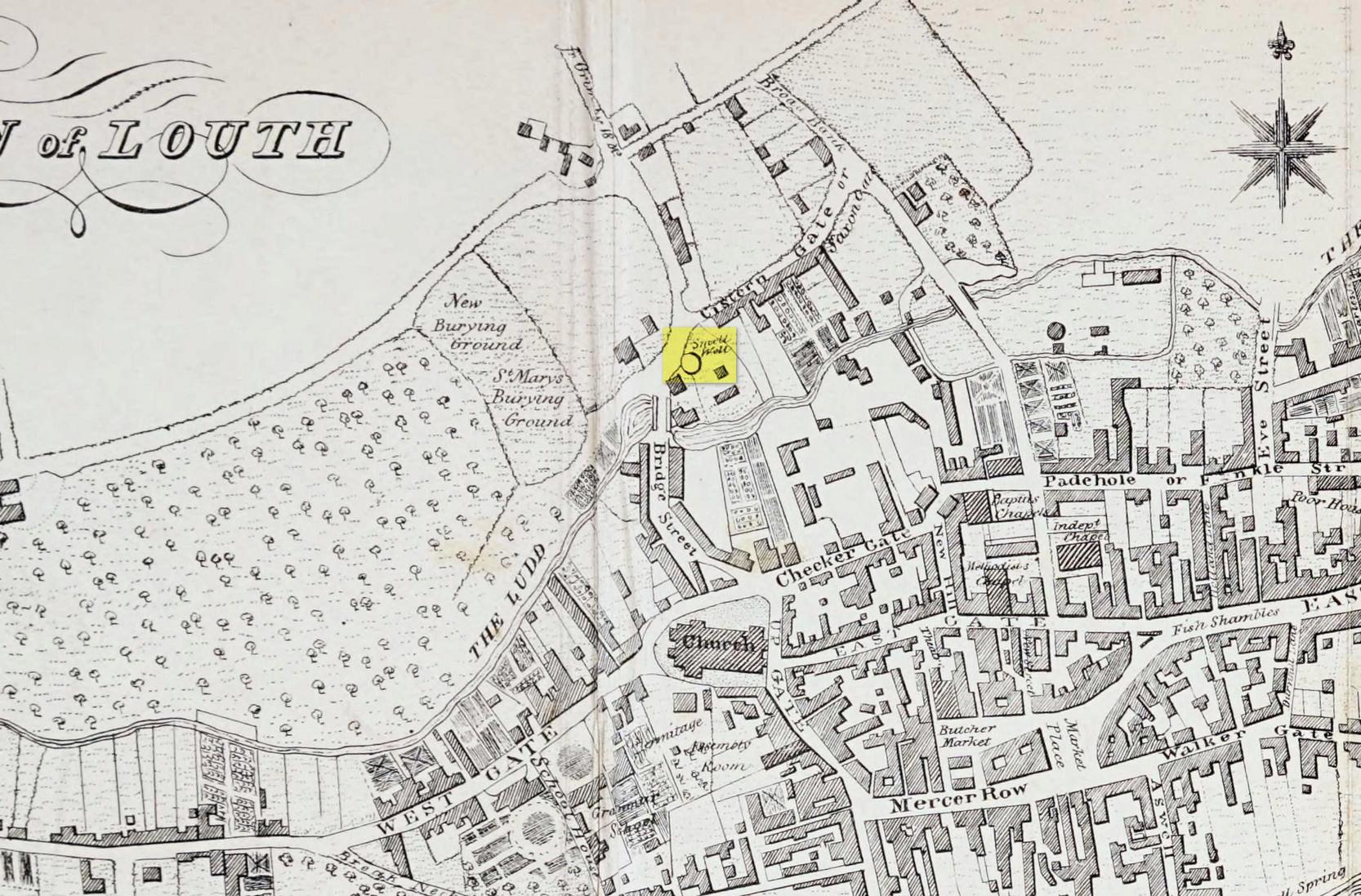
Healing Well: OS Grid Reference — TA 199 096
Also Known as:
- Ragged Well
Getting Here
The site can be found along Wells road, just after the turning for Healing wells farm and after the mirror. One may need to beat through the thickets to reach it.
Archaeology & History

The Ragged Spring
Some confusion exists over the relationship between the wells and the parish name. This is possibly an ancient site, as the earliest name for the parish is ‘Heghelinge’ and perhaps derive from the springs. However, this is at variance to the view of Kenneth Cameron (1997) in his Place-Names of Lincolnshire, where it is noted that ‘Hægelingas’ is derived from “the sons or followers of a man named Hægel” rather than healing, although it is of course a strange coincidence!
The springs are still marked on the current OS map, as Healing Wells, in a small plantation, but they are, as the photo shows, only marked by circular indentations in the ground. The first spring is the easier one to trace and it appears to have holes, although these may be made by animals. The springs are now quite dry, perhaps that the clogging of the springs noted above continued as the waters were forgotten, resulting in the current situation. There is no clear lining around the well or other structures. Lying around the springs are a range of metal buckets in various stages of decay and some metal pieces which may be remains of a metal fence around it. Sadly, I was unable to find any sign of rags although the man I asked in the whereabouts referred to them as “the ragged springs.”
Folklore
The Ragged Springs fed a stream where people paddled or hung garments on bushes to acquire good health strangely rather than the wells themselves. Gutch and Peacock (1908) in their County Folklore note that a,
“Mr. Cordeaux visited them not long since for the purpose of discovering whether pins are ever dropped into them, but the bottom of the water in both cases was too muddy and full of leaves to allow accurate examination.”
According to Gutch and Peacock (1908) each well had a different use, one spring being a chalybeate one was done for eye problems, whereas the other was for skin problems. They continue to note that a:
“F S, a middle-aged man, who grew up in an adjoining parish, states that when he was a lad, one spring was used for bathing, and the second for drinking. The latter was considered good against consumption, among other forms of sickness. . . . What the special gift of the bathing well was F S cannot say. He often plunged his feet into it when a boy, but he does not venture to assert that it had any great power in reality, although ‘folks used to come for miles,’ and the gipsies, who called the place Ragged Spring or Ragged Well, frequently visited it. A Gentleman who hunts with the Yarborough pack every winter, says that he notices the rags fluttering on the shrubs and briars each season as he rides past. There is always a supply of these tatters, whether used superstitiously or not, and always has been since his father first knew the district some seventy years ago.”
This would appear to be the site recorded as below under Great Cotes by R.C. Hope (1893) in his Legendary Lore of Holy Wells:
“there is a spring celebrated locally for its healing properties. It rises from the side of a bank in a plantation, and is overshadowed by an ancient thorn, on the branches of which hang innumerable rags, fastened there by those who have drunk it waters.”
The custom apparently continued until the 1940s. Indeed a visitor in the 1920s noted that even the trunks were covered with longer pieces of rag. A picture in the 1995 edition of Lincolnshire Past and Present journal shows a number of rags on the bushes. It is worth noting that perhaps the presence of a large thorn perhaps suggests a great antiquity to the site.

References:
- Cameron, Kenneth, The Place-Names of Lincolnshire – volume 5, EPNS: Nottingham 1997.
- Gutch, Mrs & Peacock, Mabel, County Folk-lore – volume v: Examples of Printed Folk-lore Concerning Lincolnshire, David Nutt: Folk-lore Society 1908.
- Hope, Robert Charles, Legendary Lore of the Holy Wells of England, Elliott Stock: London 1893.
- Parish, R.B., Holy Wells and Healing Springs of Lincolnshire. Pixyled Publications 2013
Links:
- Holy & Healing Wells
© R.B. Parish, The Northern Antiquarian

The map could not be loaded. Please contact the site owner.