Cairns (destroyed): OS Grid Reference – SE 053 261
Archaeology & History
There’s really nowt to see around here nowadays (apart from a lovely view of the hills and the Calder valley), but it seems that not-too-long ago there were several burials in evidence upon this hill. F.A. Leyland (1867) gives a quite detailed account of the urns and their discovery, which have been variously thought of as Roman, then Saxon, then prehistoric — with them finally ascribed as Bronze Age in Watson’s (1952) survey of the region. Not too far away could once be found the legendary Robin Hood’s stone circle, which might have had some relationship with the burials here — though we’ll probably never know for sure! Leyland’s (1867) lengthy notes of this site told:
“An interesting discovery was made in…recent times, of a number of cinerary urns in the township of Warley. The site of the interments was at Tower Hill, a position on a line of military defences which extended from the entrenchments of Hunter’s Hill to Camp End in this township. The urns were found in the process of quarrying for stone; but, owing to the nature of the operations, and the unlooked for discovery of such relics as these or the total absence of all knowledge of their value, by the people employed, many similar remains are known to have been demolished as worthless objects.
“On one occasion, however, an urn, bleached by the tempests of an entire winter, was observed to protrude half its own bulk from the stratum of soil in which it had been originally buried.
“The curiosity of the labourers was excited, and the relic was removed. It was found to contain bones and ashes which the people, ever prone to the marvellous, held to be the remains of a child which had been destroyed by foul means and there buried. This opinion was noised abroad, and the true nature of the interment explained. We examined a fragment of this relic: it was rudely constructed of sun-burnt clay, and was grimed in the inside as if by the smouldering embers of the funeral pyre, and the smoking ashes of the dead, on their introduction to their narrow urn.
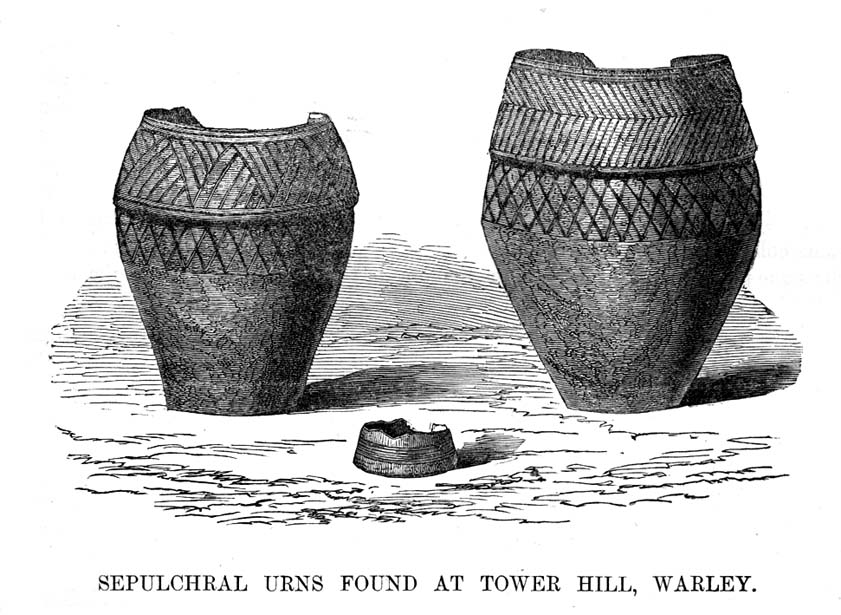
“This had been filled with these human exuviæ; and appeared to have been lined with moss mixed with fibres of plants which, after the urn had fallen in pieces, adhered firmly to its contents. It was thirteen or fourteen inches high, and was no doubt made by the hand alone. Within a few yards of this, another urn was found, containing bones and ashes, but so far decomposed as to preclude the possibility of its preservation: near the same place the smaller urn in our illustration was discovered buried in the dark soil peculiar to the locality; it was filled with calcined bones and ashes and, like the one found at Upleton—and in the possession of Dr Young of Whitby—had a small clay vessel placed within it, which is represented in our engraving. The urn was, moreover, protected by a lid, resembling the inverted stand of an ordinary flower-pot: the relic measured six inches high.
“During the winter of 1848, a date subsequent to the above discoveries, there was a fall of earth from the same spot, into the quarry at Tower Hill; the soil, thus precipitated from the moor, impeded the operations of the labourers; and, on its removal, the larger urn of our illustration was brought to light. This relic measured nine inches high and was twenty-two in circumference; but, in the rubbish, there were observed numerous fragments of other cinerary urns, and equally numerous relics of cremation.
“These discoveries lead one to one of two conclusions: either that Tower Hill was the field of some formidable engagement, in which numbers fell; or, that it was used as a place of frequent sepulture by the primitive inhabitants of the locality. It is not at all improbable that these urns were the produce of some local pottery, if not made by the same hand, as the one described by Watson (1775), the patterns indented on the two upper compartments of the smaller vessel being of the same kind, and occupying the same positions as the one referred to.
“The larger urn, as will be observed, is divided like the others into three compartments, the upper one standing out in relief, but having a different kind of decoration resembling herring-bone masonry; while the smaller one of our illustration, and that of Watson, are furnished with a zigzag design. But, although there is this slight variation in the upper moulding of the larger vessel, they all possess the lozenge-shaped decoration in their central compartments.”
We haven’t yet explored this site diligently and also know that if we have to await the slow hand of archaeology here we’d be waiting an aeon, but Tower Hill’s position in the landscape would tend to indicate the latter of Leyland’s earlier suggestions regarding the nature of the finds, i.e., the hill was a prehistoric graveyard, though of unknown size.
References:
- Leyland, F.A., The History and Antiquities of the Parish of Halifax, by the Reverend John Watson, M.A., R.Leyland: Halifax n.d. (c.1867)
- Roth, H. Ling, The Yorkshire Coiners, 1767-1783; and Notes on Old and Prehistoric Halifax, F.King: Halifax 1906.
- Watson, John, The History and Antiquities of the Parish of Halifax, T. Lowndes: London 1775.
- Watson, Geoffrey G., Early Man in the Halifax District, HSS: Halifax 1952.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian
The map could not be loaded. Please contact the site owner.