Cross: OS Grid Reference – ST 49875 38924
Also Known as:
- Glastonbury Cross
Archaeology & History
The present day Market Cross that stands in Glastonbury’s High Street, ornate though it may look, replaced a much earlier and more memorable monument. The one we see today, said Charles Pooley (1877),
“at the junction of the four streets, was erected in 1846, after the design of B. Ferrey, Esq., at the instance and the cost of a private individual. It is a Gothic pinnacled structure of a simple type, with no pretensions to elaborate architectural display.”
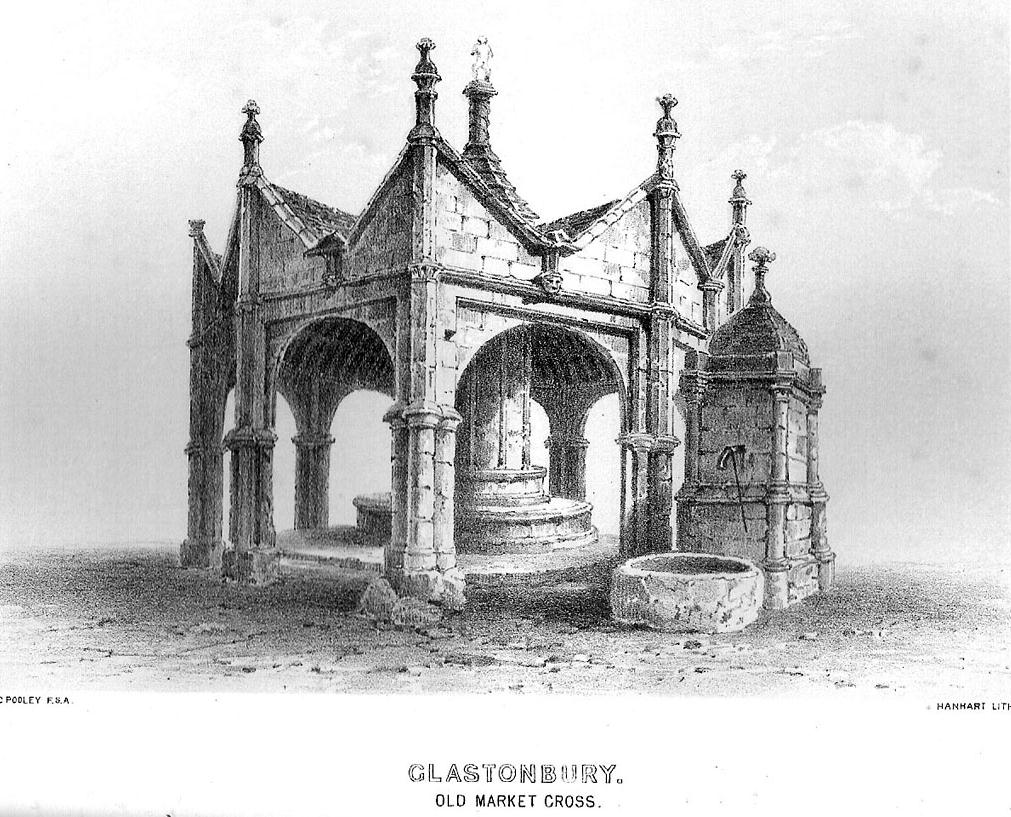

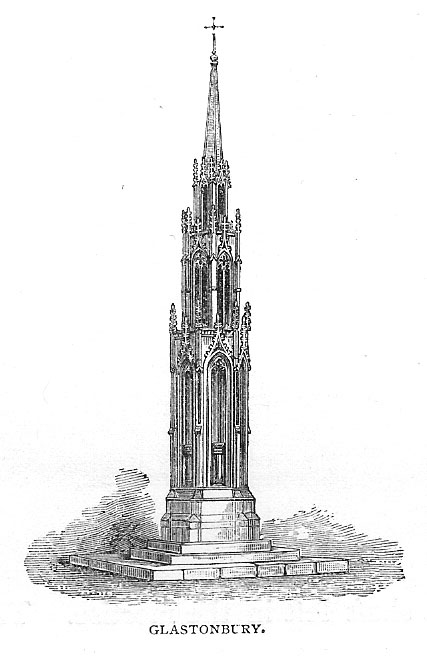
A very poor substitute for the cross that stood in its place in earlier centuries, from all accounts. Before the modern spire was erected, an earlier, larger and more ornate structure — that seems to have been first described in John Leland’s classic Itinerary (1744 ) in the middle of the 18th century, simply as “the Market Crosse in the West Ende” — was the meeting point for the tradesmen and villagers of Glastonbury. Although Rahtz & Watts (2003) followed Leland in giving only passing mention to this once ornate structure, thankfully a number of earlier antiquarians gave the old cross a bit more literary attention. Mr Pooley (1877) again informs us:
“Warner, who was in Glastonbury in 1799, says, “In my way to the Abbey, I passed the Market Cross, and old polygonal structure, its apex crowned with a little naked figure, bearing strong marks, in its position and employment of that grossness of taste, in which the sculptors of the 15th century so frequently indulged.”
Other writers weren’t as puritanical in their descriptions. In John Britton’s (1807) tour of the architectural curiosities of the region he remarked:
“Though a large and extremely curious structure…it is scarcely noticed in the topographical annals of the county; its history is, therefore, perhaps entirely lost. Since the drawing was taken in 1802, the Cross had been suffered gradually to fall into ruins, part of the centre column then only standing.” He continued: “There is something peculiarly unique in the shape and ornament of this building. A large column in the centre, running through the roof, and terminating with a naked figure, clustered columns at each angle with odd capitals, bases, etc., and gables with pinnacles of unusual shape, all unite to constitute this one of the eccentricities of ancient building. From the time of the Norman Conquest to the Dissolution of the Engilsh Monasteries, the varied and progressive styles of architecture are satisfactorily defined, and a very general uniformity prevails in all the buildings of particular eras; but the specimen before us differs from anything that we have yet met… In the year 1802 there was a mutilated inscription on it, with the year 1604, but we cannot say that this date refers to the time of its building. There were also some armorial bearings carved on different parts of it. Among these were the arms (a cross between two cups) of Richard Beere, the last Abbot but one of Glastonbury. The presence of the canting device of Richard Beere would probably determine the date of its erection.”
Mr Pooley’s (1877) own description of the old cross told that,
“It was built of hewn stone on an octagonal plan, having clustered pillars ranged round a central column supporting the roof. Three steps, the lower one benched, surrounded the base of the shaft, for the convenience of the market people. The gables were terminated by moulded pinnacles, and the central shaft, which rose above the roof, was surmounted by a statue. Adjoining the cross was an ancient conduit, having a vaulted roof, and supplied with water from a reservoir at the uper part of town. These structures being in want of repair…it was determined to pull them down, which was done accordingly in the year 1808.”
So the next time anyone visits Glastonbury’s tall spired cross in the middle of the town, remember its old and much more ornate predecessor. Perhaps some of you arty-types down there could do a replica of the old thing with its naked figurines and resurrect it from its forgotten past…
References:
- Britton, John, The Architectural Antiquities of Great Britain, Longman, Hurse: London 1807.
- Leland, John, The Itinerary, James Fletcher: Oxford 1744.
- Michell, John, New Light on the Ancient Mystery of Glastonbury, Gothic Image: Glastonbury 1990.
- Pooley, Charles, The Old Stone Crosses of Somerset, Longmans, Green & Co.: London 1877.
- Rahtz, Philip & Watts, Lorna, Glastonbury: Myth and Archaeology, Tempus: Stroud 2003.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian
The map could not be loaded. Please contact the site owner.
A very interesting piece. You might like to know that the effigy, known as ‘Jack Stagg’, was saved and is now to be found in the Glastonbury Abbey museum – see http://www.compusmall.co.uk/benedictsark/index.php/stephen-batty/68-jack-stagg-s-swagger