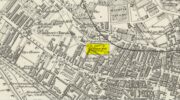
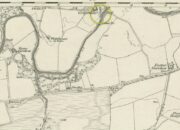
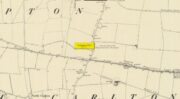
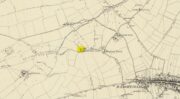
Holy Well: OS Grid Reference – NS 9125 9122
Archaeology & History
A little-known holy well on the south-side of the village has seen better days – if indeed it’s still there! Located 500 yards due south of the destroyed Lady Well, this spring of water gained it name, according to local lore, from its proximity to an ancient chapel—remains of which have been frugal to say the least! Shown on the earliest Ordnance Survey maps and continued to be shown until the 1950s, it seems that the first written account of it was in the Object Name Book of 1861 where it was told:
“A Spring well adjacent to Chapelhill. It is cut in a freestone rock, from which issues a constant supply of pure spring water even in the dryest Seasons. It is not impregnated with any Kind of Mineral. A Chapel Stood near it at one time, the site of which Cannot be pointed out by any person in the neighbourhood.”
A visit by one of the Ordnance Survey lads here in 1950 found the well to be blocked-up by silt and soil; and on a quick visit I made here today I could find no remains of the well, but it may have been beneath the mass of excessive vegetation. A subsequent visit in the winter may prove more fruitful – he sez, hopefully…..
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian