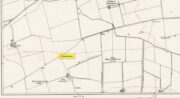
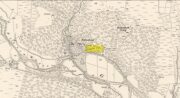
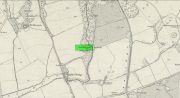
Hillfort: OS Grid Reference – NO 2900 7600

From Kirriemuir town centre up the B956 Kinnordy Road, turn left where it goes along the B955 road for several miles towards Cortachy. Keep going on the B955 for a few more miles into Glen Clova, past the Caddam stone and eventually, after going over the bridge into Clova village, you turn left and go up towards the mountains. Nearly 3 miles along you see the very conspicuous and impressive rising crag, like a small volcano on the right-hand side of the road, which is Dun Mor. Walk up the steep climb round to the back of it – and you’re in the middle of the old ruins…
Archaeology & History
Highlighted on the 1865 OS map of the region, Dun Mor is Gaelic for a “large or great fort” – and such it is! Those of you with a nose for these sorts o’ things will no doubt take to the remains pretty quickly. Its position in the landscape is a bit of a gem! On its north-side— invisible to anyone in the glen below—an overgrown arc of walling some 3 feet high and about 70 yards long bends towards the crag of rocks on each side, with a notable “dip” or entrance about 8 feet wide in the middle of it. The walling itself averages about 4 yards wide all along its arc.

It’s quite impressive once you get a good feel of the place and envisage it as it once was. The sheltered fortress within the rise of Nature’s crags is about 100 yards across and would be ample space for several families to live in when it was first built, in those mythic times of so so long ago. It was probably constructed in the Iron Age, although several ruined rectangular stone structures inside it are thought to be mediaeval shelters; and even in those more recent times, the people here would have regularly heard the howl of the wolves, whose names are kept in the hills above as reminders of a world not too long past….
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian