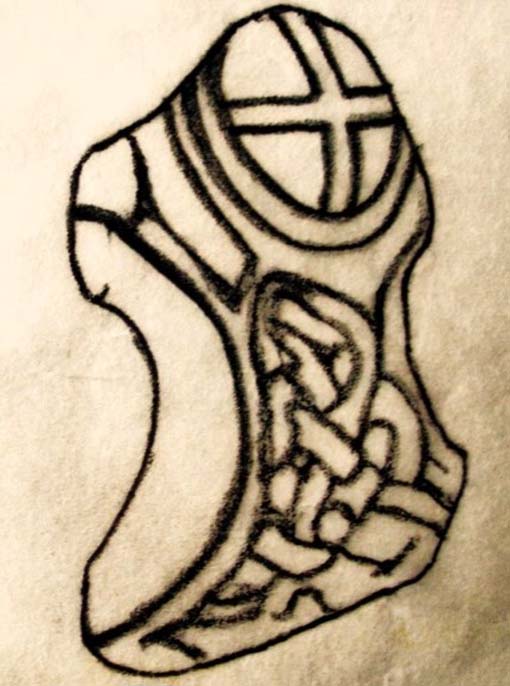
Cross: OS Grid Reference – NZ 67724 02092
Also Known as:
- Ralph’s Cross
- Young Ralph’s Cross
The cross stands high-up on Danby High Moor between Hutton-le-Hole and Castleton, just by the junction of two moorland roads to Rosedale and Westerdale, in north Yorkshire. The monument stands on private land. (Ed. – though in Yorkshire, many of us ignore such signs)
Archaeology & History
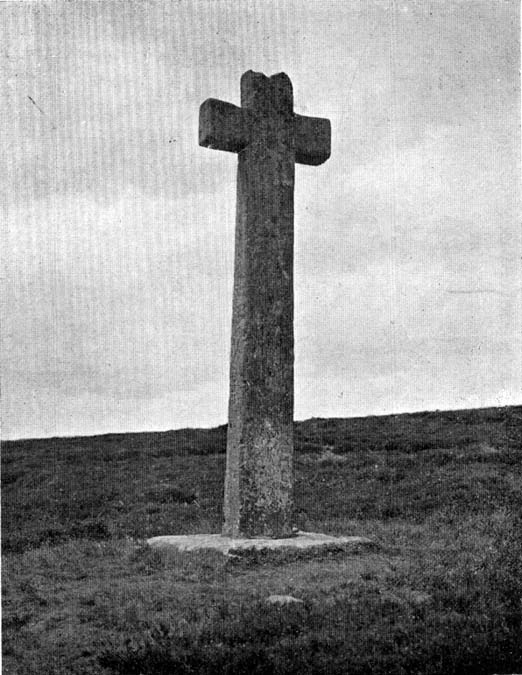

First described in old deeds from the early 13th century, Ralph’s Cross stands nine feet high on a solid stone base. There is uncertainty about its age; the present-day cross could date from the 18th century though some historians date it to around 1200, certainly the base could date from that time. It seems likely that a much older cross once stood on this site — perhaps an Anglo-Saxon one that was actually made of wood. At that time it may have been referred to as ‘The Roda Cross’ (Rude Cross). More than likely the cross acted as a medieval highway marker because it stands at the junction of two moorland roads. Originally there were some letters carved on the cross, one in particular, being the letter “R” for Ralph was carved on the south face.
Over the centuries the cross has suffered damage and vandalism by being knocked down, particularly in the 1960s and again in 1984 after which it lay in two pieces. However, in 1985 the cross was lovingly restored and re-erected by some local men, Mr Robert Dixon, Mr Tom Rudd and Mr Michael Smith, at the English Heritage Commission’s stone masonry workshop at Mount Grace Priory. The middle section of the cross was made from new stone from nearby quarries; the top section was not badly damaged, but a section of delta metal was inserted inside the shaft to make a secure link between the sections and the cross-head. The cross is a listed monument.
A few hundred yards to the south stands another cross called ‘Old Ralph’ which is just 5 feet high and is located on Blackey Ridge. This cross dates from the beginning of the 13th century and is perhaps a memorial to Ralph, bishop of Guisborough.
Folklore
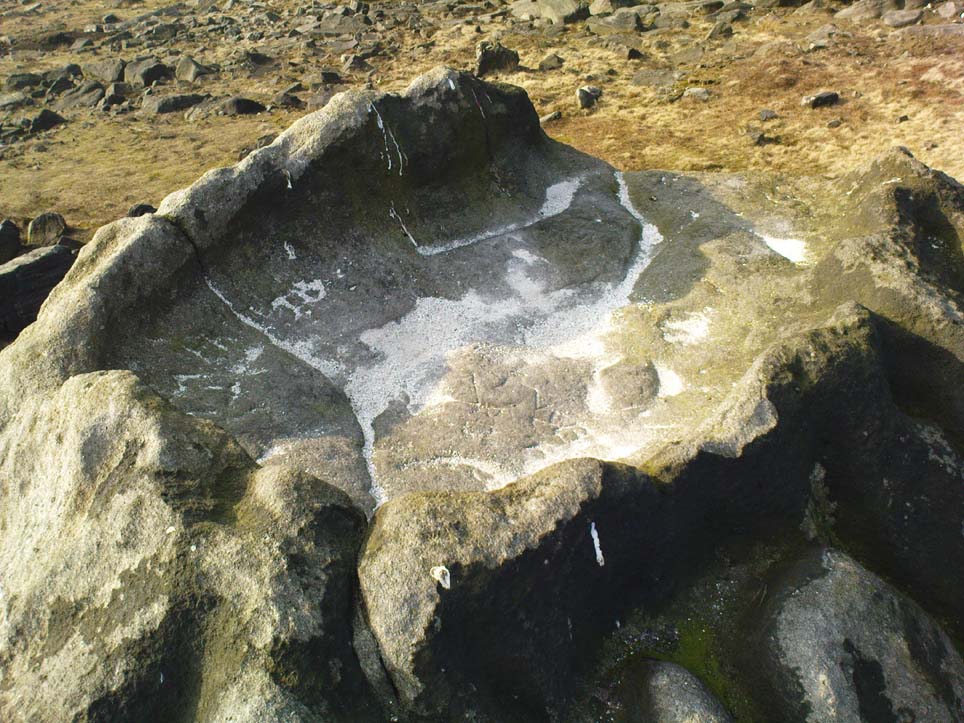
According to legend, the cross was set up to mark the resting place of a monk from Farndale and a nun from Rosedale. They would often meet here and a romantic liason of sorts occurred, but they were found out by their superiors and came to a nasty end, possibly with their deaths. But the most common folk-tale tells us that a farmer called Ralph from Danby found the dead body of a traveller at this spot. He was so moved by this that he decided to erect a cross in memory of this poor unfortunate traveller, who had starved to death and was found to be penniless. Ralph had a hollow carved into the top of the cross so that more wealthy travellers, those on horseback, might place a few coins for the benefit of any less fortunate travellers, or as a thanksgiving for having reached this point on their journey. The poor traveller was able to take a coin, if he/she could reach the hollow, and buy a hot meal at the nearest inn. Ralph then vowed that such a terrible thing would never ever happen again, and it seems to have worked, thanks to him.
References:
- Ford, Joseph, Some Reminiscences and Folk-Lore of Danby Parish & District, Horne and Son: Whitby 1953.
- Ogilvie, Elizabeth & Sleightholme, Audrey, An Illustrated Guide to the Crosses on the North Yorkshire Moors, Village Green Press: Thorganby 1994.
- Woodwark, T.H., The Crosses on the North York Moors, Whitby Literary & Philosophical Society 1934.
© Ray Spencer, 2011
The map could not be loaded. Please contact the site owner.