Stone Circle: OS Grid Reference – NN 99766 07093
Also Known as:
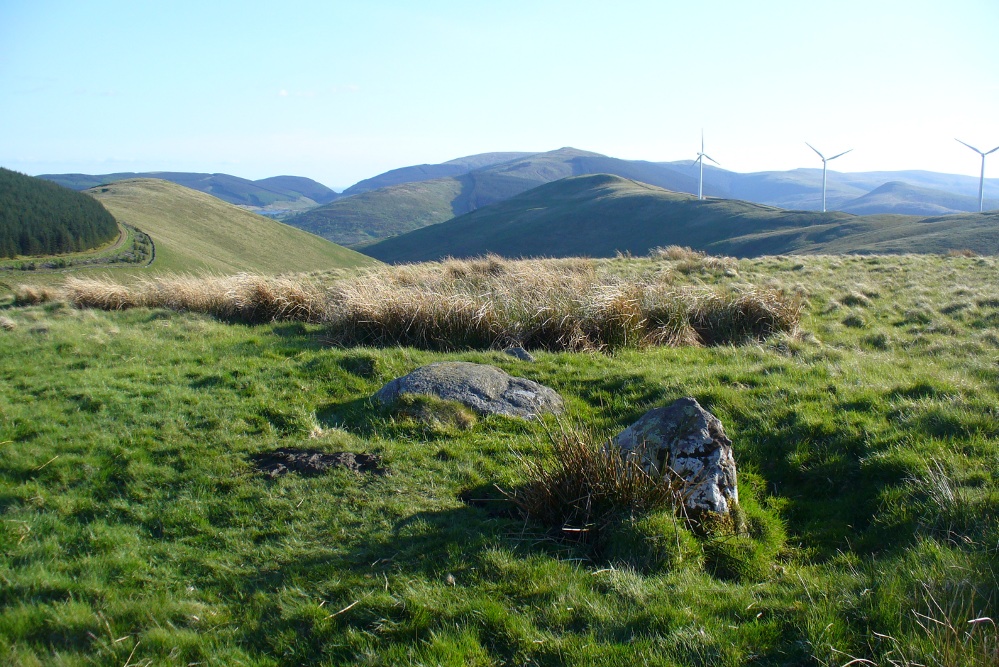

Takes a bitta finding this one. Best found by going along the gorgeous, little-known Dunning Glen in the eastern Ochils, till you reach Littlerig house. Cross the road from there and follow the line of the burn and forest till it veers sharp left. Keep along the fencing until the marshland levels out and streams fall away both east and west. From here, walk uphill until you reach level ground, then, looking down the Borland Glen, zigzag downhill for 100 yards. Keep your eyes peeled for stones emerging from the Juncus grasses.
Archaeology & History
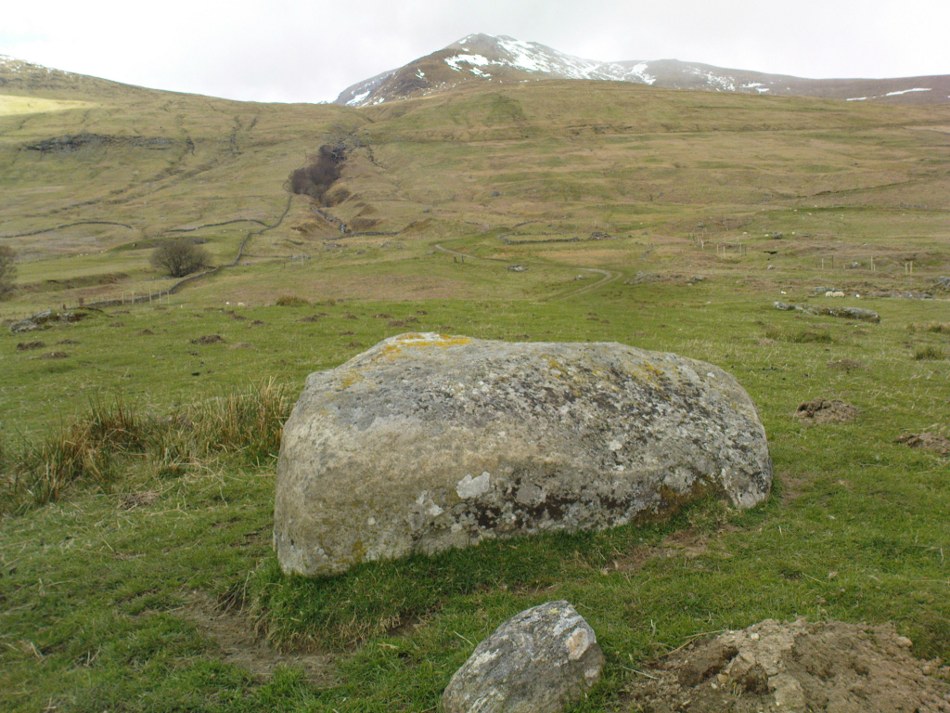
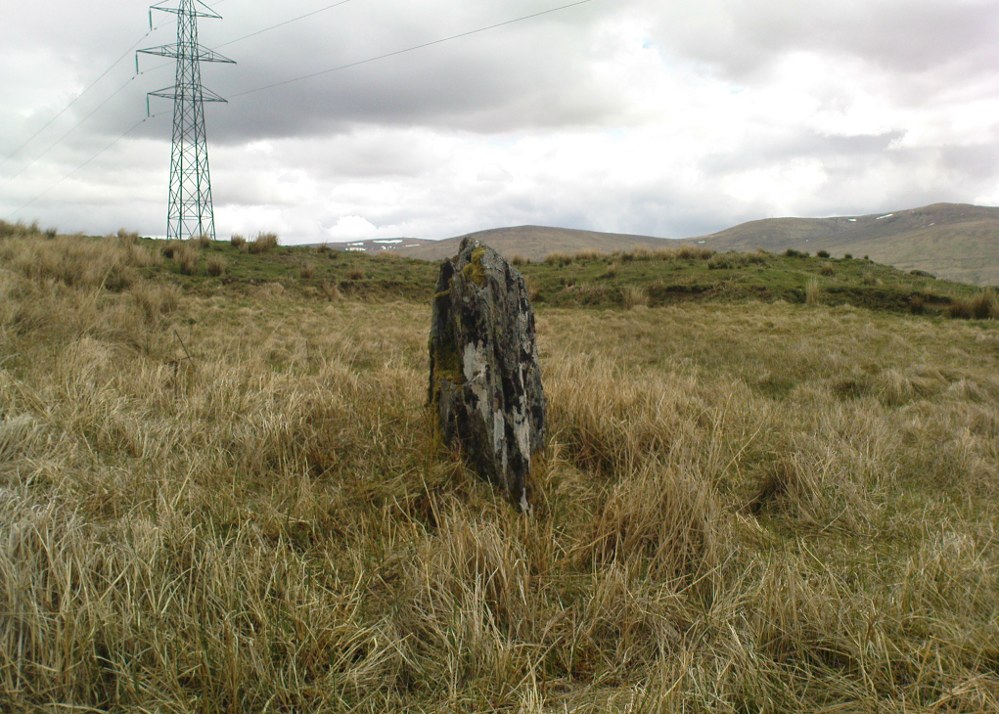
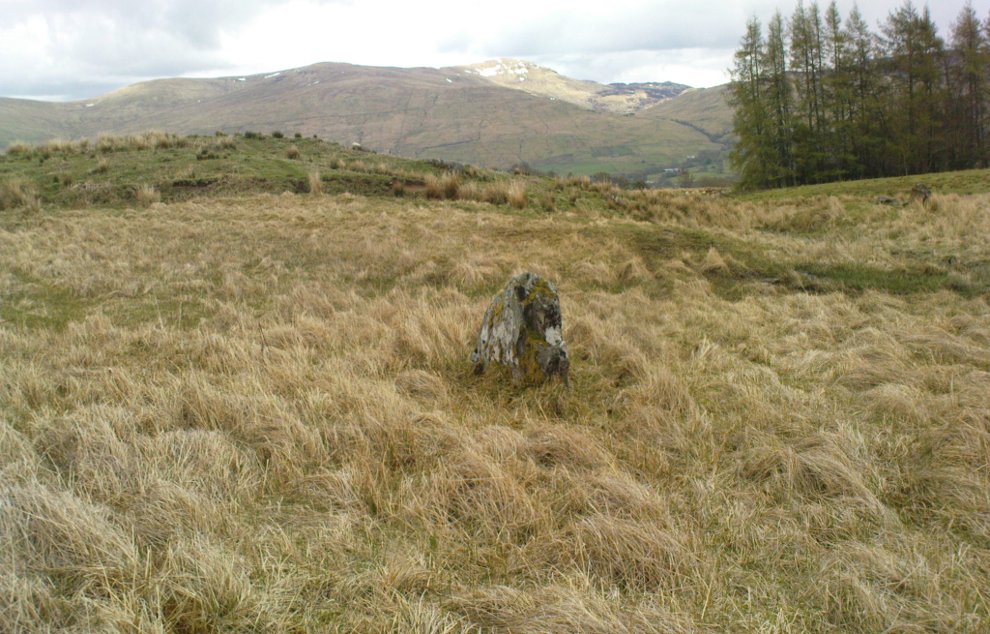
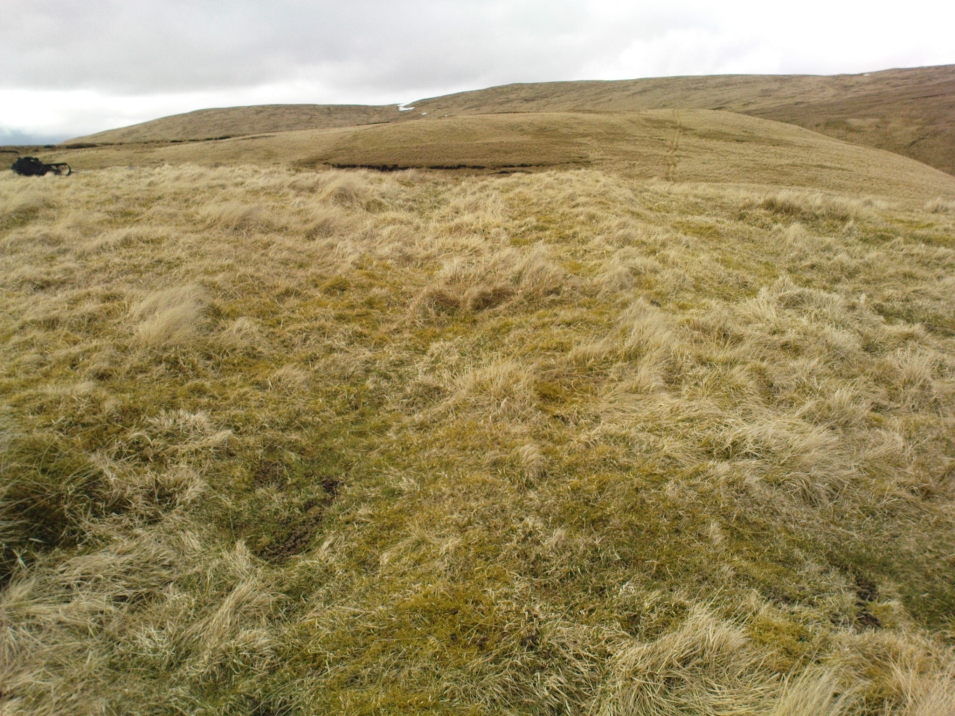
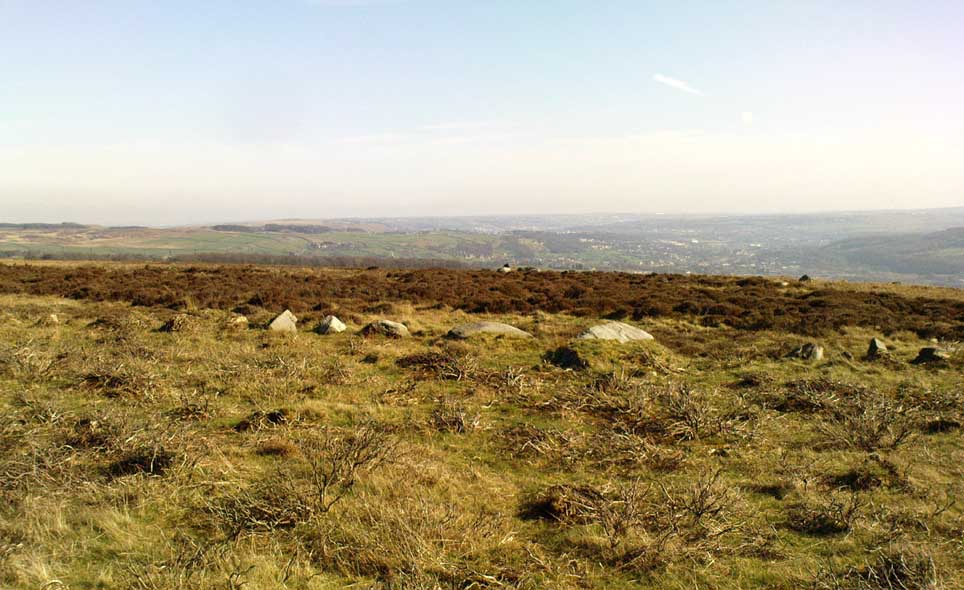
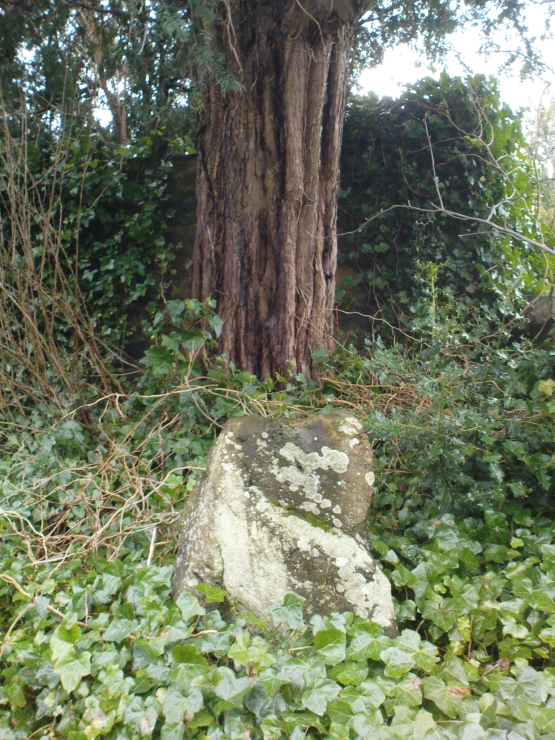
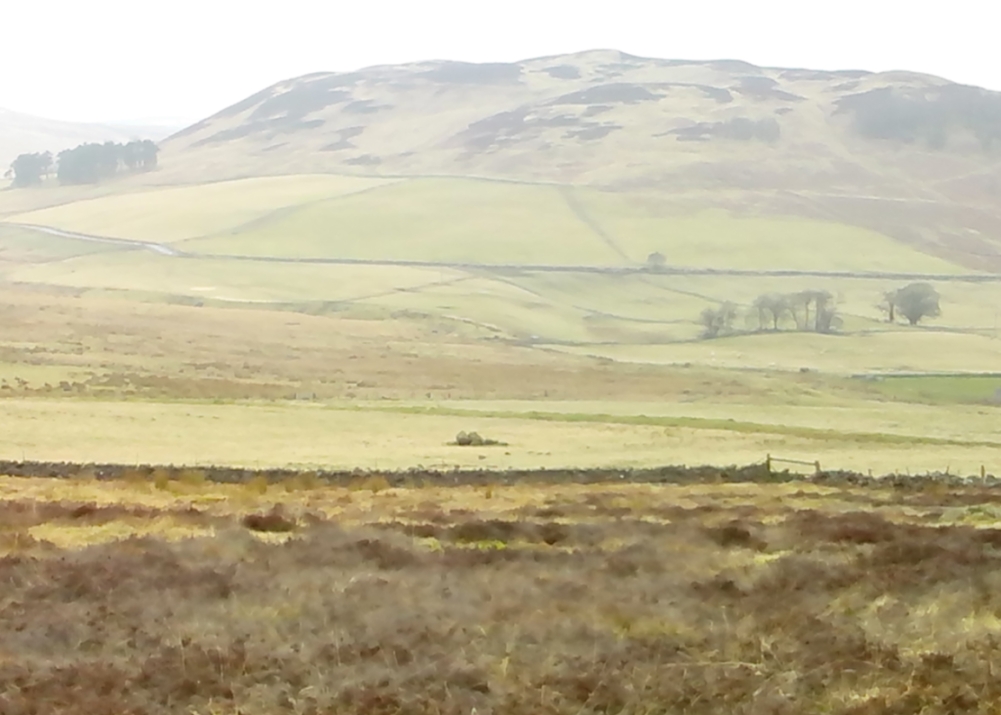
This four-poster stone circle isn’t included in Aubrey Burl’s (1988) survey of that name, nor his 2000 AD magnum opus on megaliths. The site appears to have only recently been rediscovered. Shown on modern OS-maps in non-antiquated lettering, this may be due to verification being required to authenticate its prehistoric status. It’s certainly in a peculiar position in the landscape here — and seems more likely to have been built just 100 yards uphill on the level grassland plain where views east, south and west open up almost with the majesty of Castlerigg!
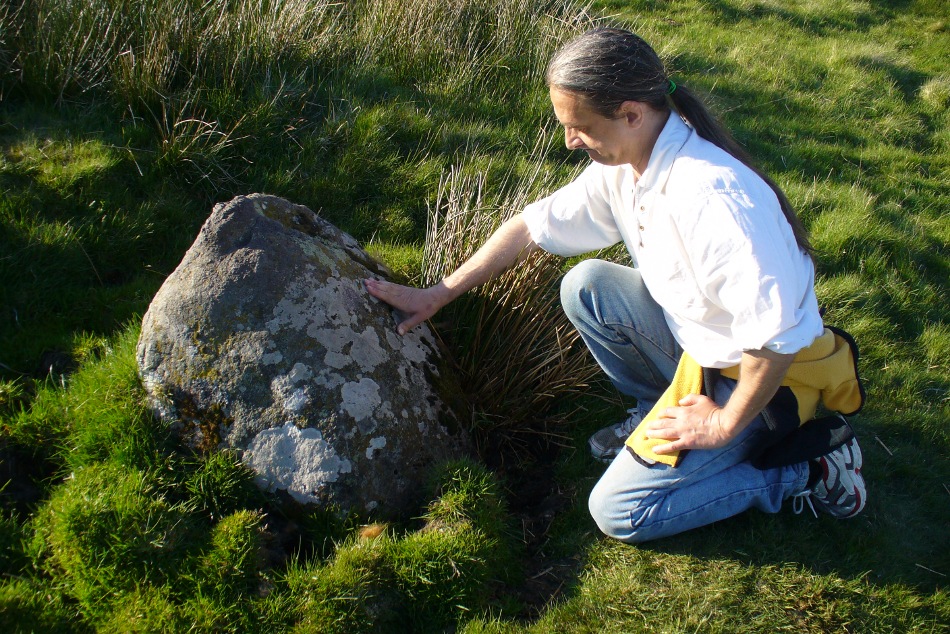

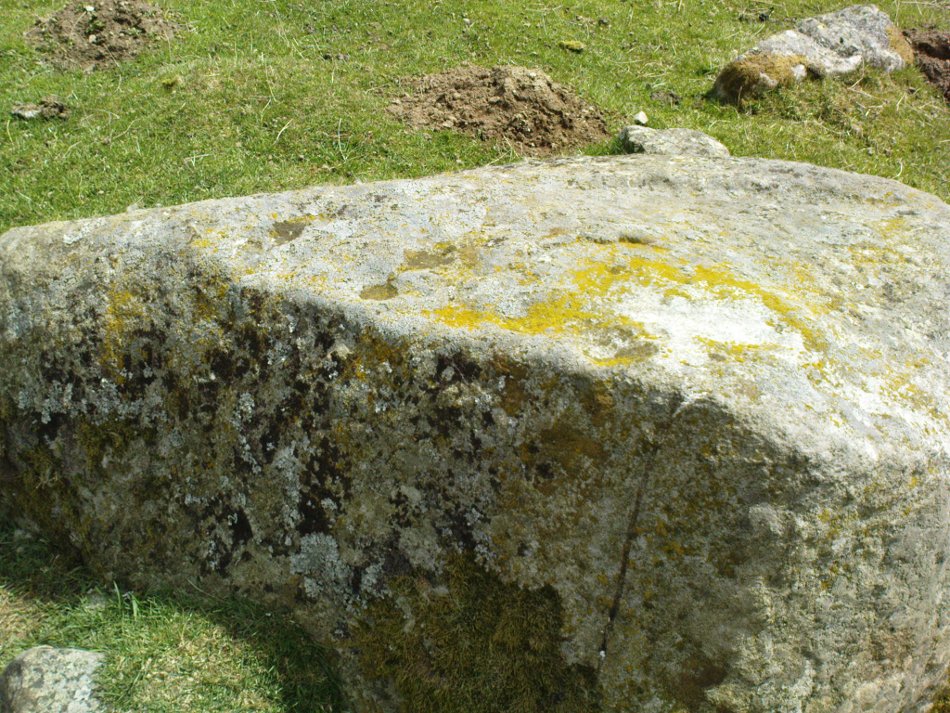
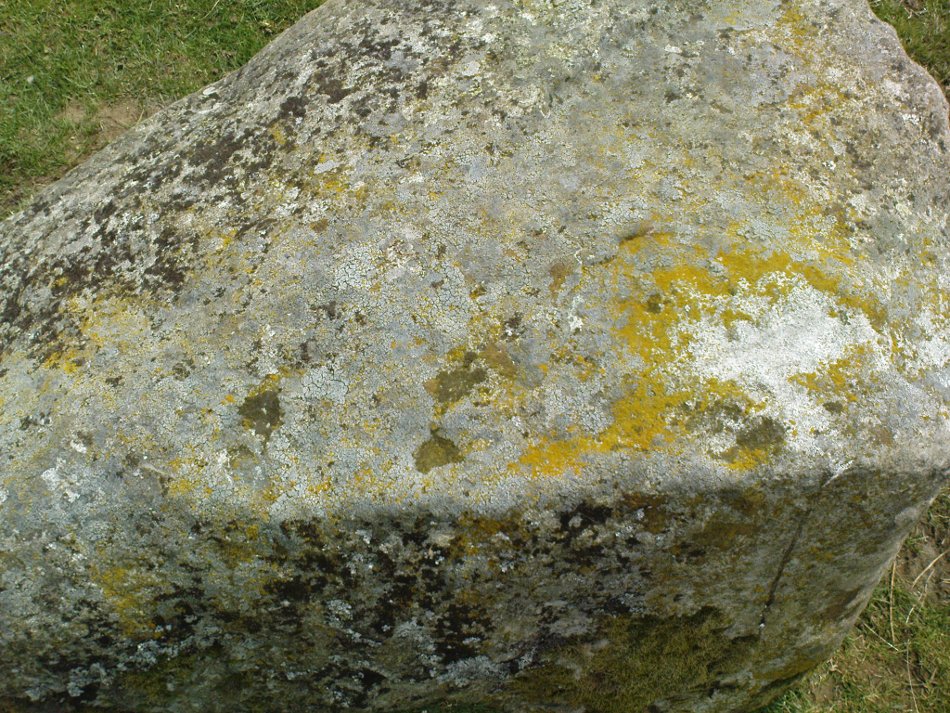
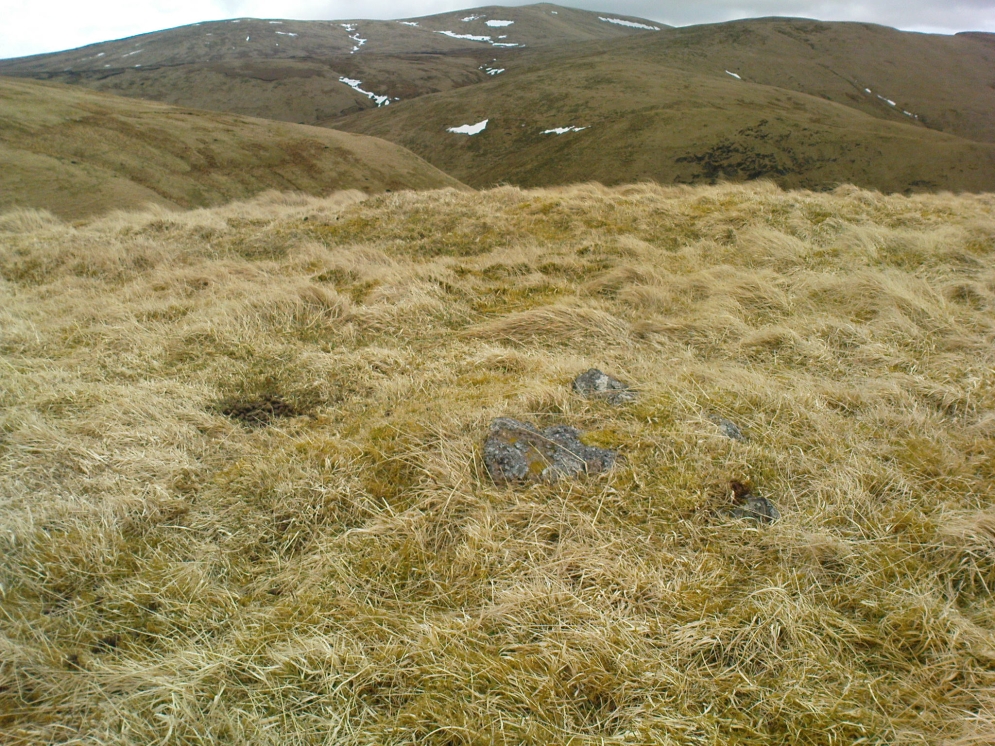
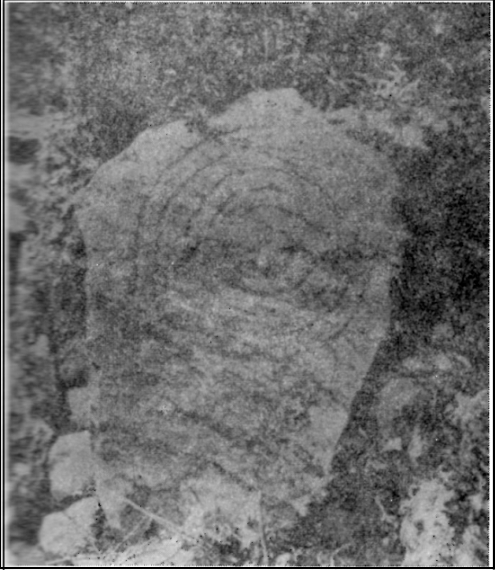
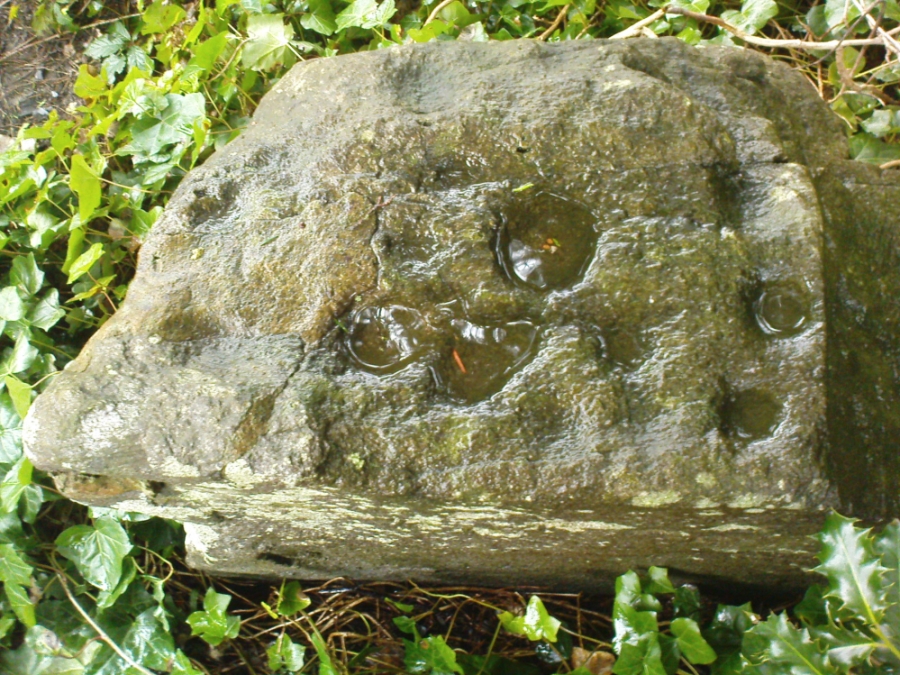
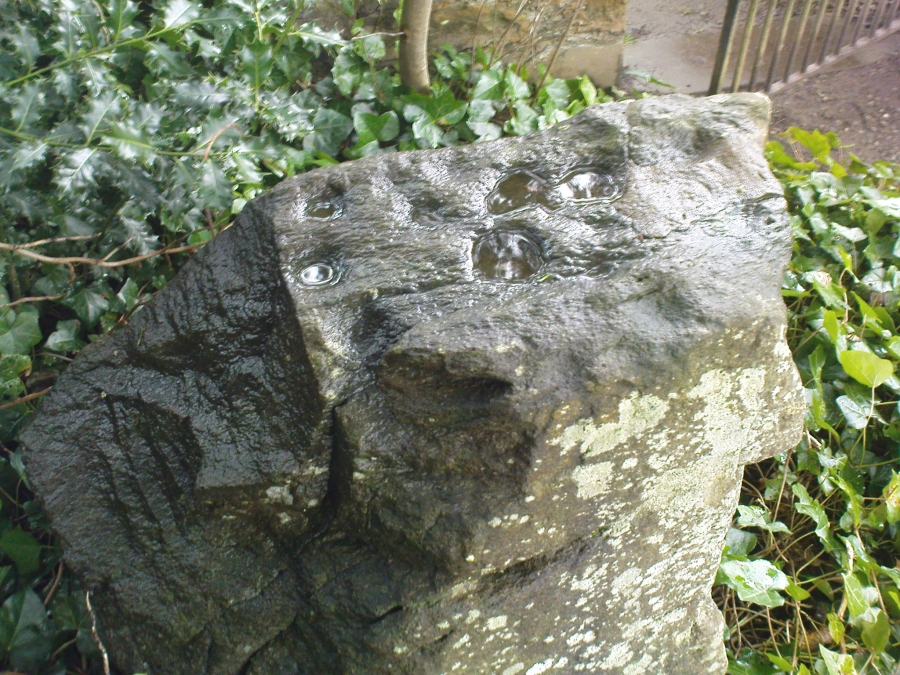
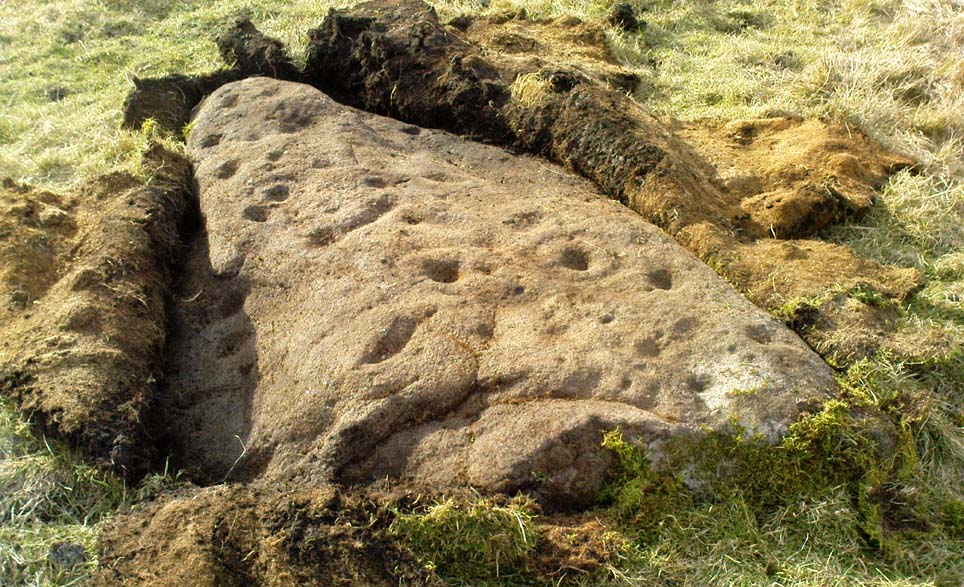
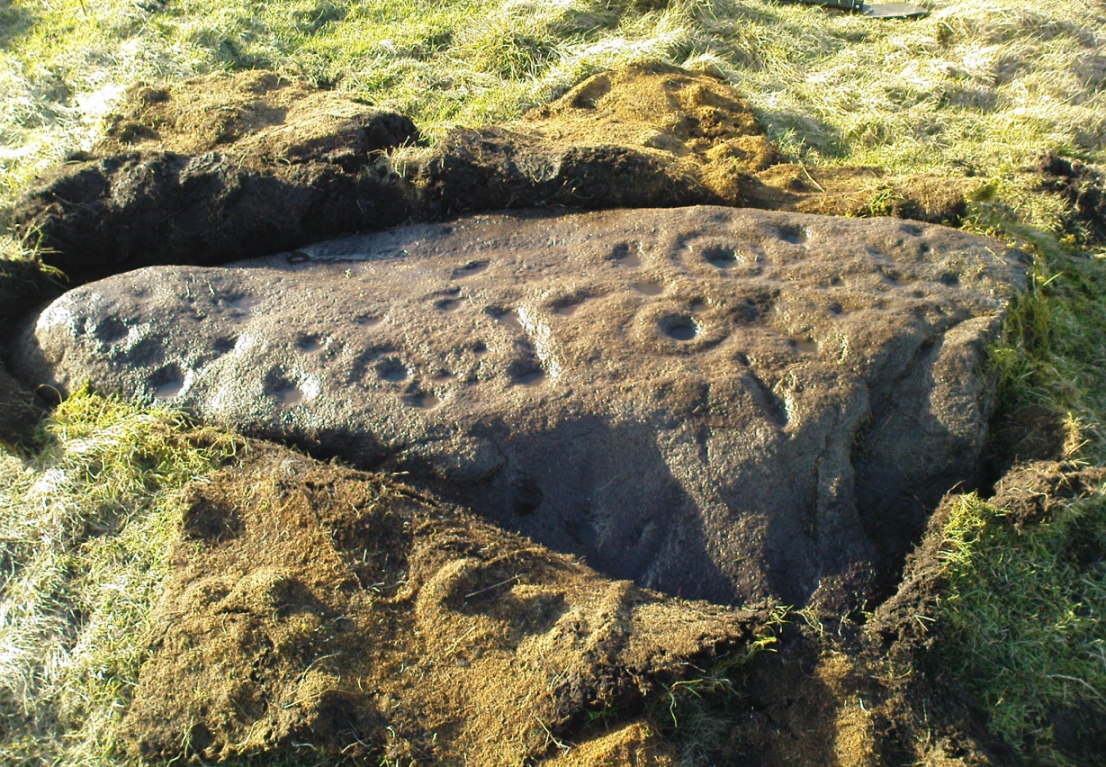
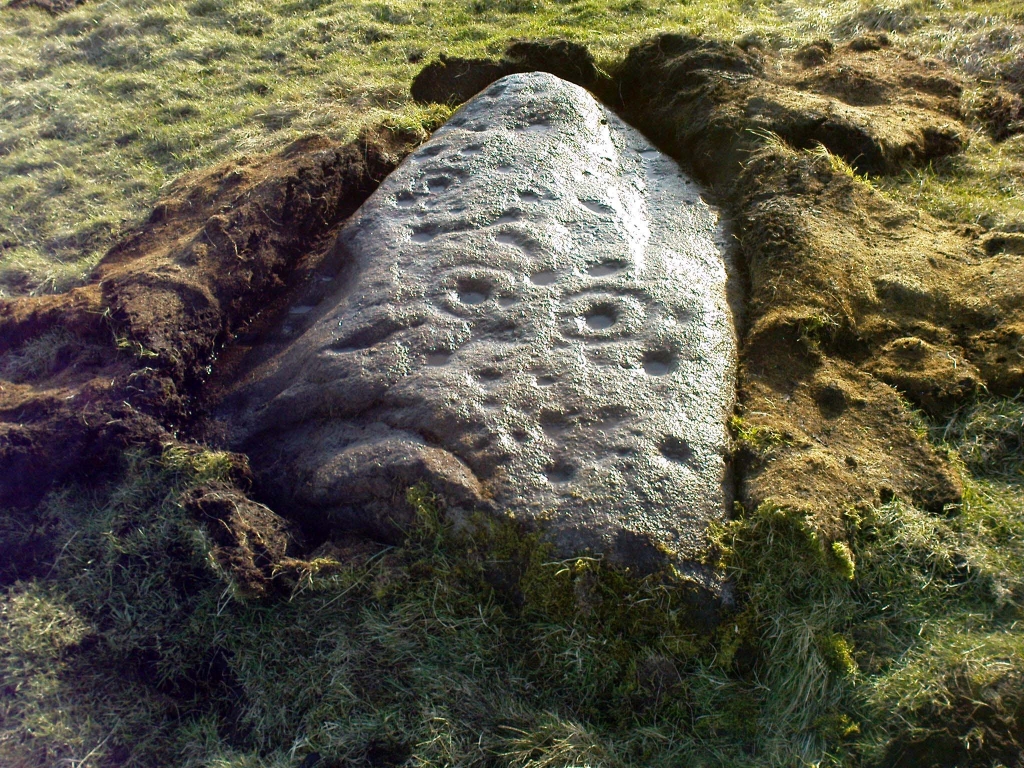
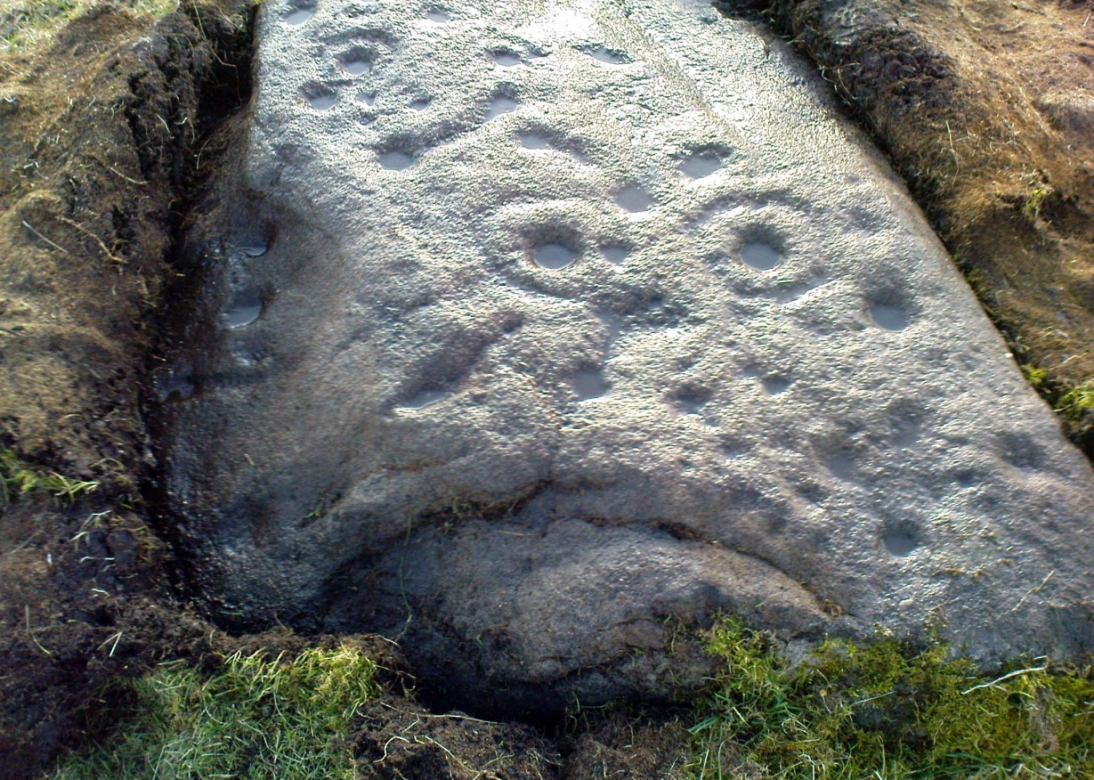
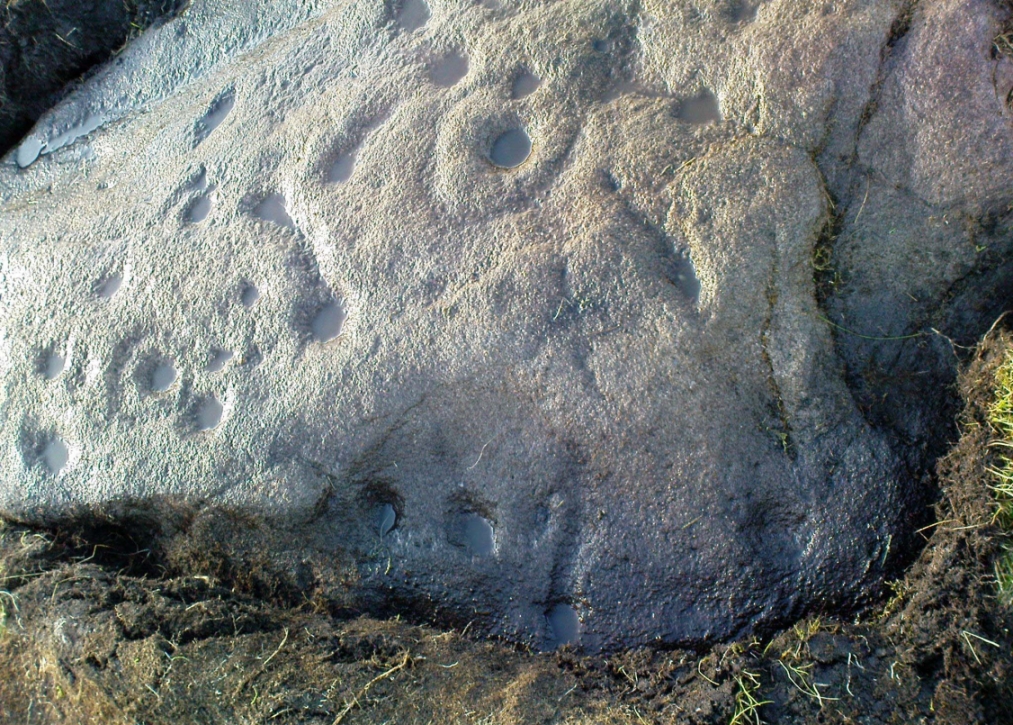
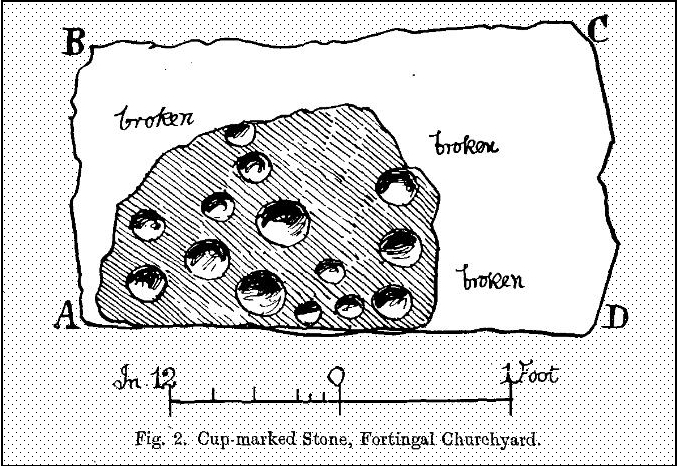
When Paul Hornby and I ventured here yesterday, we mistook the arc of three stones on the flat plain with the ring of stones that are down the Borland Glen slope ahead of us, so good was the position! But at least one thing came of this: of the arc of three stones shown in the photos here, one of the rocks possesses cup-markings, which you can make out here in one of the close-ups.
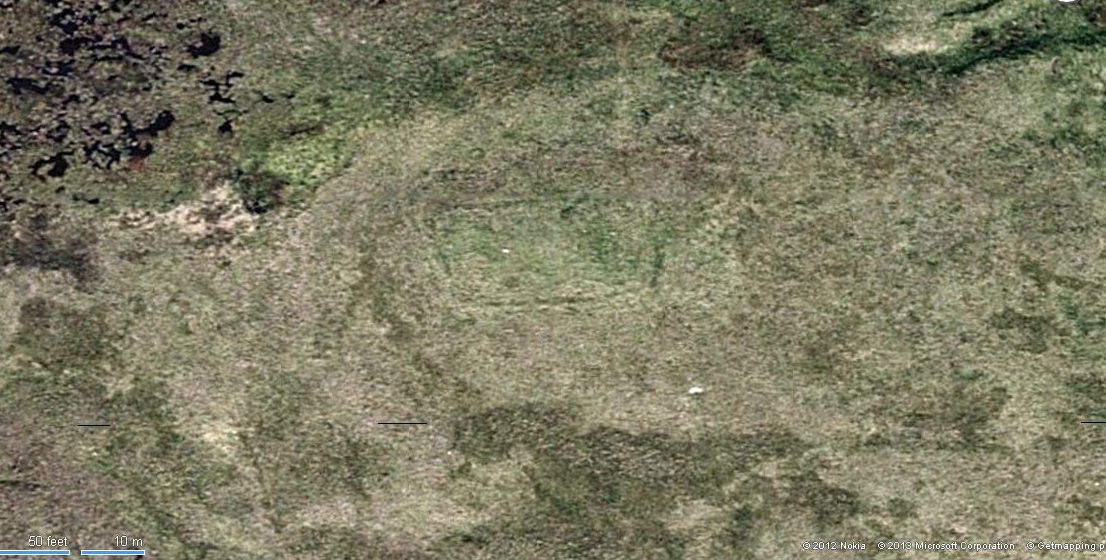
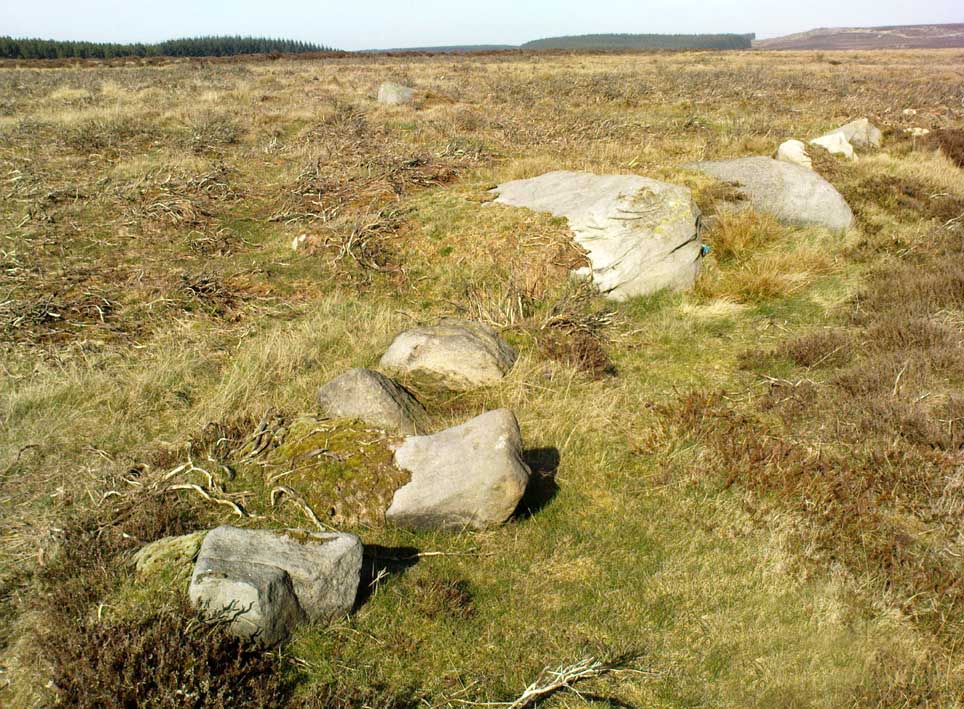
The dimensions of the four stones that make up the ‘circle’ down the slope was measured and described by the Scottish Royal Commission lads as follows:
It comprises four stones, which define a trapezium measuring 3.2m along its N and W sides, 2.7m along the S and 2.5m along the E. All the stones are set square at the corners with their long axes lying E and W, and they present a long flat face to the interior. The two on the N are markedly larger than the others, and that on the NW is also the tallest. The dimensions of the stones are as follows: NW – 1m by 0.5m and 0.65m high, NE – 0.8m by 0.4m and 0.3m high, SE – 0.73m by 0.43m and 0.2m high and SW – 0.73m by 0.38m and 0.4m high.
One of the most notable features a visitor to this site will find, is the utter silence as you walk up the slopes to reach the place. And then, once away in the opening landscape, a view of velvet Earth in all Her beautiful shades surrounds you – assuming you go here on a sunny day! Well worth the wander if quiet hidden megaliths are your pleasure…
References:
- Burl, Aubrey, Four Posters: Bronze Age Stone Circles of Western Europe, BAR 195: Oxford 1988.
- Burl, Aubrey, The Stone Circles of Britain, Ireland and Brittany, Yale University Press 2000.
Acknowledgements:
Many thanks to Paul Hornby for use of his photos.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian