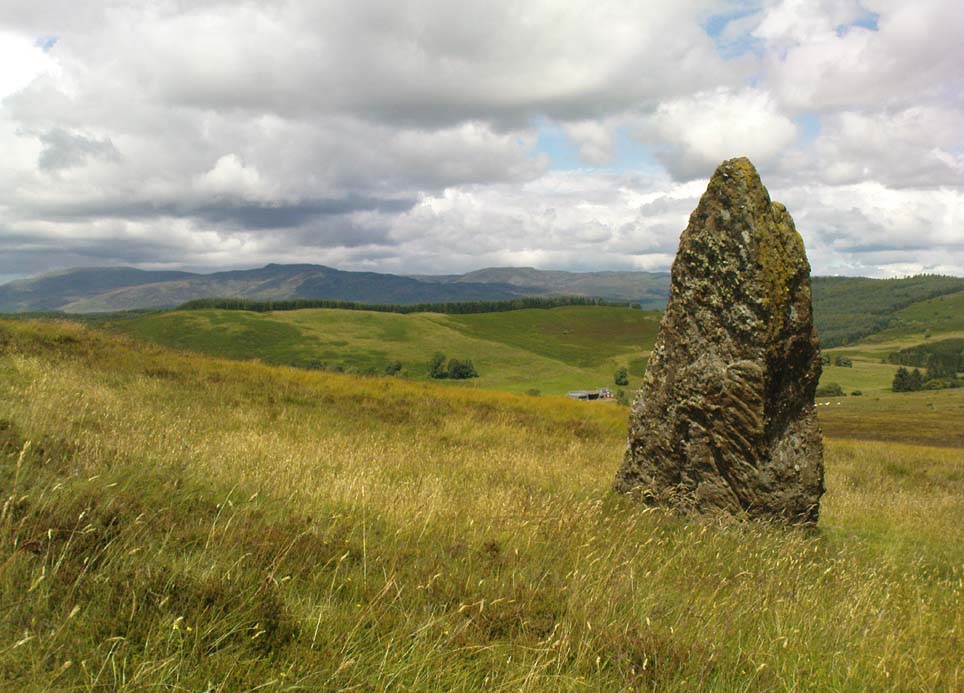
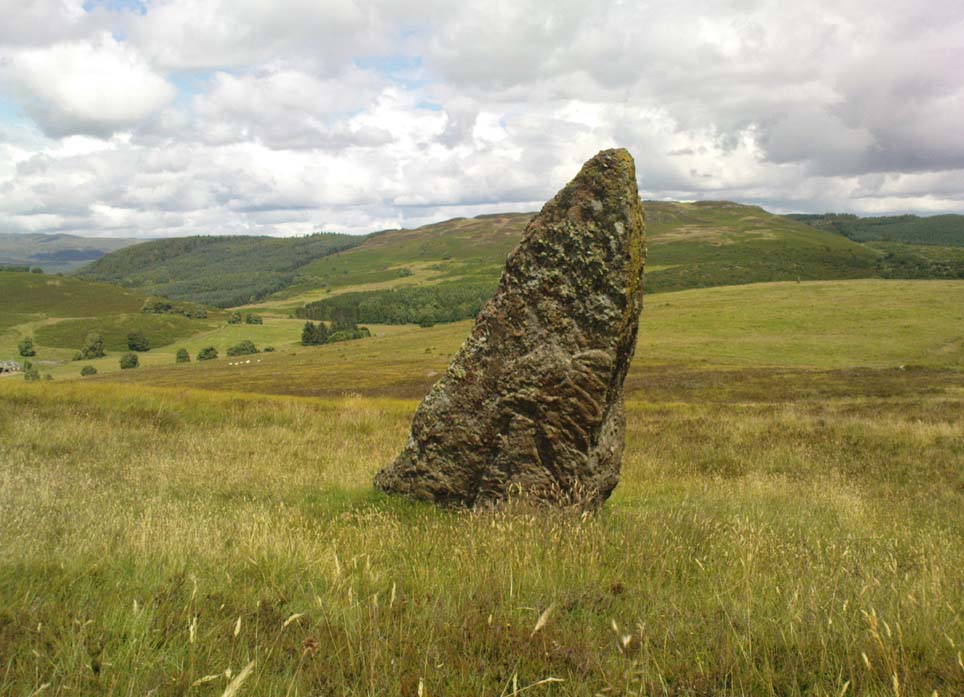
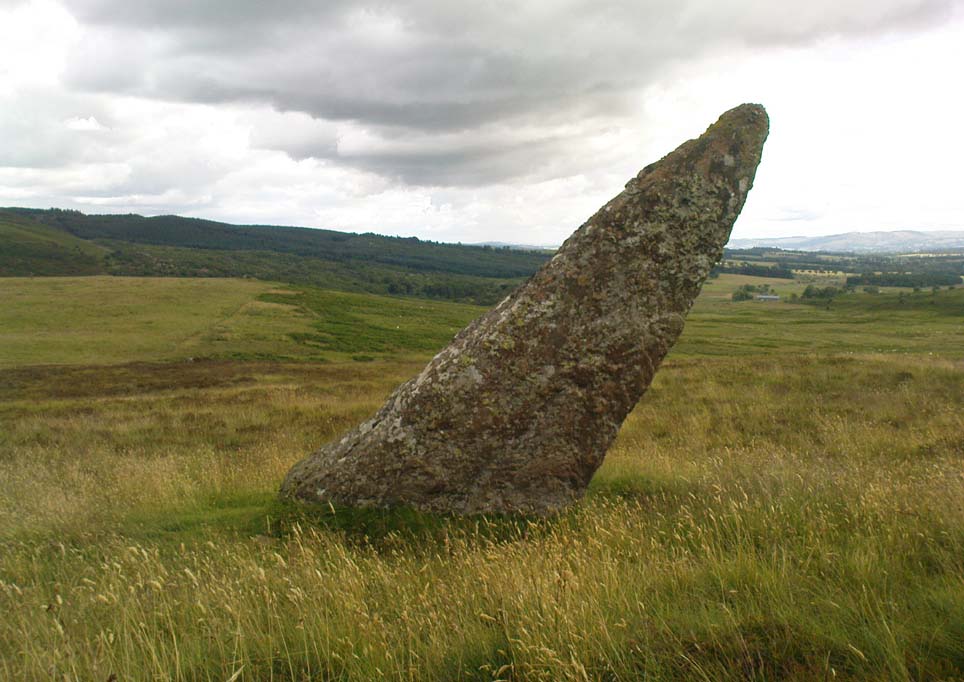
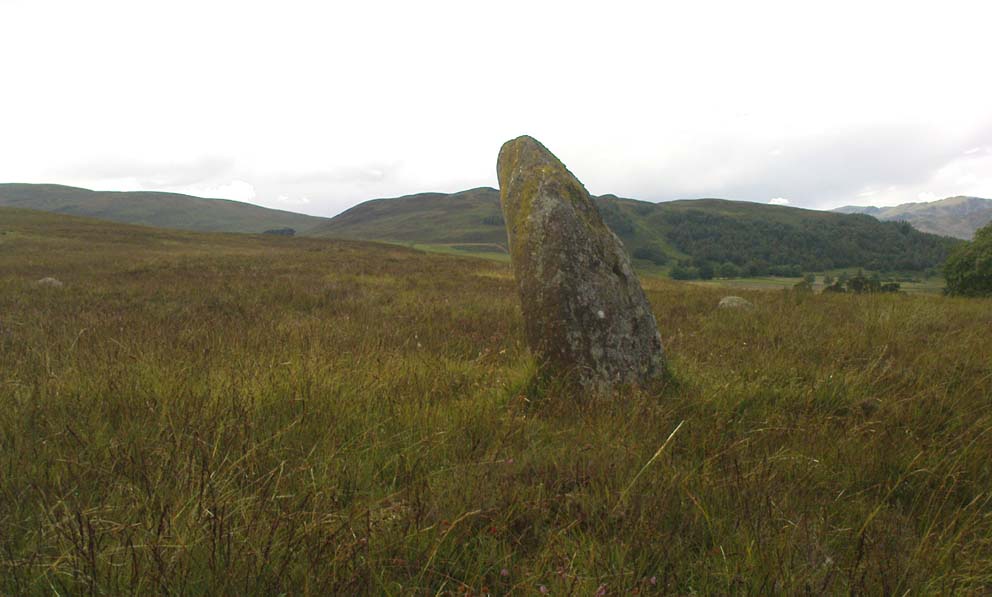
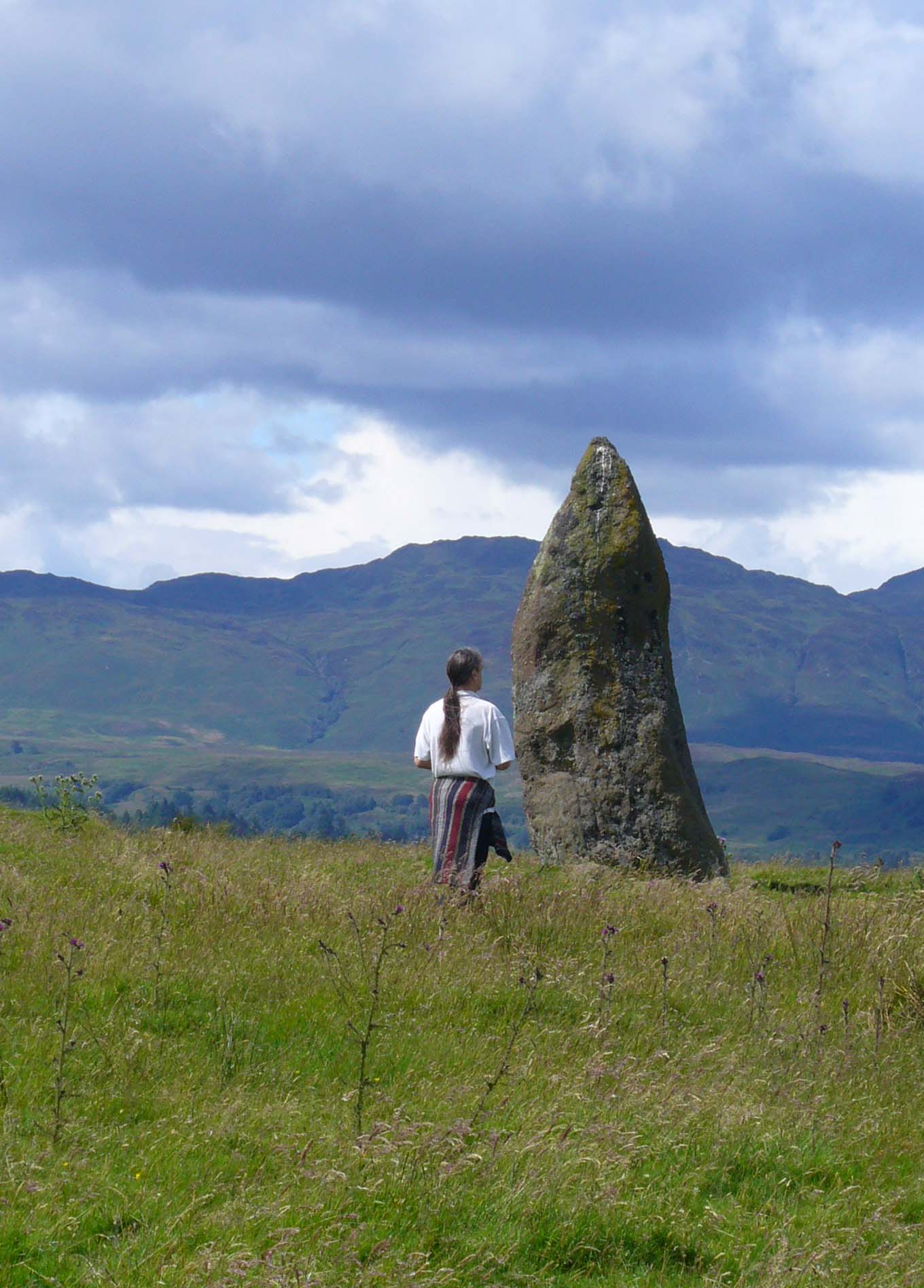
Stone Circle: OS Grid Reference – NN 78030 21266

Also Known as:
- Canmore ID 24857
- The Court Knoll
- Dalginross
- Dunmhoid
- Judgement Mound
- Muirend
- Roundel
From the main road running through lovely Comrie, take the south B827 road over the old river bridge. Go dead straight for several hundred yards until the road bends right; but take the left turn here. 100 yards or so along note the trees on your right, and the road begins to swerve round here. Just round the corner in the trees, the stones are in the clearing right by the roadside. You can’t miss them! (if you hit the graveyard, you’ve gone past them)
Archaeology & History
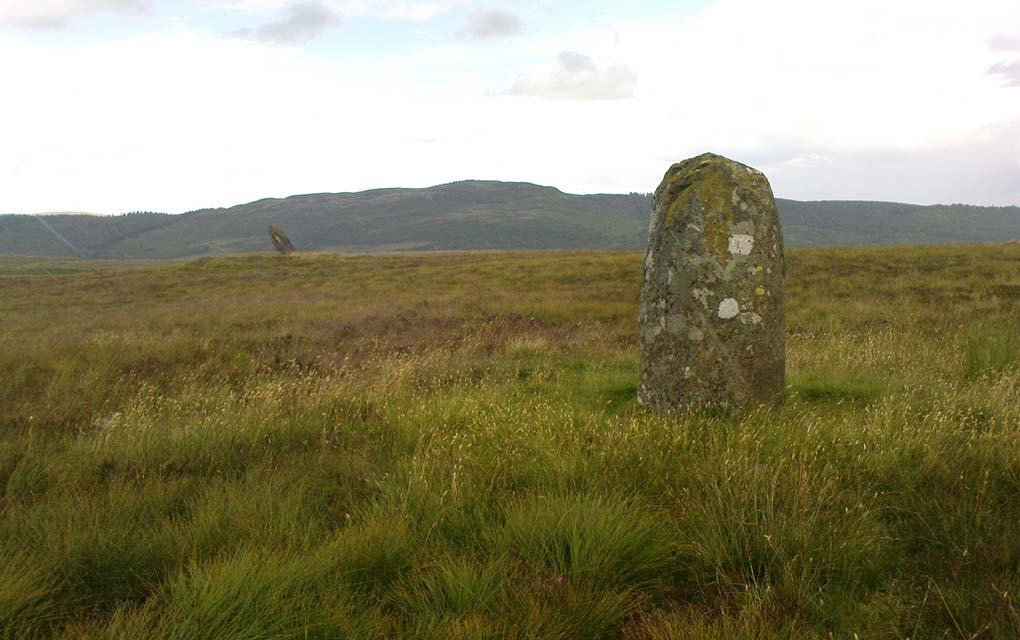
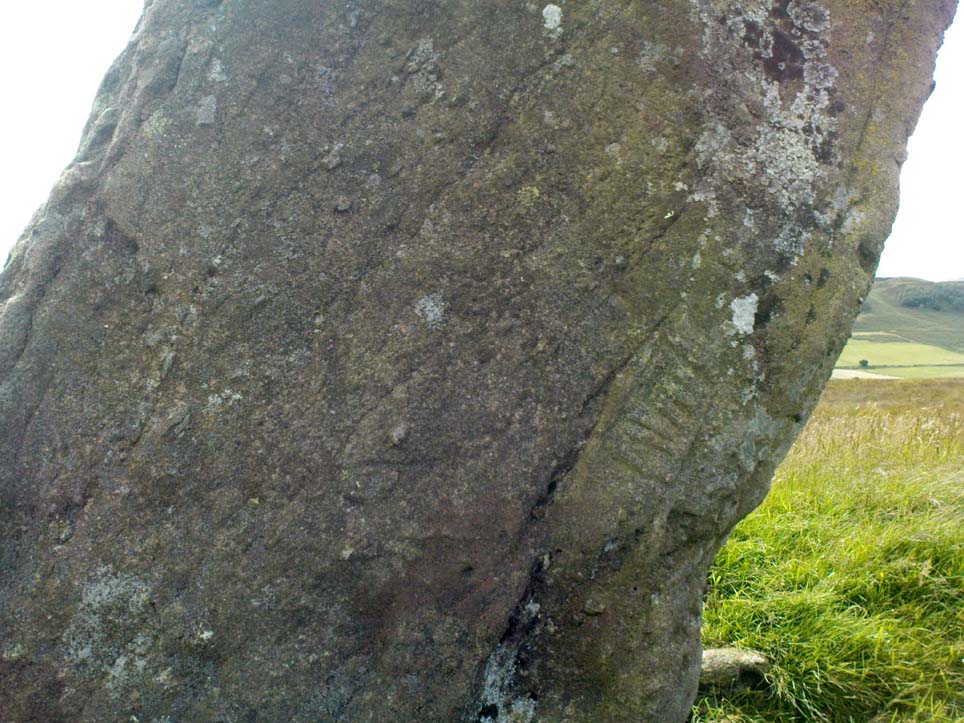
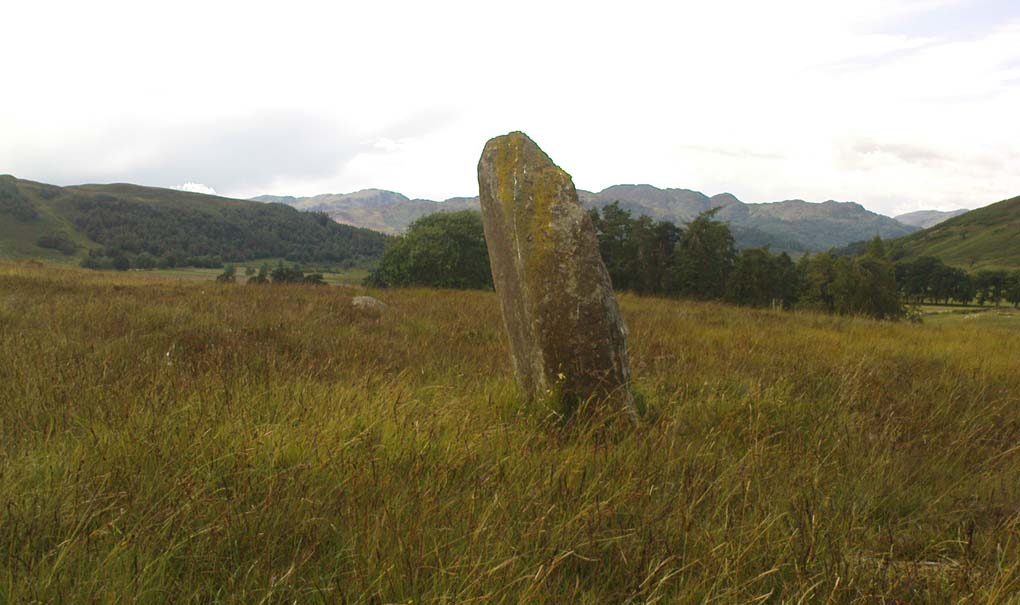
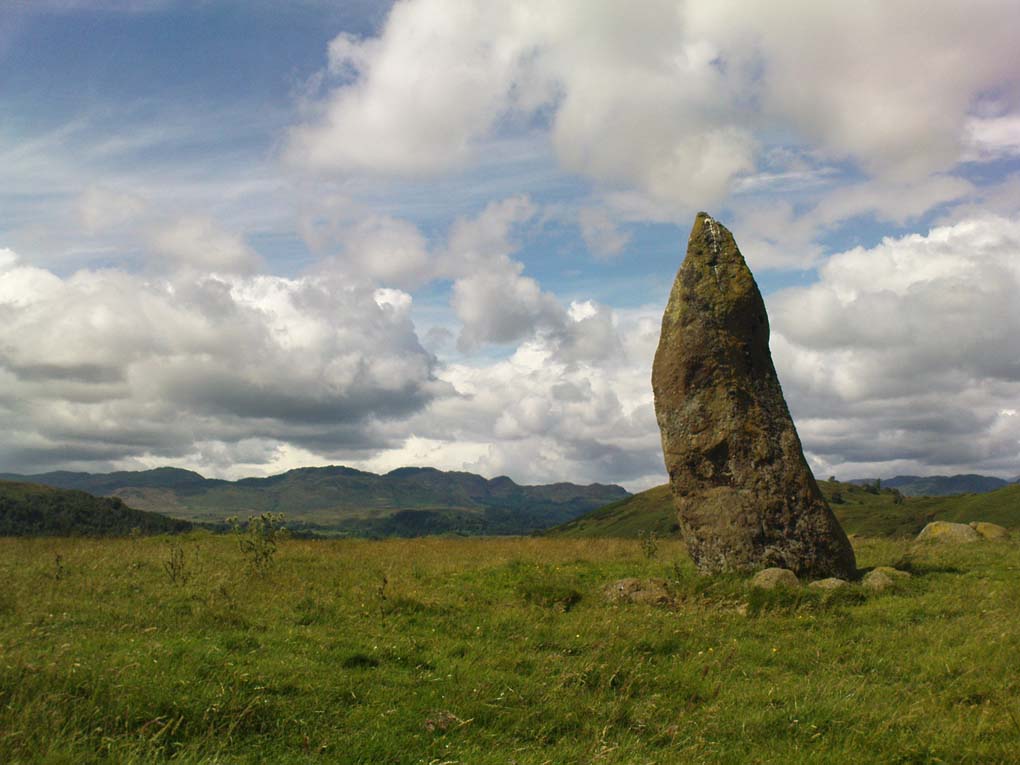
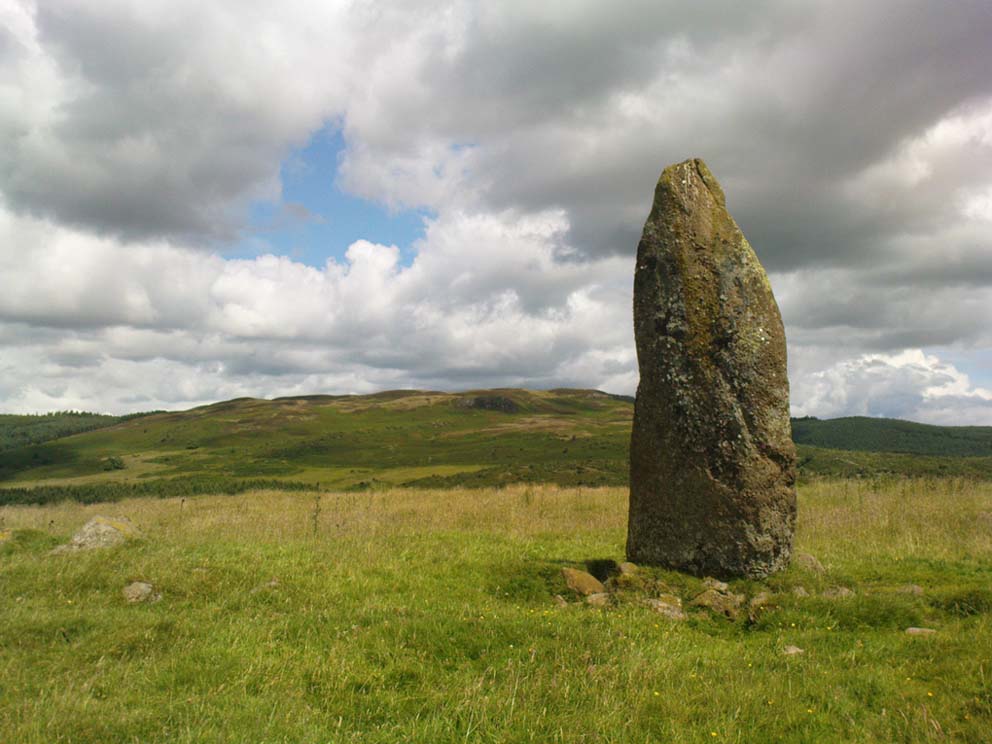
This is a truly lovely, almost warming enclosed megalithic site—albeit damaged by the ruin of centuries; but on the occasions I’ve been here it feels quite nurturing and elicits a quite natural meditative state. Whether or not this is due to the surround of trees, or the natural electromagnetic field, or just me, I dunno….
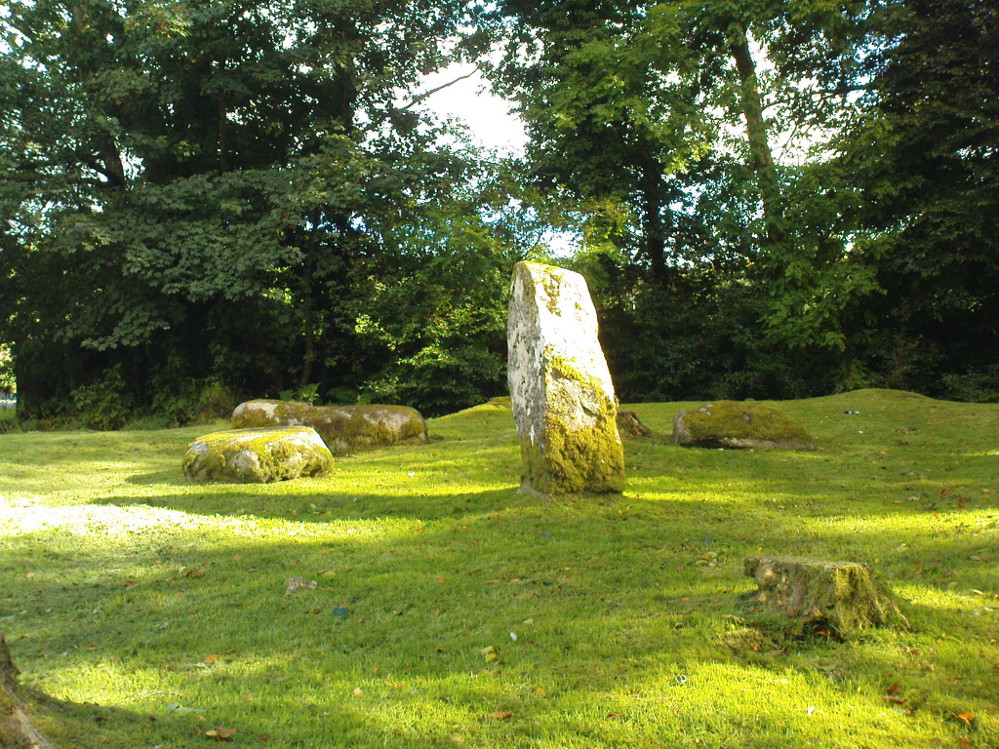

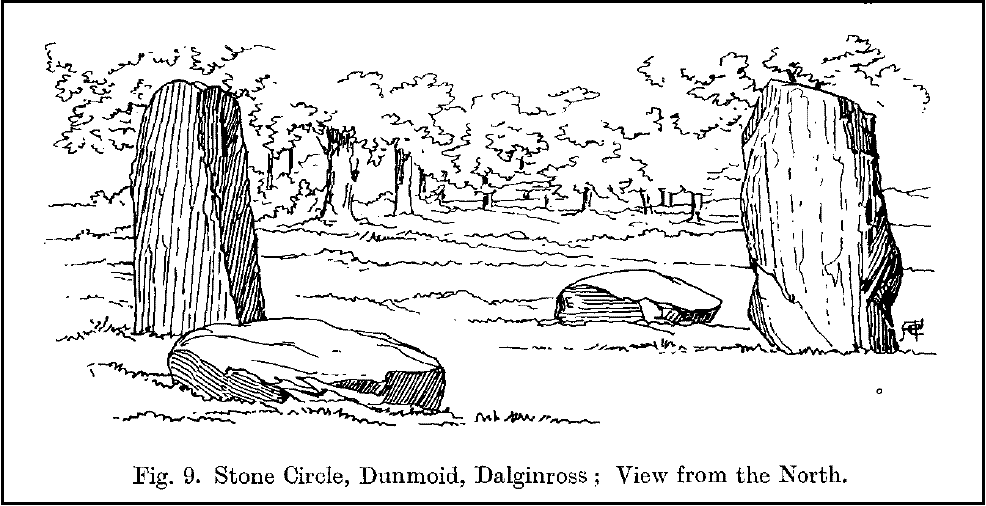
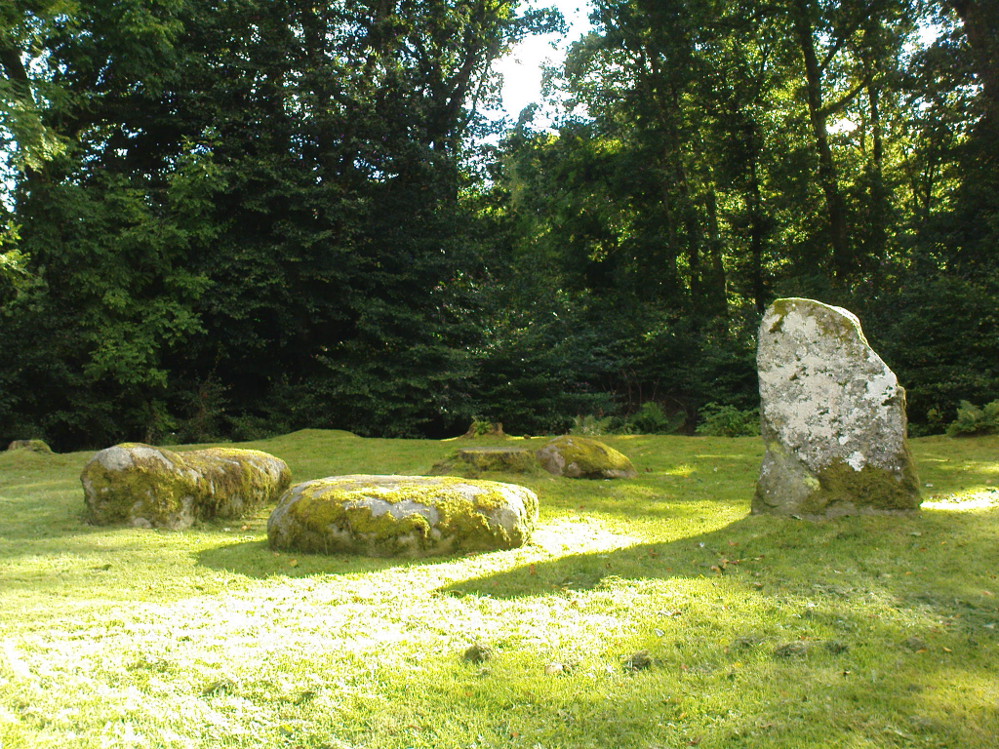
The ‘circle’ is constructed upon a flat rounded section of ground, surrounded by a ditch on two-thirds of its edges, very reminiscent of a typical henge monument—but there is no mention of this in modern surveys. One of the earliest accounts of Dunmoid was written by John MacPherson (1896) who gave us as much of the known history of the site as is still known by any modern academic. He wrote:
“At the west side of the new cemetery, close to the public road, there is a curious round knoll, which at one time must have been used as a place for the burial of the dead. The attention of the writer of this was drawn to it about twenty years ago. There were three large slabs of stone lying upon the ground, which apparently had been at some former period placed erect by some loving hands to mark the last resting-place of some departed friend or hero. By the aid of some of the Comrie masons the stones were placed in a standing position. Curious to know what lay beneath the surface, we dug up the earth in front of the largest slab, and came upon a stone cist placed north and south, 7 inches long, 1 foot 8 inches broad, and 1 foot 3 inches deep. The only remains discovered was a thigh-bone, but whether it at one time formed a part of the leg of a Celt, a Roman, or a Saxon we could not tell. An old man who then lived in the village of Comrie told us that in his young days the same mound was dug up, when an urn filled with ashes was discovered. This, perhaps, would indicate that it formed a place of burial for Romans rather than for Caledonians. The spot is called Dunmoid, or ‘hill of judgment.'”
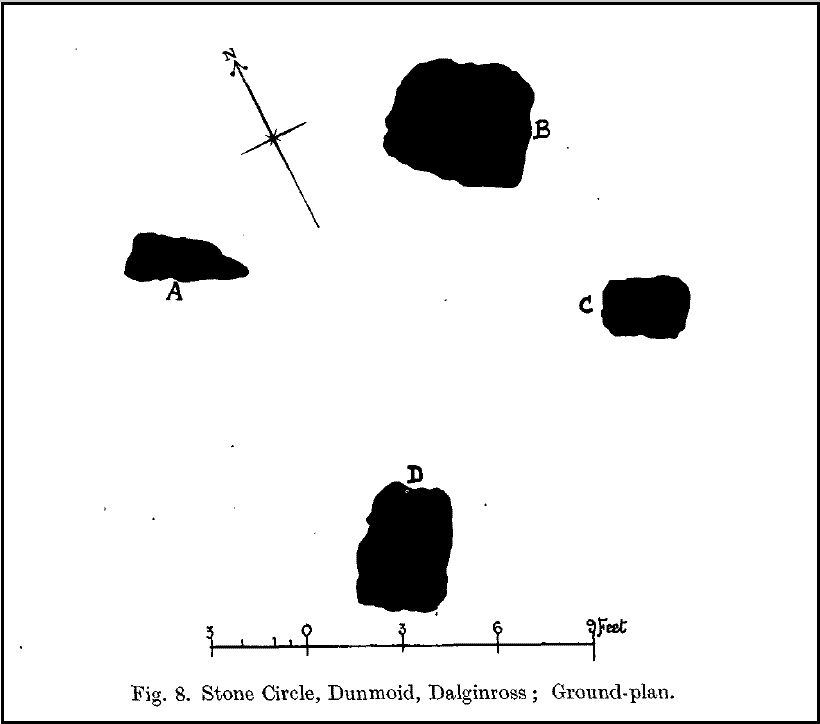
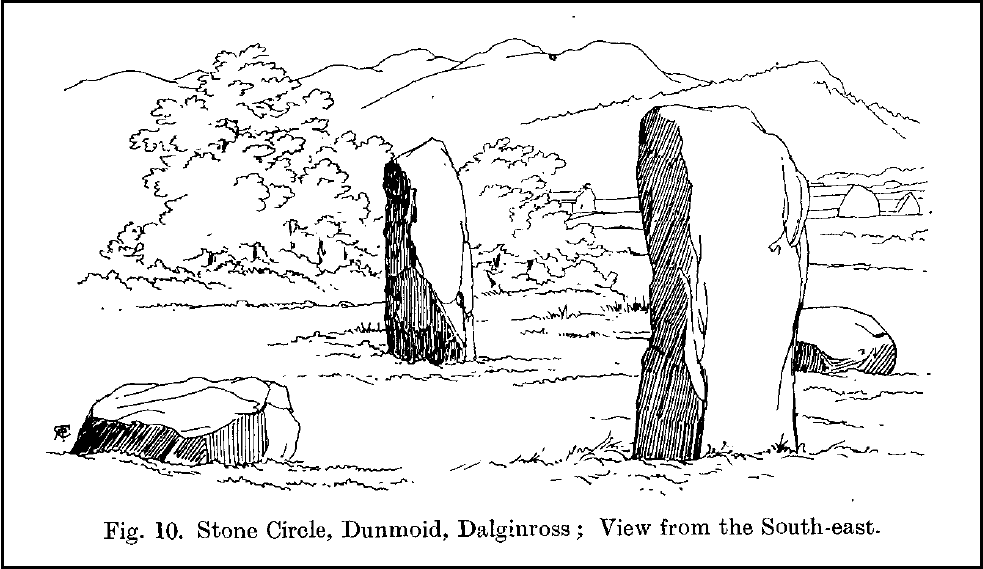
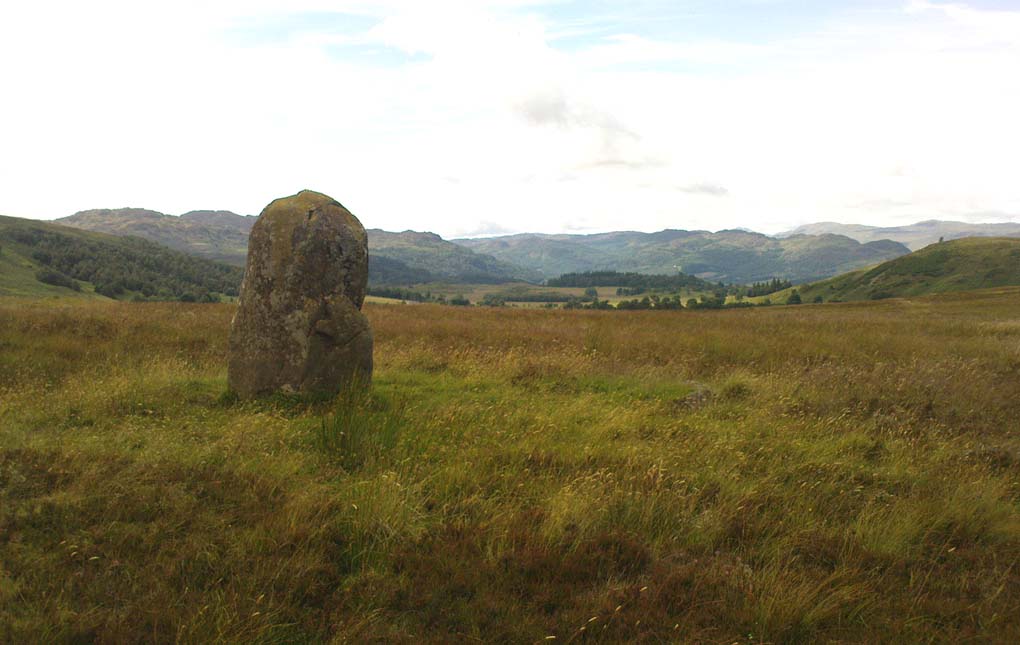
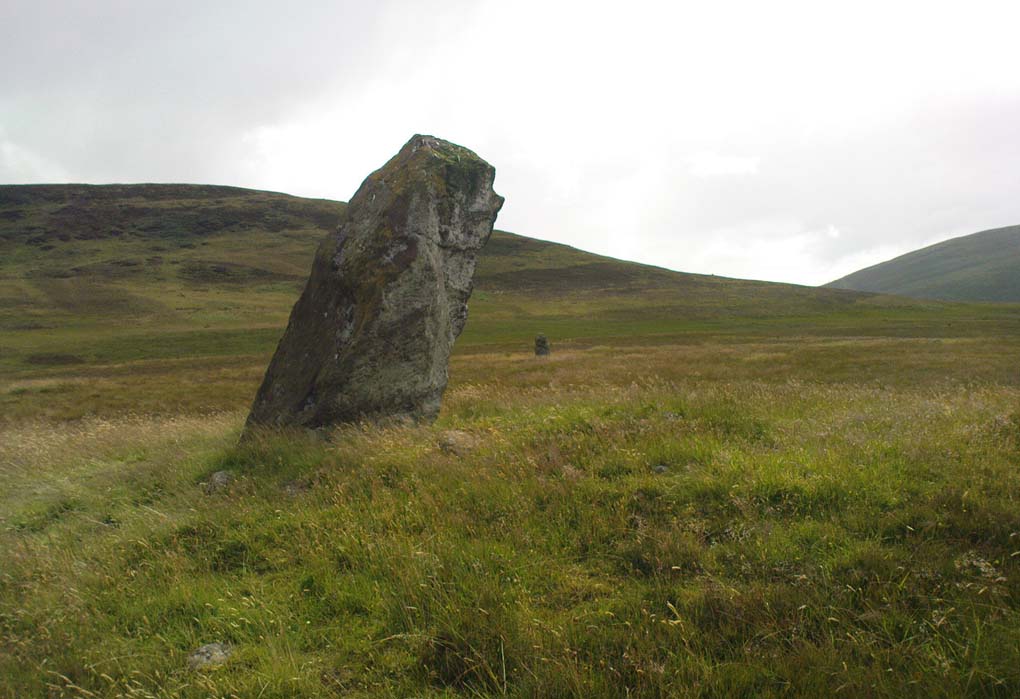
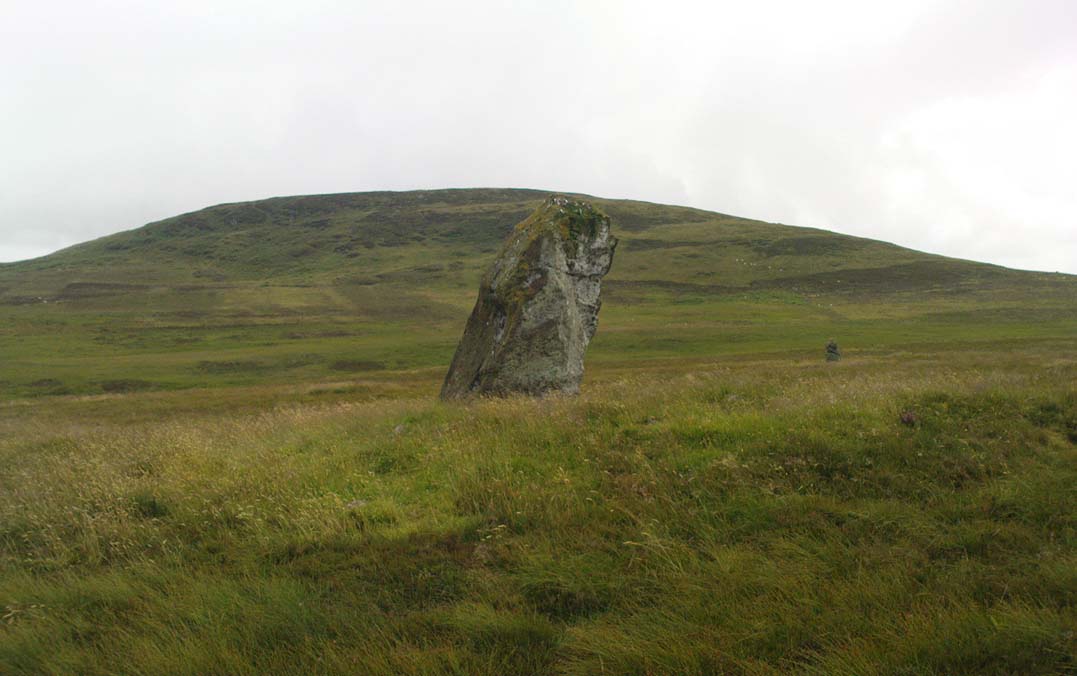
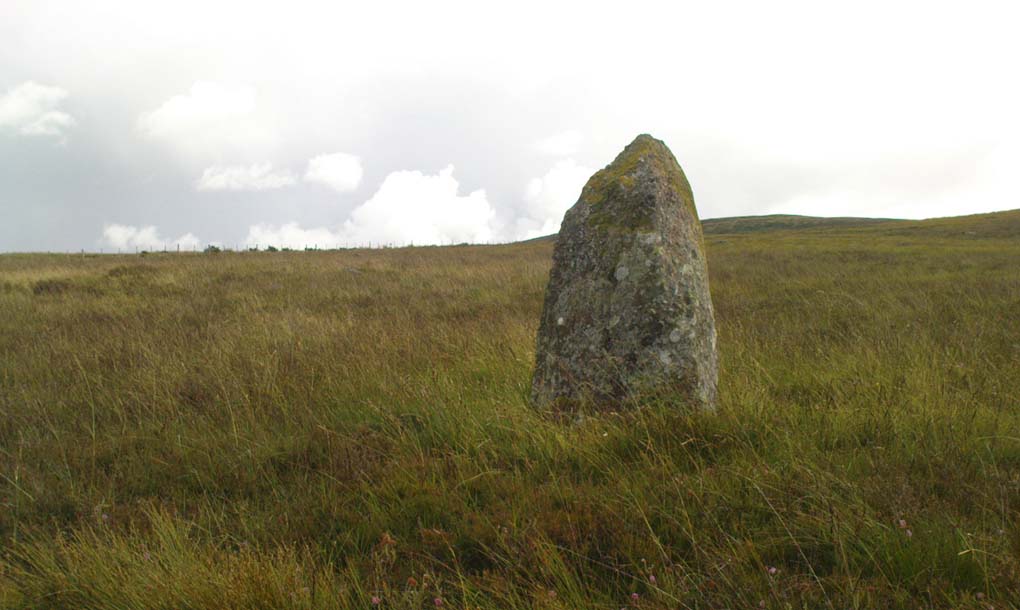
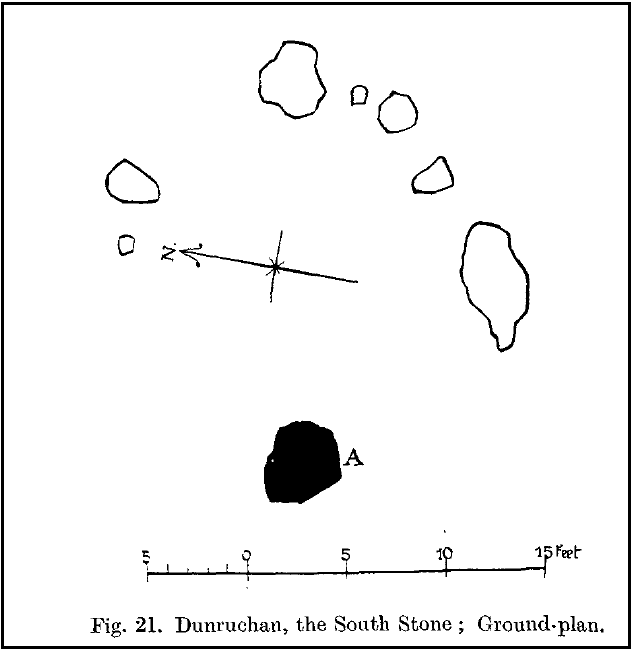
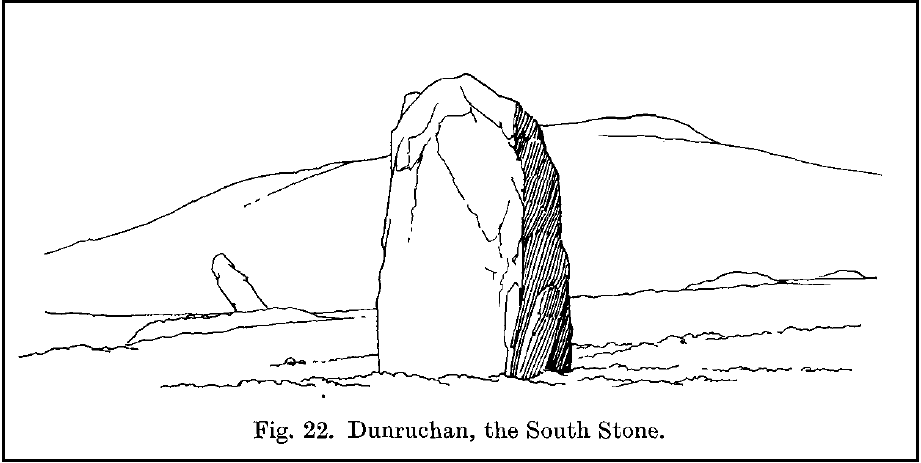
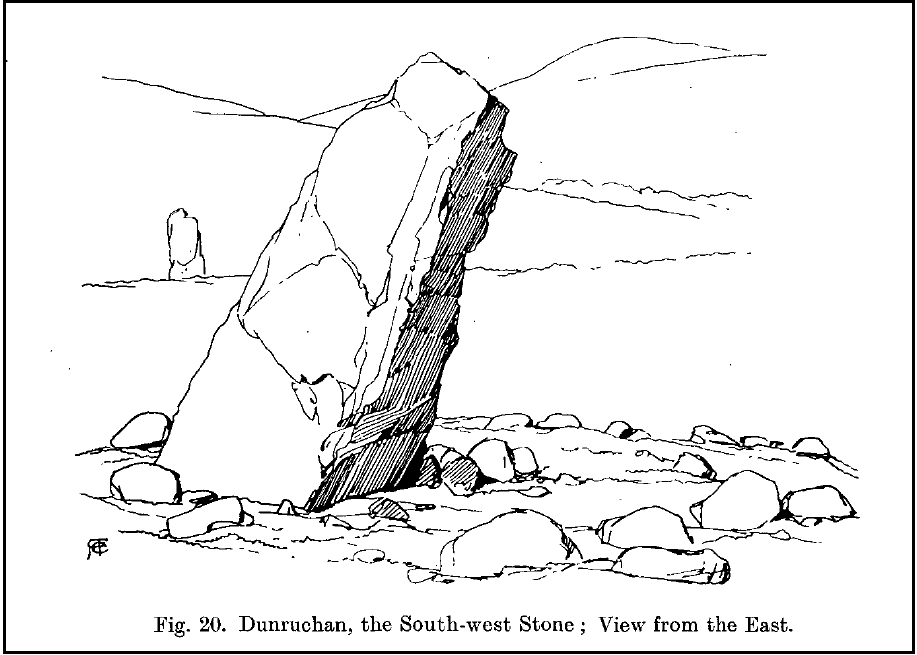
The circle gained the attention of the prolific Fred Coles (1911) in his Perthshire surveys, whose drawings and measurements are still repeated in the modern textbooks more than a century later. When he visited the site, two of the stones were still upright, but today only one still stands. In Aubrey Burl’s (1988) survey on ‘four-poster’ stone circles, he reiterated Coles’ words, telling:
“Originally four stone stood at the corners of a rectangle on a mound some 75ft (23m) across and 2ft (60cm) high. Coles’ plan showed the NW stone standing 5ft 4ins (1.6m) high and the SE, opposite, 5ft 2ins (1.6m), with the thick NW stone prostrate, 4ft 6ins (1.4m) long, with the more slender SW pillar also supine and 4ft (1.2m) long. The longer SE and NW sides of the oblong were roughly 9ft 6ins (2.9m) long and the others 9ft (2.7m) in length. The circle on which the stones had been placed had a diameter 13ft 2ins (4m), of which the Megalithic Yard is not an integer.”
The circle is included in Andrew Finlayson’s (2010) modern survey of the region.
References:
- Burl, Aubrey, Four Posters: Bronze Age Stone Circles of Western Europe, BAR 195: Oxford 1988.
- Finlayson, Andrew, The Stones of Strathearn, One Tree Island: Comrie 2010.
- Hunter, John (Ed.), Chronicles of Strathearn, David Philips: Crieff 1896.
- Hutchison, A.F., “The Standing Stones of Stirling District,” in The Stirling Antiquary, volume 1, 1893.
- MacPherson, John, “At the Head of Strathearn,” in Chronicles of Strathearn, Crieff 1896.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian
The map could not be loaded. Please contact the site owner.