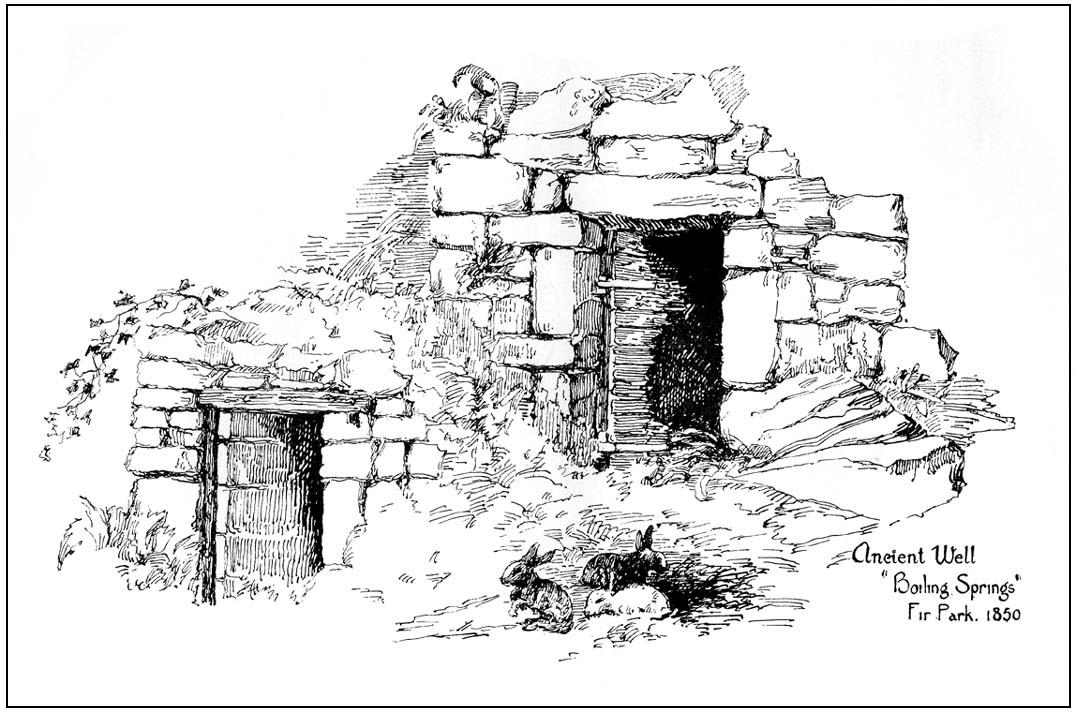
Holy Well: OS Grid Reference – NS 7781 9251
Also Known as:
- Bruce’s Well
- Canmore ID 46248
- Christ’s Well
Along the Main Street in Cambusbarron, walk down Mill Hill for a hundred yards or so, to The Brae. Just here, a paved footpath goes to the right. Walk along here for about 120 yards until you reach a small footbridge crossing the stream. On the other side of this bridge you’ll notice a notice board and a sign. You’re here!
Archaeology & History
Today, all that remains of this spring of water that was sacred in the animistic pantheon of our ancestors, is a notice board and an epitaph, reading “Site of the Chapelwell (or Christ’s Well)”; but in times past this simple spring of water was a place of considerable activity. Not only did the local people of Cambusbarron get their water supply from this (and others close to the Main Street), but it was also a place of ritual and reverence. We know this from early church accounts—most of which were complaints about the traditions performed by local people, in contravention to the christian cult.
The best account of the site is found in J.S. Fleming’s (1898) work, in which we find it also referred to as the ‘Christ’s Well’. This attribution adds further mystery and controversy regarding another Christ’s Well a few miles away at Blair Drummond, whose position by the academic community is questioned by local historians. Be that as it may, Mr Fleming’s words on this Chapel Well are worth reading. He wrote:
“the most famous of all the Stirling Holy Wells, was, early in this century and is still, known by the name of ‘Chapel Well,’ and its water, up till a recent date, was used for domestic purposes by the villagers. It originally consisted of a square, stone-built, open well, with parapets, but its walls are now built up and roofed, and it has a door, now shut up, however, and the well closed by the sanitary authorities of the district. The well is situated on the brink of what we assume to be Glenmoray Burn, here crossed by a rustic wooden bridge in a part of the Chapel Croft garden, containing the alleged site of the chapel, from which it is distant a few feet. The stump of an ancient thorn is shown on the right hand of the sketch. The overflow of water empties itself into the adjoining burn. The site of this famous well has been so variously described as to almost challenge its identity, but the authorities examined, all, with one single exception, afternoted, virtually agree in its situation:
“1) Sutherland, about a hundred years ago, writes: “Not far from St. Thomas’ Well there is another, on the farm of Chapel Croft, called ‘Christ’s Well,’ of great repute, and visited by women, etc.”
“2) Dr. Rogers, later, after referring to the Chapel of Cambusbarron, says ”two of the three wells connected with the establishment still exist near its site by the margin of Glenmoray stream.”
“3) Another writer says: ‘”Christ’s Well,’ now called ‘ Chapel Well,’ is at bottom of a small dell called Glenmoray, immediately adjoining Cambusbarron, and there is a tradition that here the water was got for the religious services at the Battle of Bannockburn, one redeeming quality of the superstition which would consecrate its water.”
“4) A writer, over the initials “S.I.,” in the Stirling Observer of 27th September, 1866, says: “Within its Chapel King Robert the Bruce partook of the sacrament on the eve of the Sabbath preceding the Battle of Bannockburn, and its sacred font was the resort at Beltane of the superstitious of a former age, as may be seen from extracts from kirk session records.”
“These all agree that ‘Christ’s Well’ was situated not far from St. Thomas’ Well, on Chapel Croft; that it and other two wells existed some few years ago near the site of the Chapel, on the margin of Glenmoray stream, by the name of “Chapel Well”; ” is situated in a small dell called Glenmoray, and is immediately adjoining Cambusbarron; and that it retains, and is presently known by, no other name than the “Chapel Well.” Further, a small distillery, now removed, situated a few yards from the Chapel on this burn, taking its name from the glen and burn, was called Glenmoray Distillery…”
“However, a writer in the Stirling Observer of 7th September, 1871, in an article on “Touch Glen,” says that not far from the road leading to the three reservoirs on Touch Hills, two of the three Wells connected with the Chapel (which, he states, is 1000 yards distant from Gartur Lodge) still exist, and may be seen near the brink of a little burn which trickles from the miniature glen of Glenmoray, visible on the hillside just below the lowest reservoir. This burn is crossed by a small stone bridge on the main road, and is known as “Johnnie’s Burn.” These Holy Wells, including Chapel Well, would thus, according to this writer, be about a mile, if on “Johnnie’s Burn,” and if near the lower reservoir, on Touch Hill,’ fully a mile and a half from Chapel Croft and the Chapel…
“…The Church dealt severely with the devotees—principally women—who resorted to the virtues of “Christ’s Well,” as is shown by the session records, from which we make a few extracts: —
“July 12, 1610. — The quhilk day compeirit Grissal Glen and Marioun Gillaspie quha for ther superstitione in passing in pilgrimmage to ‘Christe’s Well’ as they confessit the last day ar ordeinit to mak publick repentance the next Sonday in lining claithis.”
” 1 June, 1630. — The quhilk day compeirit Elspet Aiken, spous to Anclro Cuyngham, tinckler; Jonet Harvie, William Huttoune, cutler; Margaret Mitchell, dochter to Alex Mitchell; Jonet Bennet, dochter to James Bennet, cuick; James Ewein, son of John Ewein, wobster, Margt. Wright, James Watsoune, who confessis passing in pilgrimmage to ‘Christe’s Well’ in Mai, and thairfoir they ar ordeaned to mak publik repentance the nixt Sabbat in thair awin habeit, under the paine of disobedience.”
” Lykway I, Mr. Patrik Bell, am ordeaned to desyre the breithren of the Presbyterie to appoint ane actuale minister for to preach upon Sonday nixt for to tak ordour with the said persounes above writen.” (Note — This offence seems a mere ploy of young people observing May morning, as is done at the present day on the first of May, and the responsibility “of asking” an “actual minister’s aid” to take “order” with the accused seems treating the offence too seriously.)
“6 October, 1631. — The quhilk day compeirit Jonet Norbell, in Cambusbarron, for going for water to help her sick son; and Jonet Main, in Cambusbarron, going to ‘Christe’s Well’ for water for help to her bairns; “and for another offence are ordained” to sair the pulpit on Sonday nixt in her ain habit to mak repentance.”
Mr Fleming seemed to think the traditions of Mayday a healthy thing and wrote well of local traditions, speaking of the healing virtues of the dew on May morning, used by people all over the country; also remembering a song that would be sung in honour of “the delightful custom of maying”:
I, been a rambling all this night,
And some time of this day ;
And now returning back again,
I brought you a garland gay.
Why don’t you do as we have done
The very first day of May ?
And from my parents I have come,
And would no longer stay.
The fact that Mr Fleming cites the Chapel Well to be known locally as the ‘Christ’s Well’ needs to be remembered when you visit a site of the same name 5 miles northwest of here at Blair Drummond. It was a place of considerable renown and much used by local people for a variety of indigenous rites and customs for many miles around. The ancient Scottish practices were still very much alive…
References:
- Fleming, J.S., Old Nooks of Stirling, Delineated and Described, Munro & Jamieson: Stirling 1898.
- MacKinlay, James M., Folklore of Scottish Lochs and Springs, William Hodge: Glasgow 1893.
- Morris, Ruth & Frank, Scottish Healing Wells, Alethea: Sandy 1982.
- Roger, Charles, A Week at Bridge of Allan, Adam & Charles Black: Edinburgh 1853.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian
The map could not be loaded. Please contact the site owner.