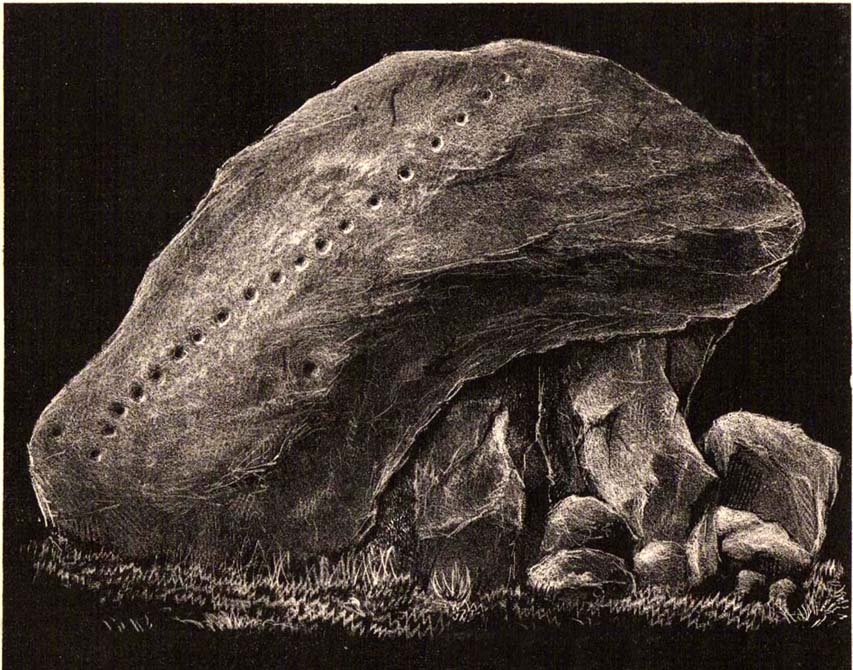
Holy Well (destroyed): OS Grid Reference – NT 2611 7600
Also Known as:
-
Bonnington Mineral Well
Archaeology & History
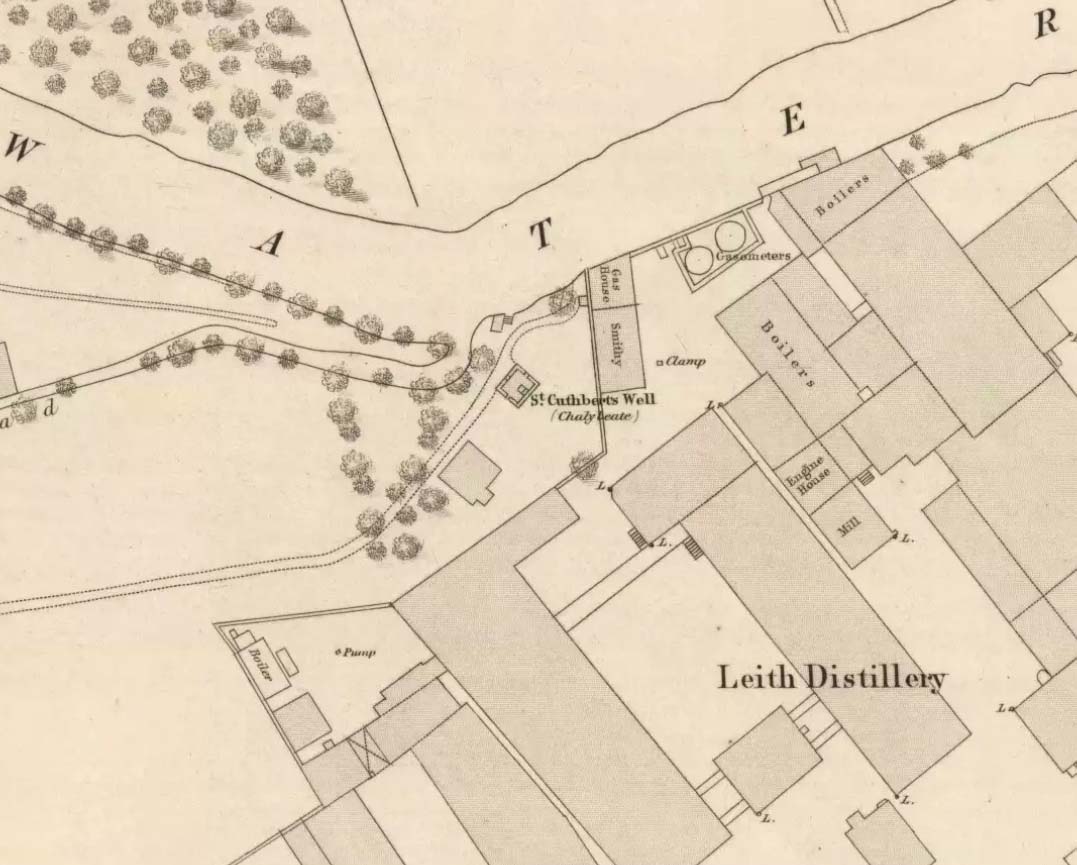
If we’d have lived 200 years ago and walked several miles downstream from St Bernard’s Well on the Water of Leith, we would have eventually come across this little-known sacred site, sadly destroyed in the 19th century. It was shown on the earliest OS-map on the south-side of the river, enclosed in a small square building with what looks like two entrances, and what appears to be a covering of the spring on the southeast side. Marked as a chalybeate, or iron-bearing well, this would have obviously have had repute amongst local people and would have worked as a tonic or pick-me-up, aswell as fortifying the blood and a having a host of other benefits.
The Ordnance Survey lads wrote short notes about St. Cuthbert’s Well in the Name Book of 1852-53, where they told:
“A Well Situated at Bonnington. Supposed to have been dedicated to St Cuthbert; about 34 years ago the proprietor repaired the well and at the same time erected a house over it, and fitted it up for Visitors who are charged one penny for a drink. The Water of the well has been analysed by Professor Jameson and Doctor Turner and it was found to Contain Salts of Iron; Soda, magnesia and Lime, also Iodine under the form of Hydrisdate of Potash.”
About the same time as Jameson & Turner’s analysis of St. Cuthbert’s waters, one Dr Edward Schweitzer (1845) wrote one of the most detailed chemical essays on wells, ever!—using Bonnington’s holy well as his primary focus. A near-thirty-page essay found that, along with an excess of iron, the medicinal aspects of the waters were due to the following compounds found, per grains, in each pint of water:
Sulphate of Potassa — 2.46554 gr
Sulphate of Soda — 1.51227 gr
Sulphate of Lime — 6.28816 gr
Iodide of Sodium — 0.00728 gr
Bromide of Sodium — 0.07886 gr
Chloride of Ammonium — 9.49939 gr
Chloride of Sodium — 3.82963 gr
Chloride of Magnesium — 3.12017 gr
Nitrate of Soda — 2.02154 gr
Carbonate of Magnesia — 1.70443 gr
Proto-Carbonate of Iron — 0.05807 gr
Proto-Carbonate of Manganese — 0.01535 gr
Ammonia (united to organic matter) — 0.42285 gr
Alumina — 0.02245 gr
Silica — 0.18651 gr
In 1837, a Mr Robert Fergusson was known to be “the keeper of the Mineral Well, Bonnington,” but much of its traditions and history have fallen outside of memory. The site was soon to become another mid-Victorian ‘Spa Well’, where local people would have to pay for water they had always used as Nature intended. In truth, the waters and its well-house were to become a place where the rich Industrialists could heal their infirm mind-bodies, hoping that the destitution they lacked emotionally and spiritually would be washed away in the sacred waters. But it didn’t last long! What little is known about it historically was best described in John Russel’s (1933) essay on Bonnington in the Old Edinburgh Club journal. He wrote:
“Just where the Bonnington mill lade joins the Water of Leith once flowed St. Cuthbert’s Well, an ancient spring named after the patron saint of the once extensive parish of St. Cuthbert’s, and like the now forgotten mineral well of St. Leonard’s near Powderhall, a relic of a superstitious age. As to when this well was so designated history is silent but it was probably before 1606, when the Leith portions of Bonnington, Pilrig and Warriston were, by the Scots Parliament, included in the Parish of North Leith…
“In May, 1750 St. Cuthbert’s Well was found to be possessed of medicinal properties. The Scots Magazine of that year refers to many persons frequenting it. The Well formed part of a building which included a pump room and a reading room. From advertisements in the periodicals of 1819 we learn that it was open from 6 o’clock in the morning and that newspapers were to be found on the table all day. The tenant also issued handbills headed “St. Cuthbert’s Mineral Well, Bonnington”, giving a chemical analysis of the water and a list of the ailments for which it had been found beneficial. The Well disappeared with the re-construction of Haig’s Distillery in 1857. It now lies beneath the buildings immediately west of the chimney stack of Messrs John Inglis and Sons.”
St. Cuthbert’s feast day was March 20 (Spring Equinox) and September 4.
A half-mile southwest of here could once be seen the waters of St. Leonard’s Well, which Ruth & Frank Morris (1982) erroneously thought to have been this Well of St. Cuthbert.
References:
- Bennett, Paul, Ancient and Holy Wells of Edinburgh, TNA 2017.
- Geddie, John, The Water of Leith, W.H. White: Edinburgh 1896.
- Morris, Ruth & Frank, Scottish Healing Wells, Alethea: Sandy 1982.
- Rhind, William, Excursions Illustrative of the Geology & Natural History of the Environs of Edinburgh, John Anderson: Edinburgh 1836.
- Russel, John, “Bonnington: Its Lands and Mansions”, in Book of the Old Edinburgh Club, vol.19, 1933.
- Schweitzer, Edward G., “Analysis of the Bonnington Water, near Leith,” in Philosophical Magazine & Journal of Science, volume 24, 1845.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian
The map could not be loaded. Please contact the site owner.