Cup-and-Ring Stone: OS Grid Reference – NC 56428 64071

Along the A836 road between Durness and Tongue, take the minor road north to Melness. Keeping to the right all the way along, drive almost to the very end, shortly before which is a double right-hand bend uphill. Park here and walk back along the road, north, past the cottage of Dun Bhuidhe for about 100 yards until you see the large sloping rock face with the telegraph post sticking out of it. That’s the place!
Archaeology & History
Not previously recorded, this cup-and-ring stone is right by the roadside up the far, lonely but beautiful glen west of Melness, which runs to a dead-end and into the heart of the silent moors high up in Sutherland’s remote landscape — and it’s a damn good one! It’s also the most northern example known of a Neolithic or Bronze Age petroglyph on the British mainland. The carving has been etched onto a large easterly sloping rock, fractured into several sections, with the decayed broch of Dun Bhuidhe rising to its immediate southwest. The setting alone is outstanding!

It was rediscovered on 25 August, 2015, after Prof Hornby and I had analysed the chambered tomb south of Dalvaid about half-a-mile away. In walking back to explore the aforementioned broch, I cut across the bottom of a nearby rock and found three distinct cup-markings etched near the bottom of its sloping face. Calling out to Prof Hornby, he retreated in his direction to the broch and came back to look at the top of this very large rock surface.
“There are some more cups on this section of the stone!” he called – and began to count them. “At least ten in this little section,” he said. There were indeed!
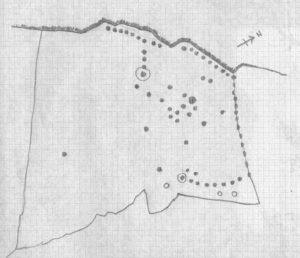
By the time we’d finished counting, drawing and assessing the design etched onto the rock surface, amongst at least two cup-and-ring elements we found at least 67 cup-markings, mainly carved onto the northwest portion of the stone. The first three that I’d seen were on the much lower eastern part and were etched in deliberate isolation from the primary design. However, of these three isolated cups, it looks as if one of them may have a spiral element curving out of it. This needs assessing in much better lighting conditions, because when we found it the skies were very grey and overcast, making an accurate survey very difficult (cup-marks on rocks can be hard to see unless daylight conditions are just right) – and, after a short while, the legendary Scottish midges appeared and began to feast on us, which stopped us in our work. The little buggers!
On a subsequent visit here with Sarah MacLean of Borgie in the summer of 2018, she found several more cup-marks beneath the lower arc shown in the above drawing (which I need to update, obviously).
The most notable feature to this carving is the arrangement of the great majority of the cup markings. They were quite deliberately carved along the very top of the stone, close to its edge, in two contiguous lines of nine with a small gap separating them. At the northwestern end of this, a very notable feature occurs: a natural crack in the rock runs down the stone and, almost all the way down, we find a line of cups have been pecked onto the stone along the natural crack, with some of them near the top that are unfinished. These cup-marks are more elongated in form than the usual circular status; but this is due to them being etched into the cleft itself. From top to bottom there are 13 such cups. At the bottom of this line, another linear stretch of cups change direction and move back onto the main rock surface, just above another large long natural crack cutting across the rock. This gentle arc of cups (with two other possible cups beneath these) ends at a cup-and-ring, above which are two extra cups next to each other. Above these are a number of other cups of roughly similar size and depth, with a notably large one that gives the impression that the smaller cups around its edges are satellites to its larger parent body.
Without any doubt there are other faint features that have been carved onto the stone, but due to the poor visibility factor at the time of its discovery we could not see anything other than the elements highlighted in the rough sketch. In looking through the many photos we took of this carving, there seem to be other faint lines, rings and cups within the overall design, but until we revisit the site (or someone else does!) such further features cannot be added to the drawing.
As the images of this petroglyph clearly shows, the primary feature defining it is the extensive line of continuous cup-markings running along the edges and enclosing a smaller number of internal cups. It’s an unusual element. Sequential line features such as these, defined by cups, are not common. My impression of this feature is that it was a pictorial representation of the horizons, inside which is played the story of….. something… But horizons they seem. Of course, this is a simplistic interpretation and is open to criticisms of any form. I care not! Much more importantly as far as I’m concerned is the fact that we’ve uncovered yet another unrecorded carving – and according to the official records, no such carvings exist here; but where one such carving exists, others are close by!
Watch this space…..
Acknowledgements: Considerable thanks must be given to Prof Paul Hornby, for use of his photos and without whose help this carving might never have been located. Cheers dood!
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian
The map could not be loaded. Please contact the site owner.





