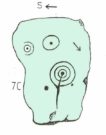
Cup-and-Ring Stone: OS Grid Reference – SE 08497 47097
Also Known as:
- Carving no.44 (Hedges)
- Carving no.212 (Boughey & Vickerman)
- Piper’s Stone

Follow the directions to reach our superb Swastika Stone from Ilkley, visible due to the iron railing that surround and protect the carving on the cliff edge. From here, keep walking west along the Millenium Way footpath, over the stile of the first wall, then the second wall—six in all—for ⅔-mile (1km), where you’ll see another small crag of rocks on your right, just yards from the footpath. You’re damn close!
Archaeology & History
When the great J. Romilly Allen (1882) visited the Ilkley petroglyphs in 1878, the Piper Stone was one that he wandered over to see—and he had this to say of it:
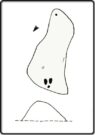
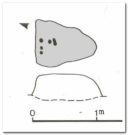
“At the edge of Piper’s Crag is a horizontal rock-surface, and on a portion of it, measuring 5ft by 7ft, are carved a series of fifteen cups varying in diameter from 2 to 3 ins. Of these, one is surrounded by a single ring, four by a double ring, and one by a triple ring.”
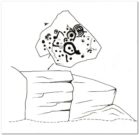

This type of description, whilst accurate on the whole, rarely does justice to the carving. It was echoed more than 100 years later in John Hedges’ (1986) survey, when he described the large rock jutting out to possess merely, “a complicated design of cups, rings and grooves.” When Boughey & Vickerman (2003) did their follow-up survey, they added nothing more.
In an attempt to give some sort of meaning to the carving (and many others), the late great Eric Cowling (1940; 1946) placed it within Henri Breuil’s (1934) classification system, which assigns all carvings different degrees of complexity and form, from Classes 1-4. The Piper Stone entered Breuil’s Class 3A, being one “with deeply cut and smoothed down grooves.” Whilst this may sound good on the surface, in truth such classifications are utterly meaningless outside of the tables and graphs of statisticians and the boring. They give the appearance of quantitative research, but they have as much bearing on the nature of the carvings as an energy dowser healing the place with crystals.


In the flesh, in the real world—so to speak—from the Piper Stone we are looking, not just at the carving, but its place in the landscape: an ingredient that more and more emerging archaeologists are recognizing has a synergistic relationship with some petroglyphs. And here we have an impressive landscape that reaches out ahead of us for many miles. We look primarily to the north: the Land of the Dead in many traditional northern cultures. But our panorama here is 180º, with east and west horizons having the potential for measuring equinoctial periods in the cycle of the year. But in truth this is sheer speculation.
It’s a worthwhile carving to see, both for its views and its excess of non-linearity. In its form, Rorscharch impressions of early humans emerge; the usual solar and lunar symbols can be seen; star systems seem apparent; maps or settlement ground-plans could be there. We know that somewhere within it is the animistic ‘spirit’ of the rock itself, but the forms it exalts are, once again, all but lost on us modern folk…
References:
- Allen, J. Romilly, “Notice of Sculptured Rocks near Ilkley,” in Journal of the British Archaeological Association, volume 38, 1882.
- Allen, J. Romilly, “Cup and Ring Sculptures on Ilkley Moor,” in The Reliquary and Illustrated Archaeologist, volume 2, 1896.
- Anonymous, Walks around Cup and Ring Stones, TIC: Ilkley n.d. (c.1990).
- Baildon, W. Paley, “Cup and Ring Carvings: Some Remarks on their Classification and a New Suggestion as to their Origin and Meaning,” in Archaeologia, volume 61, 1909.
- Bennett, Paul, “Cup-and-Ring Art”, in Towards 2012, volume 4, 1998.
- Bennett, Paul, The Old Stones of Elmet, Capall Bann: Milverton 2001.
- Boughey, Keith & Vickerman, E.A., Prehistoric Rock Art of the West Riding, WYAS: Wakefield 2003.
- Breuil, Henri, “Presidential Address for 1934,” in Proceedings Prehistoric Society East Anglia, 7:3, 1934.
- Collyer, Robert & Turner, J.H., Ilkley: Ancient and Modern, William Walker: Otley 1885.
- Cowling, E.T., ‘A Classification of West Yorkshire Cup and Ring Stones,’ in Yorkshire Archaeological Journal 1940.
- Cowling, E.T., Rombald’s Way: A Prehistory of Mid-Wharfedale, William Walker: Otley 1946.
- Hedges, John (ed.), The Carved Rocks on Rombalds Moor, WYMCC: Wakefield 1986.
Acknowledgements: Huge thanks to Josh Millgate and James Elkington for use of their photos in this site profile. Cheers guys. 🙂
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian