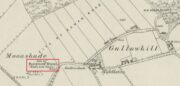
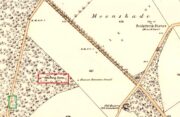
Stone Circle (destroyed): OS Grid Reference – NO 1730 3515
Also Known as:
- Canmore ID 28503

Travelling north from Perth on the A94, take the left hand turn to Strelitz as you go into Burrelton, and follow that road for two miles, and park up about 300 yards past the turning to Gallowhill. The circle stood at the far end (south-east) of the field on your left. Keep the distant gap in the hills in sight and the probable site of the circle is in a dip in the land in front of the ditch.
History & Archaeology
The circle had been destroyed by the middle of the nineteenth century, but was remembered by locals who gave this description to the Ordnance Survey bods:
‘The authorities quoted says that this is the site of a number of standing stones, they formed a circle, and one stood in the centre and according to tradition they were the remains of a Druidical Temple.’
In 1969 an Ordnance Survey archaeologist wrote:
‘There is no trace of this circle, the site being in a level arable field. Immediately to the SE in a ditch running parallel to the fence are about a dozen large boulders cleared from the field, possibly from the site of the circle.’
The boulders have now gone but there are some broken stones on the banks of the drainage ditch which may or may not be the sorry remains of some of the stones. There is a depression in the field just in front of the ditch which is the likely site of the circle based on the position shown on the 1867 map.

What is interesting is the gap in the horizon facing south east from the site of the circle. On the left of the gap is Black Hill, and on the right Dunsinane Hill of Macbeth fame. My reading of the angle from the probable site of the circle to the gap using a hand held compass was around 135° to 140°, and that may indicate a midwinter sunrise alignment from the lost circle. Something to be checked out when winter comes.
And there is a legend of a giant who leaped from Black Hill to Dunsinane who also tossed a boulder which stands between the two hills – whether this legend has anything to do with the possible solstitial sighting line from East Whitehill is an intriguing question.
Reference:
Acknowledgements: Big thanks for use of the 1st edition OS-map in this site profile, Reproduced with the kind permission of the National Library of Scotland.
To be continued…
© Paul T Hornby 2021
The map could not be loaded. Please contact the site owner.