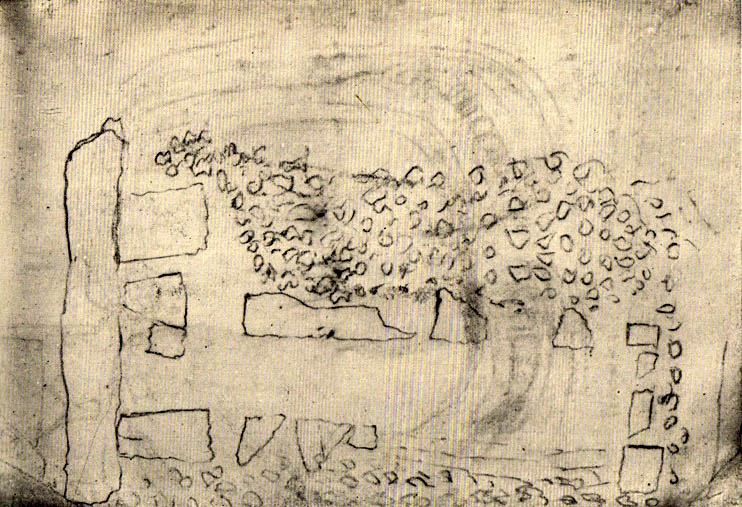
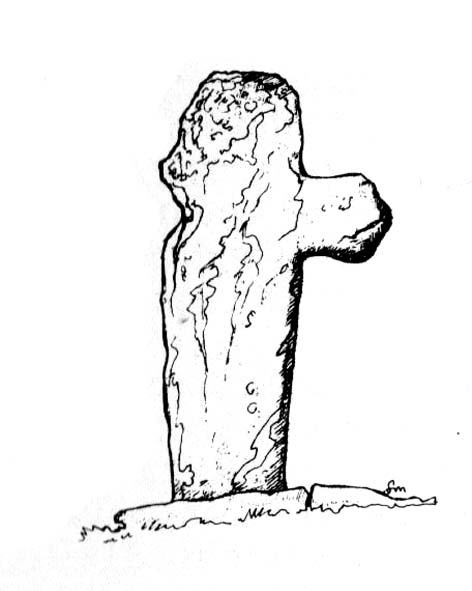
Cup-Marked Stone: OS Grid Reference – NN 58759 23087
Also Known as:
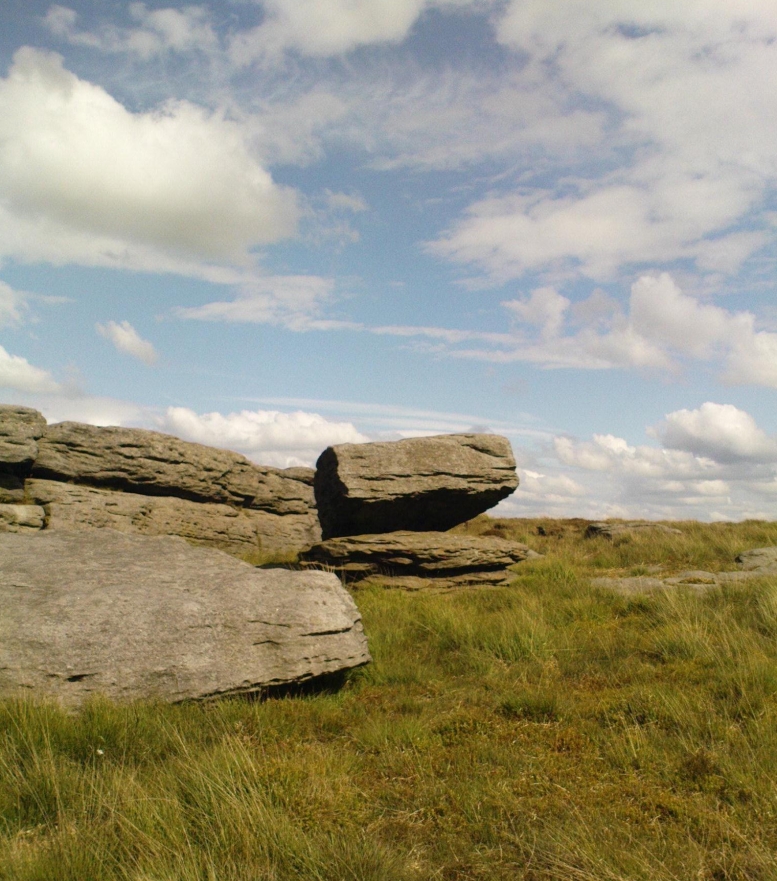
Follow the same directions as if you’re going to the much overgrown, earthfast Druidsfield 01 carving. Adjacent is an upstanding block of large rock, right next to which is the flat surface of this Druidsfield 2 carving. If it’s overgrown, rummage around. You can’t miss it!
Archaeology & History
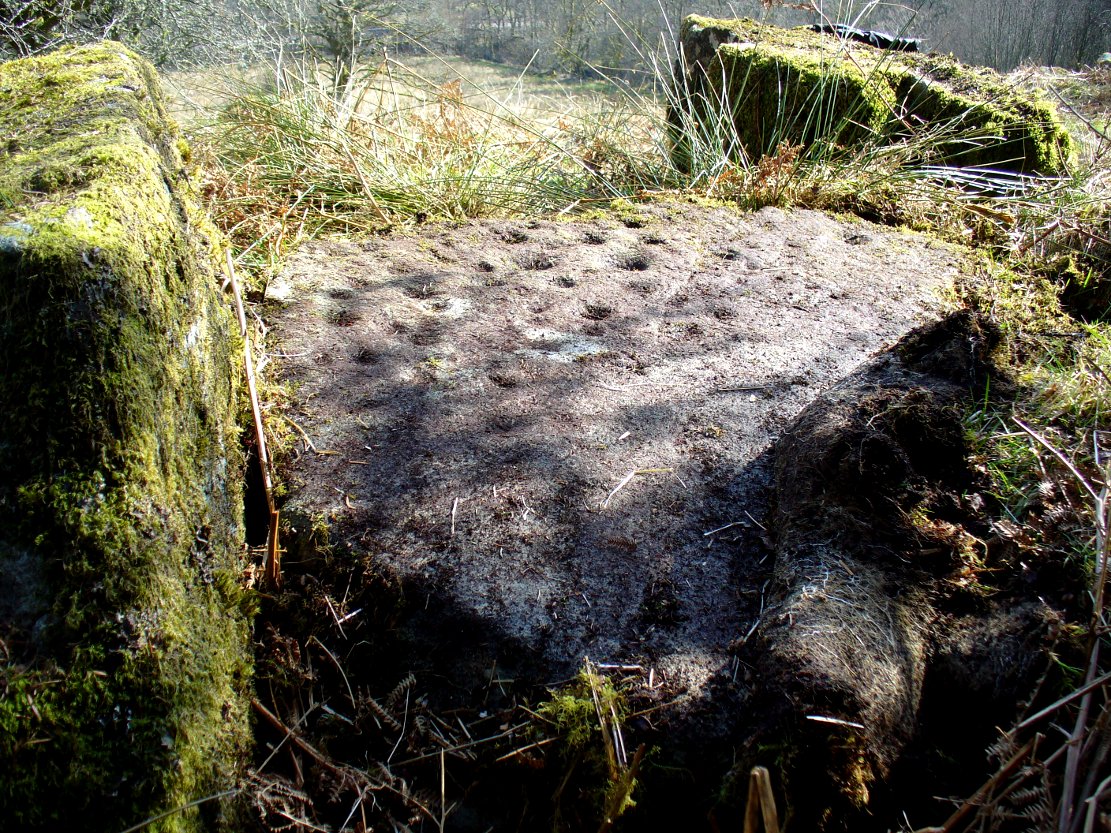
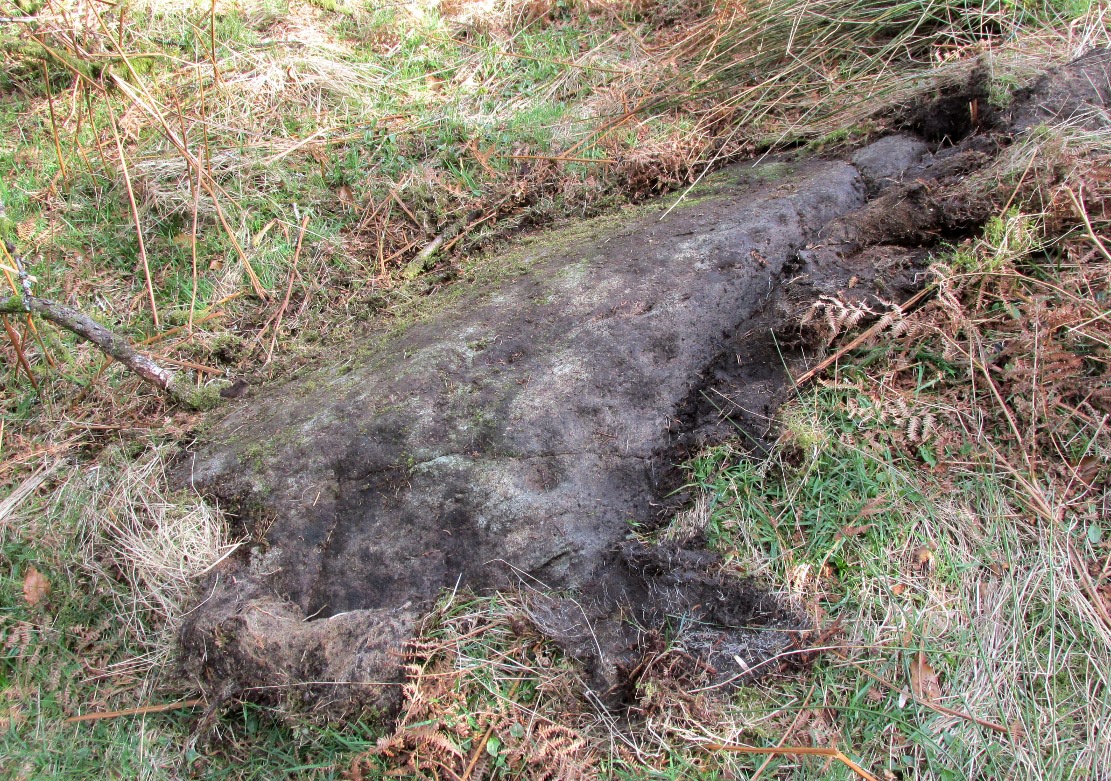
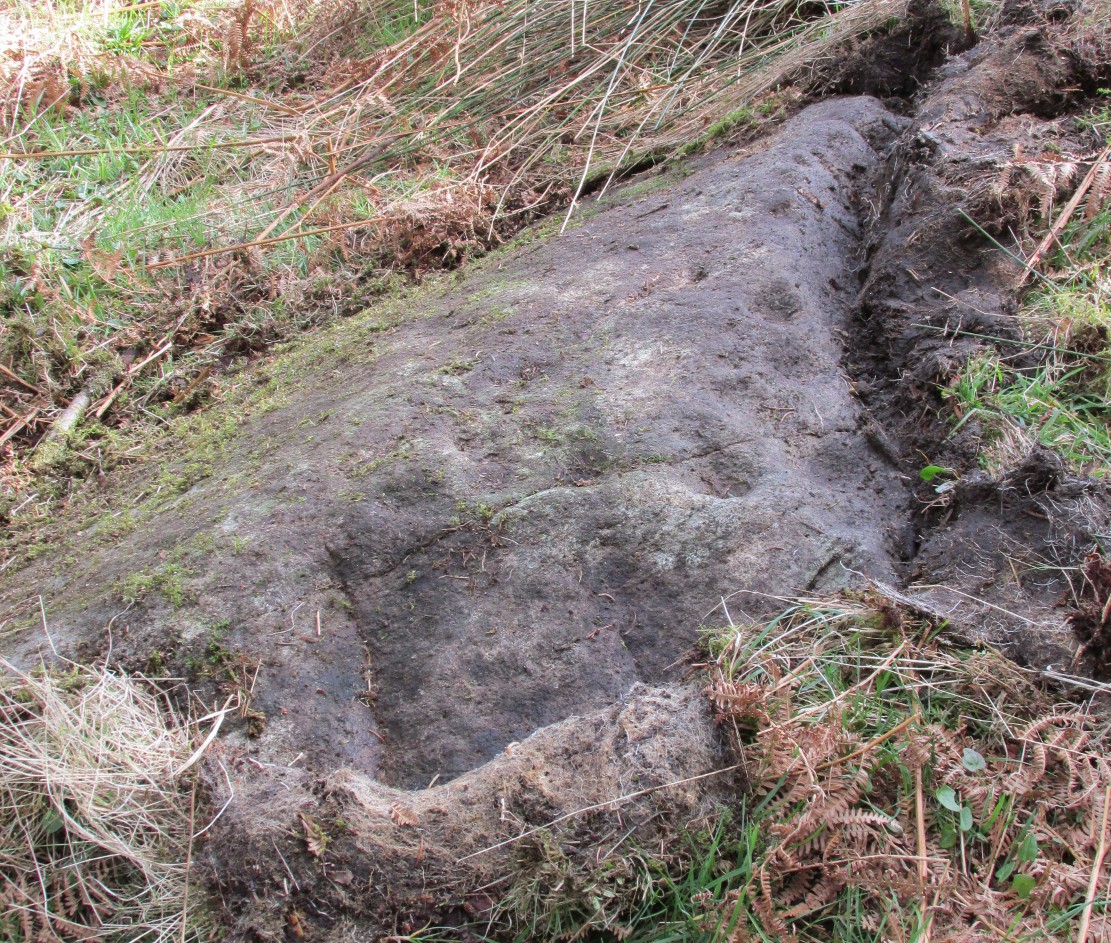
This carving and its compatriots have almost been forgotten about it seems. Buried beneath rolls of vegetation, this long flat rock covered in cup-markings seems to have played a part in some larger megalithic structure—but whatever it was is difficult to work out. As you walk around the place it gives the distinct impression that some form of tomb was once in evidence, which may have been the case. The Scottish archaeology giant Audrey Henshall is said to have found no evidence of a chambered tomb, but this may have been something smaller, less impressive.
When Mr Haggart (1888) wrote about this carving, he too thought that the carvings had been part of a tomb—this being the horizontal surface at the bottom. He wrote that,
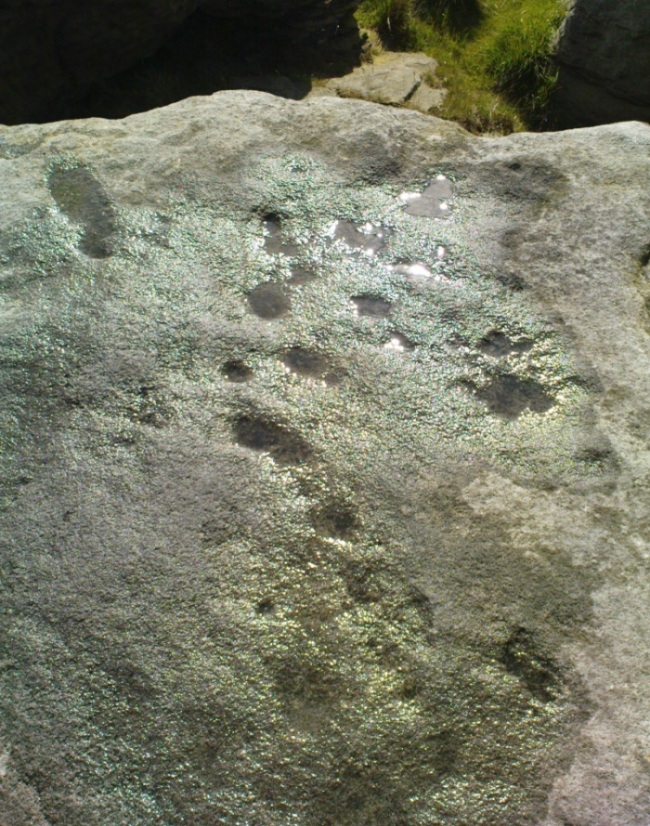
“the one forming the floor area of the dolmen being a square-shaped boulder of diorite, having fifty cups, varying from three and a half inches to an inch in diameter, the outlines of which look as fresh as if chiselled a year or two ago.”
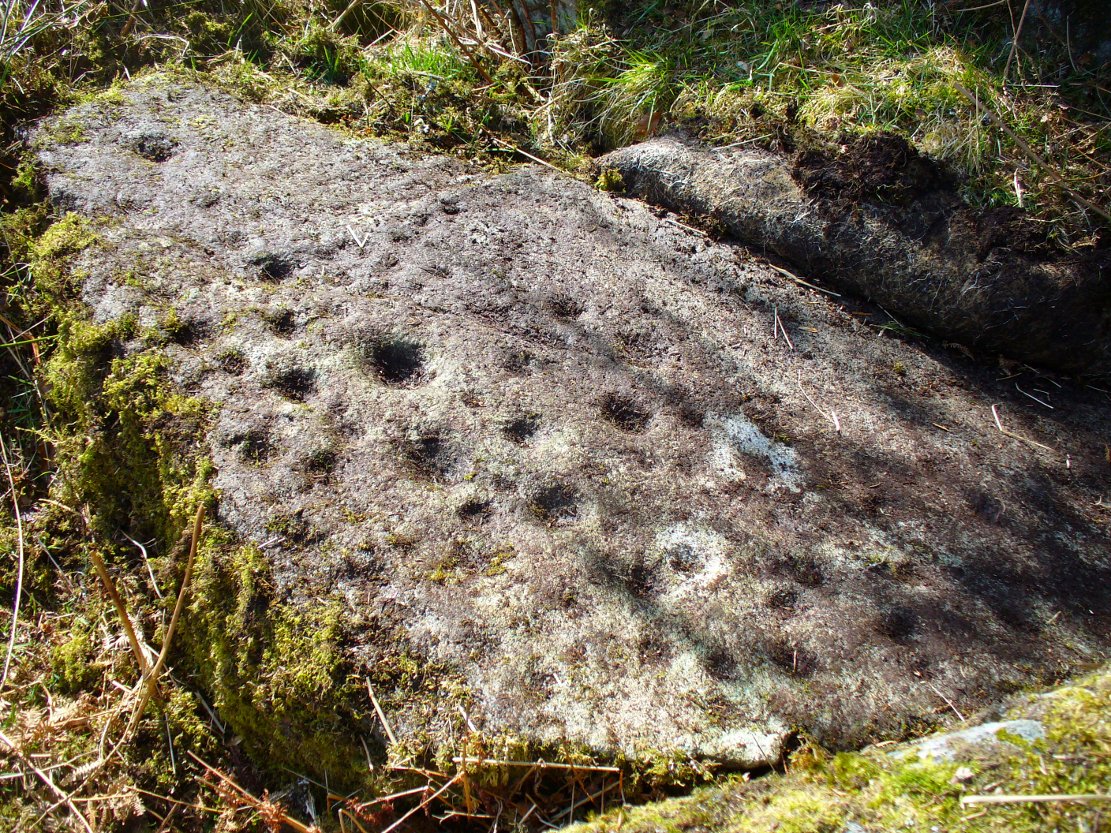

This indicates it had only recently been uncovered. There are lots of other archaeological remains scattered all round here, from different periods of history; but the other Druidsfield 1 and 3 carvings are found right next to each other, indicating this very spot was some site of neolithic or Bronze Age importance. An accurate excavation of the site and the adjacent Druids Circle would be worthwhile. I counted at least 44 cups on this rock when we visited last week, many of which are still quite clear.
The most recent Royal Commission (1979) briefing of the stone added nothing of relevance. They listed the site but it seems they never visited the place.
The portable bullaun-like deep-cut rock known as the Druid’s Stone is kept in private grounds nearby. When members of Scottish heritage came to visit an adjacent site a few years ago, the lady of the house told how they walked right past it without giving it any notice. “They didn’t even see it under their noses,” she said. Nowt new there!
Folklore
The carvings here were said by one of the locals to have been part of a “druid’s circle, which we played in as children, and were always told had been a special place of the druids in ancient times.”
References:
- Coles, F.R., “Report on stone circles in Perthshire principally Strathearn,” in Proceedings of the Society of Antiquaries, Scotland, volume 45, 1911.
- Haggart, D., “Notice of the discovery of a stone cup and cup-marked stones at Lochearnhead,” in Proceedings of the Society of Antiquaries, Scotland, volume 22, 1888.
- Royal Commission on the Ancient & Historical Monuments of Scotland, Archaeological Sites and Monuments of Stirling District, Central Region, Society of Antiquaries of Scotland 1979.
Acknowledgements – Huge thanks to Messr Paul Hornby for help and use of his photos.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian