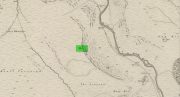
Cairn: OS Grid Reference – NO 1008 5695
Getting Here

From Kirkmichael village take the A94 road 2 miles south to the Balnabroich standing stone and another 100 yards past it, on the left (east) take the dirt-track uphill, following the directions to reach the Balnabroich hut circles. You’ll see the large prehistoric rock pile of the Grey Cairn on the near skyline just above the huts and roughly on the same level, 50 yards away to the south, you’ll see this scruffy lumpy dump of a cairn, all overgrown.
Archaeology & History

Amidst the veritable scatter of a thousand clearance cairns (yes, that’s the estimate), there are a few up here that had more funerary functions than the rest. This being one of them. When Allan Stewart (1795) wrote about them all in the Statistical Account, he couldn’t have missed this one—and yet he made no mention of it. We had to wait another seventy years before the outside world became aware of its existence. Then, along with “a band of between twenty and thirty workmen,” John Stuart (1865) set out to see what lay beneath the rocky pile. In truth, much more attention was given to the huge Gray Cairn close by (understandably so), but at least some attention was given here. Stuart described this cairn as,
“about 9 yards across, defined by large boulders, with a raised ridge around, and a cup in the centre. The raised ridges and centre were all formed of small stones and earth. A trench was cut through it from the southeast, which showed that in the centre, at a depth of 2 feet, a deposit had been made, of which the remains were charred wood and fragments of charred bone, with traces of blackish matter, which had filtered into the yellow subsoil, as in the case of the graves at Hartlaw.’ Many fragments of white quartz pebbles appeared near the centre, as in other cairns to the east.”
Indeed, at least one of the “cairns to the east” is made entirely of quartz stones! Since Mr Stuart’s dig into the tomb, it has widened out slightly as rummaging cattle and other damage has been inflicted, and the grasses have coloured the tomb with their life. Check it out when you’re up here!
References:
- MacLagan, Christian, The Hill Forts, Stone Circles and other Structural Remains of Ancient Scotland, Edmonston & Douglas: Edinburgh 1875.
- Ramsay, John S., Highways and Byways of Strathmore and the Northern Glens, Blairgowrie Advertiser 1927.
- Royal Commission on the Ancient & Historical Monuments of Scotland, North-East Perth: An Archaeological Landscape, HMSO: Edinburgh 1990.
- Stewart, Allan, “Parish of Kirkmichael,” in Statistical Account of Scotland – volume 15, 1795.
- Stuart, John, “Account of Excavations in Groups of Cairns, Stone Circles and Hut Circles on Balnabroch, Parish of Kirkmichael, Perthshire,” in Proceedings Society Antiquaries, Scotland, volume 6, 1865.
Acknowledgements: Huge thanks for use of the Ordnance Survey map in this site profile, reproduced with the kind permission of the National Library of Scotland.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian
The map could not be loaded. Please contact the site owner.