Standing Stones: OS Grid Reference – NO 1494 0432
Also Known as:
- Canmore ID 27912
- Mawcloych
Getting Here

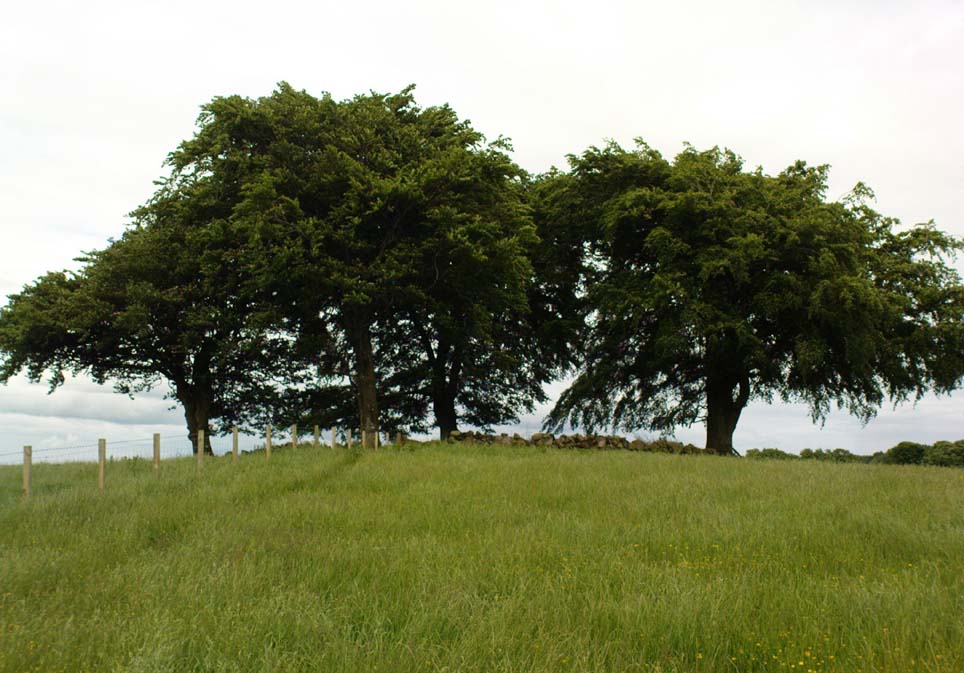
The Orwell standing stones
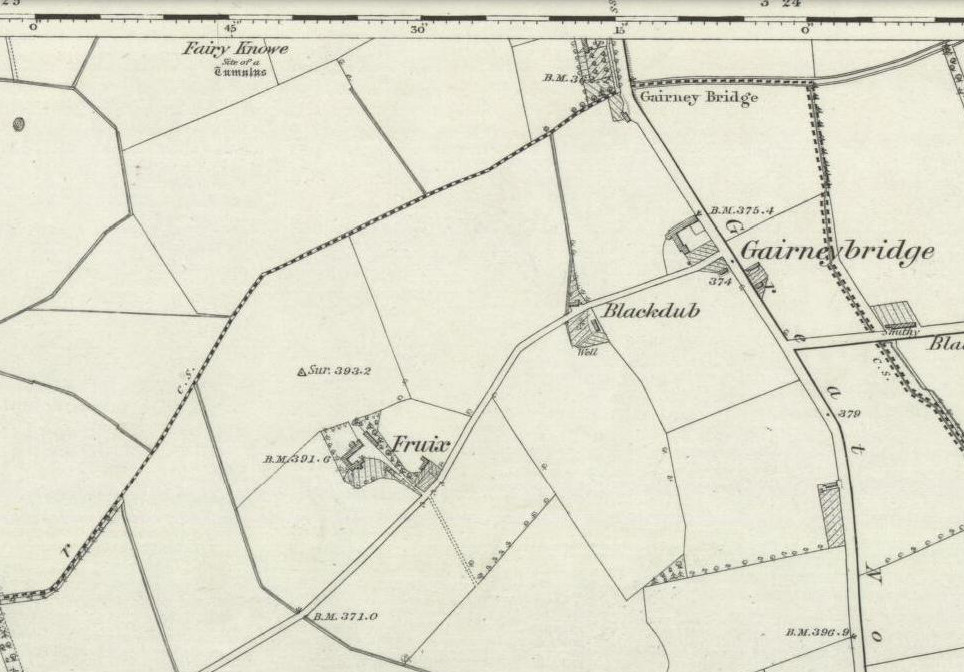
Drive from Milnathort SE down the A911 road towards Balgedie and Scotlandwell. About a mile out of the village, keep your eyes peeled on the farmed fields on your left. You’ll notice the standing stones a few hundred yards ahead and, if you, see them in time, will be able to park up by the track on your left a coupla hundred yards before Orwell Farm. Ensure you visit this site between October and March – otherwise the fields are in full crop.
Archaeology & History

Stones marked on the 1857 map
These are impressive standing stones by anybody’s standards. Although we have two impressive uprights today on the highest point in the potato fields, in the 19th century the place-name writer Liddall (1896) told that “in this district are still three large pillar stones known as the Standing Stones of Orwell.” (my italics) Their existence was recorded, he said, in early topographical accounts in an obsolete place-name Mawcloych, or “place of the stones.” But if there were three standing stones here, they must have stood prior to the article written by the pseudonymous “W.H.”, who described them in the October edition of The Scottish Journal in 1847, saying:
“About half-a-mile above the old (Orwell) churchyard, in a field by the roadside, are two large upright stones, known as “the Standing Stones of Orwell.” They are placed east and west of each other about fifteen yards apart—that to the west is flat, and about six feet in height—the one to the east is of a round form, tapering slightly to the ground, and stands nine feet high. The latter, although still of considerable size, has lost somewhat of its circumference within the last ten years, and, at the present moment, there is a large crack down one side, which, by the action of the weather, will lead to a further diminution of its bulk. It has not been ascertained to what depth these stones are embedded in the earth, but it must be considerable, in order to retain them in the position they occupy.
“The common belief is, that these stones are of Danish origin, erected in commemoration of a victory, or to mark the spot where those who had fallen in battle were interred. This supposition is so far countenanced by the fact that a stone coffin, of large size, was found on digging up the space between the stones. Similar coffins have also been turned up in the same field, and, ten or twelve years ago, the ground was dug up in several places by a neighbouring proprietor, when large quantities of bones, much decomposed and mixed with charcoal, were discovered.”

Fred Coles 1906 ground-plan

Orwell Stones, looking north
This early description telling of the poor condition of one of the stones presaged its eventual fall in the late 1960s; but this thankfully led to an archaeological evaluation which gave us more information about the site. Before this however, the great northern antiquarian Fred Coles (1906) visited the stones in August 1904, describing them with his usual meritorious detail, telling:
“They stand on a very gently rising ground, the space between them and for some distance to the south being somewhat higher than the surrounding field. In ground plan they are related as shown (attached). The east stone is the higher, standing 9 feet 8 inches clear of theground, smooth-sided and hexagonal. At the base its girth is 9 feet 9 inches, swelling up at the 5-foot level into 10 feet 8 inches. The West Stone, very rugged and angular, is 7 feet 5 inches in height, girths at the base 11 feet 1 inch, and at about 3 feet upwards, 10 feet 5 inches, its broadest side facing the East Stone. Both are of whinstone. The shortest distance between the two Stones is in a line nearly north-west, and measures 46 feet 10 inches.
“Mr R. Kilgour, one of the oldest residents of Kinross, showed me a fine partially flattened oval pebble of dark reddish quartzite, measuring 5 inches by 2⅞ inches, which he found in the ground between these two Stones. The abrasion at each end clearly shows that this pebble has been used as a pounder.
“In a book which to some extent deals with local antiquities, occurs the following passage with reference to these two Standing Stones: ‘In the same field stone coffins have occasionally been turned up by the plough; and, about the beginning of the 19th century, the ground was in many places dug up by the neighbouring proprietor, when quantities of bones much decomposed and mixed with charcoal were discovered.’”
But after the west stone fell down, J.N.G. Ritchie (1972) and his team turned up to resurrect it—and also check out what might be underneath it. His initial notes of the findings were published in Discovery & Excavation Scotland, which said:
“Excavation at the bases of these two standing stones…was undertaken prior to the re-erection of the W stone and to the embedding of both stones in cement. The original position of the fallen stone could be detected only as a slight hollow in the natural gravel, but as this corresponded with the position of the stone on Coles’ plan…the stone could be re-positioned comparatively accurately.
“A cremation deposit was found in an insubstantial stone setting in a scoop in the natural gravel some 0.5m S of the stone. The E stone, which is an impressive whinstone 3.8m in total height, had been set up in a hole 1.5m x 1.4m and 0.75m in depth. Within the pit on the SW side of the stone there was an unusual two-storeyed cremation deposit; the lower cremation was contained within a rough setting of stones with one side formed by the standing stone itself, and was covered by a flat slab. On this slab and again surrounded by a setting of small stones was the upper cremation. It seems most likely that these were inserted into the stone hole at the time of the erection of the stone. Another cremation was found at the lip of the stone hole on the SE side. The discovery of cists and cremation patches in the same field in the early 19th century suggests that the stones have acted as a focus for such burials.”

The southeasterly stone

The northwesterly stone
Ritchie (1982) later wrote how they had found “burnt dog and pig bones with the lower cremation deposit,” implying “rituals” at the site. He even posited how such deposits at standing stones “may have a bearing on their postulated use as astonomical markers,” although Alexander Thom’s (1990) exploration of the Orwell stones indicated no archaeoastronomy here. So it seems very obvious that these giant monoliths were markers for a neolithic and/or Bronze Age cemetery or necropolis in prehistoric times. Aubrey Burl (1993) defined the stones here as having “an Irish setting, with the east emphasized, as alway, by the taller stone.”

Fred Coles’ 1906 drawing
Unmentioned by the archaeologists in all of the references I have at hand, is the probable relationship the Orwell stones had with the rising background of the Lomond Hills to the east, with its archaic legends of cailleach, neolithic tomb creations and other geomantic indicators. These elements (and more) need to be explored more diligently by forthcoming students. It’s a remarkable setting as far as I’m concerned!
References:
- Burl, Aubrey, “Pi in the Sky”, in Douglas C. Heggie’s Archaeoastronomy in the Old World, Cambridge University Press 1982.
- Burl, Aubrey, From Carnac to Callanish, Yale University Press 1993.
- Coles, Fred, “Notices of Standing Stones, Cists and Hitherto Unrecorded Cup-and-Ring Marks in Various Localities,” in Proceedings of the Society of Antiquaries, Scotland, volume 40, Edinburgh 1906.
- Day, J.P., Clackmannan and Kinross, Cambridge University Press 1915.
- Feacham, Richard, Guide to Prehistoric Scotland, Batsford: London 1977.
- Jack, James W., Glenfarg and District – Past and Present, Miller & Smail: Perth 1903.
- Liddall, W.J.N., The Place Names of Fife and Kinross, William Green: Edinburgh 1896.
- Ritchie, J.N.G.,”Orwell Standing Stones,” in Discovery & Excavation in Scotland, 1972.
- Ritchie, J.N.G., “Archaeology and Astronomy: An Archaeological View”, in Douglas C. Heggie’s Archaeoastronomy in the Old World, Cambridge University Press 1982.
- Royal Commission on the Ancient & Historical Monuments of Scotland, Fife, Kinross and Clackmannan, HMSO: Edinburgh 1933.
- Simpkins, John Ewart, County Folklore – volume VII: Examples of Printed Folk-Lore Concerning Fife, with some Notes on Clackmannan and Kinross-Shires, Folk-Lore Society: London 1914.
- Thom, A., Thom, A.S. & Burl, Aubrey, Stone Rows and Standing Stones – volume 2, BAR: Oxford 1990.
- “W.H.”, “A Ramble in Kinross-shire,” in The Scottish Journal of Topography, Antiquities, Traditions, volume 1, 1848.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian
The map could not be loaded. Please contact the site owner.