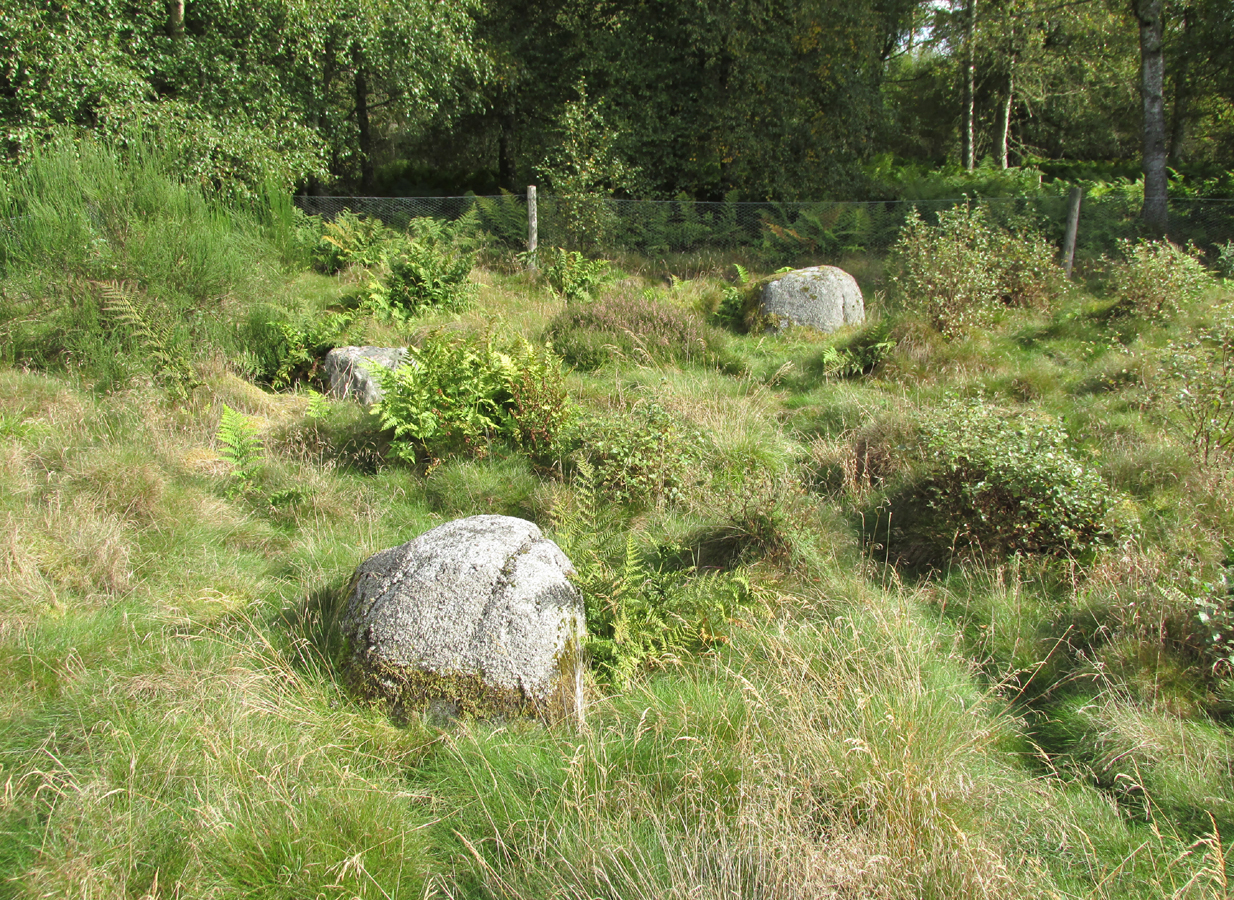
“Though nothing now remains of this Circle but one very large upright stone, measuring 5 feet 4 inches high, 9 feet in circumference at the base, and 6 feet 3 inches at the top, yet its site is plainly traceable, and is slightly raised from the ground around it. It was an immense Cairn, 40 feet in diameter according to the farmer of Newbigging, containing 400 cartloads of stones which he removed …The one Stone standing is so large that this may be considered to be the remains of a “Stone Circle” of which the large quantity of small stones formed the raised plateau, the ring of which is still visible.”
The great regional historian Andrew Jervise (1853) culled a few extra snippets of information about the place, telling us:
“Some fifty years ago, a good specimen of concentric circles stood on the farm of Newbigging, about half-a-mile north of the house, on an elevated part of the mountain; but, of the twenty or thirty large stones that enclosed an area of from fifty to sixty feet in diameter, only one remains, the rest having been carried away for various utilitarian purposes. This boulder, which is about eight feet high, is sometimes called the Druidical, but more commonly the “Stannin’ Stane of Newbiggin’,” and many flint arrow-heads have been found in its vicinity. When demolished, the middle of the area of the inner circle was found to be filled with small stones to the depth of about three feet, under which lay a quantity of black clammy earth, mixed with pieces of charcoal, while a track about two feet broad, composed of loose red sandstone, laid to the depth of a few inches, ran directly through the clammy earth and pebbles, from side to side of the outer circle.”
Alex Warden (1884) mentioned the remaining Stannin’ Stane of Newbiggin’ in his survey of the area, and the monolith was still in place when Cruikshank (1899), the local minister, wrote his detailed history book, but he added little more by way of Jervise’s description, merely telling that the stone circle
“on Newbigging must have been in its original state interesting and remarkable. It was composed of upright stones of great size, as we can see by the only one now remaining, which is known as “the Stannin’ Stane of Newbiggin’.” The blasted massive remains of the other stones form the foundation of the field dyke close by.”
It’s obvious that Burl’s idea that this circle was a recumbent one is based on Jervise’s description of it being “a good specimen of concentric circles” with the internal cairn structure giving it additional archaeomythic clout. Its complete destruction prevents us knowing anything more.
References:
- Barnatt, John, Stone Circles of Britain – volume 2, BAR: Oxford 1989.
- Burl, Aubrey, The Stone Circles of the Britain Isles, Yale University Press 1976.
- Burl, Aubrey, The Stone Circles of Britain, Ireland and Brittany, Yale University Press 2000.
- Cruikshank, F., Navar and Lethnot: The History of a Glen Parish in the North-east of Forfarshire, Black & Johnston: Brechin 1899.
- Jervise, Andrew, The History and Traditions of the Land of the Lindsays in Angus and Mearns, Sutherland and Knox: Edinburgh 1853.
- Royal Commission on the Ancient and Historical Monuments of Scotland, The Archaeological Sites & Monuments of Central Angus, Angus District, Tayside Region, HMSO: Edinburgh 1983.
- Warden, Alex J., Angus or Forfarshire: The Land and People – Descriptive and Historical – volume 4, Charles Alexander: Dundee 1884.
Acknowledgements: Huge thanks for use of the Ordnance Survey map in this site profile, reproduced with the kind permission of the National Library of Scotland.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian
The map could not be loaded. Please contact the site owner.